Soil-rock combined slope stability analysis method based on graphic trial algorithm
A technology of stability analysis and trial algorithm, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as inconsistent failure forms of rock slopes, complex shapes of slope sliding surfaces, and lack of theoretical support
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
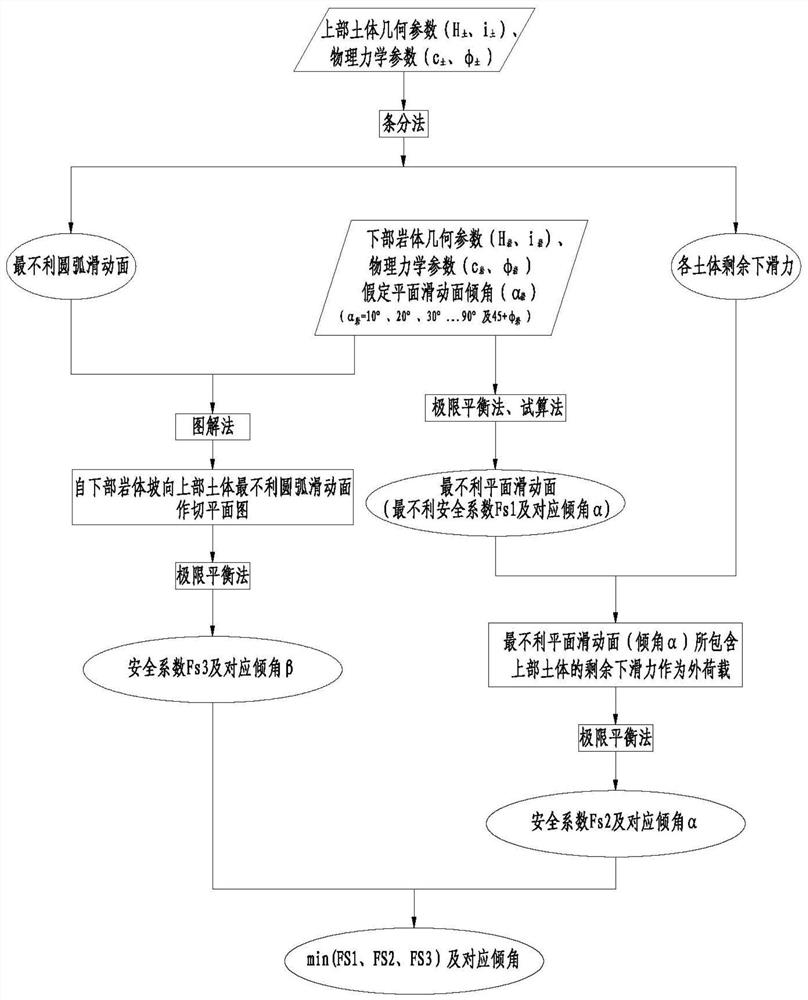
[0028] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic flowchart of a specific embodiment of the soil-rock combination slope stability analysis method based on the graphical trial algorithm of the present invention.
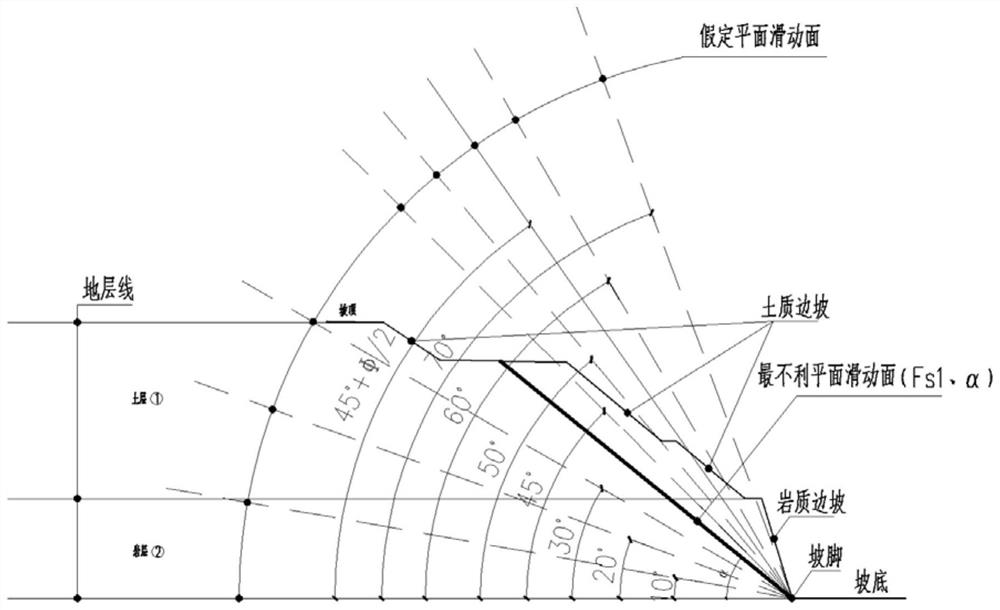
[0029] Specifically, such as figure 2 As shown, in step 1, starting from the toe of the lower rock mass, assume that the inclination angles of the plane sliding surface are 10°, 20°, 30°, 35°, 40°, 45°, 50°, 60°, 70°, 75° , 80°, and 45°+φ / 2 (φ is the internal friction angle of the rock mass), the limit equilibrium method is used to analyze the entire slope, and the most unfavorable plane sliding surface (that is, the most unfavorable dip angle α corresponding to the minimum safety factor Fs1 );
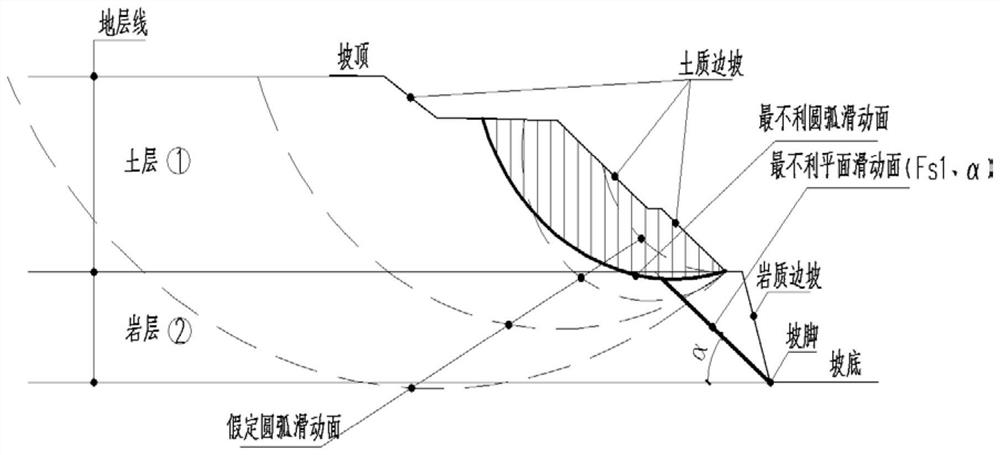
[0030] Such as image 3 As shown, in step 2, the slice method is used to search for the most unfavorable arc sliding surface for the hypothetical circular sliding surface of the upper soil mass; the most unfavorable plane sliding surface is made for the lower rock mass with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com