Multi-legged robot joint control method and device and multi-legged robot
A technology of a multi-legged robot and a control method, which is applied in the field of multi-legged robot joint control, and can solve problems such as high hardware requirements, complex calculation, and complex code.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
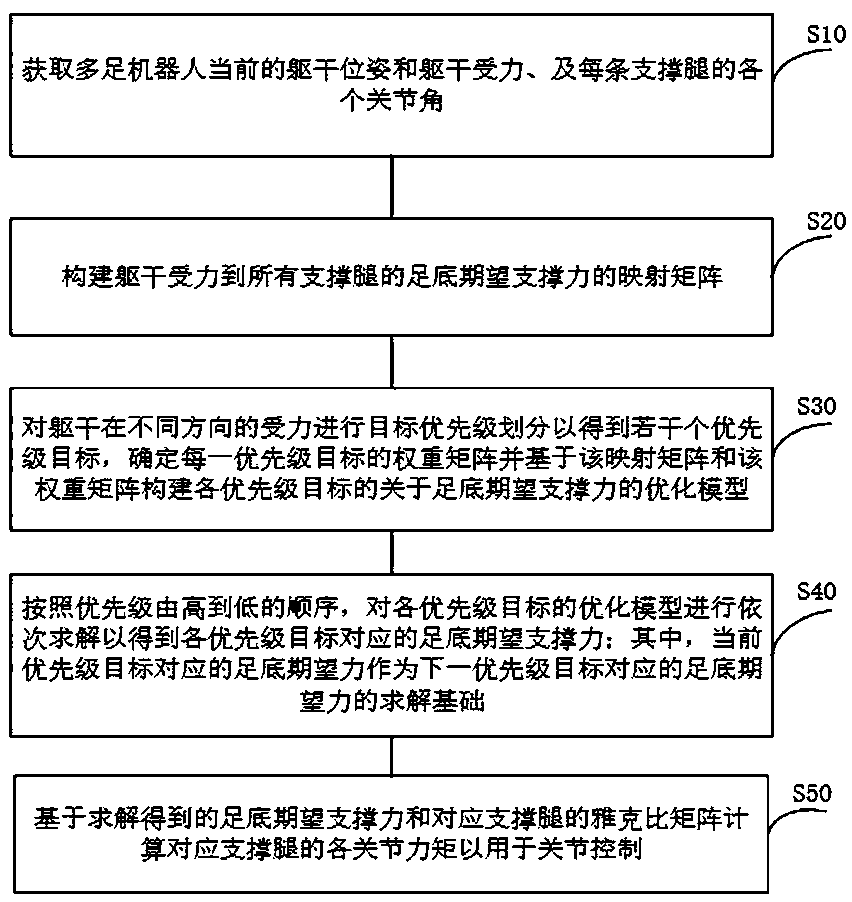
[0059] Please refer to figure 1 , this embodiment proposes a multi-legged robot joint control method. The method mainly includes the following steps:
[0060] Step S10, obtaining the current trunk pose and trunk force of the multi-legged robot, and each joint angle of each supporting leg.
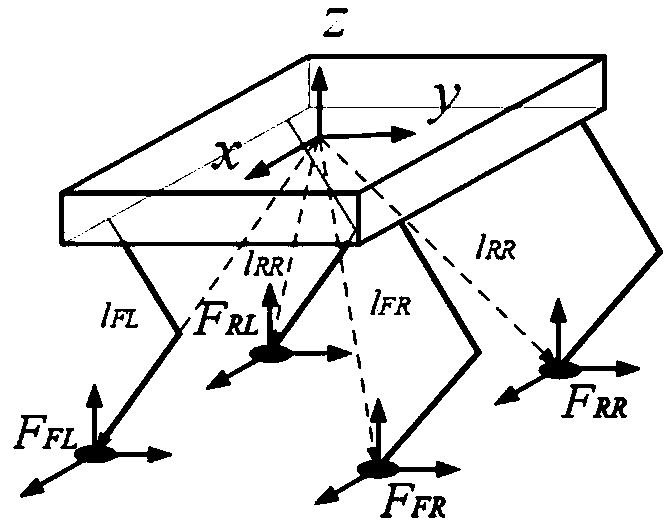
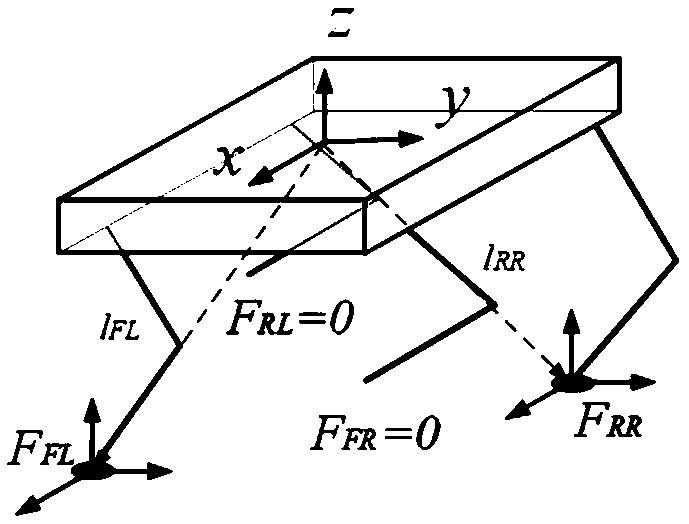
[0061] Exemplarily, the torso pose (including position and pose) of the multi-legged robot can be obtained by measuring an inertial measurement unit (IMU) or other pose sensors. The torso force can be calculated by the controller. Generally, when it is necessary to control the robot torso to reach a certain state, it is necessary to first determine the torso force required by the multi-legged robot according to the planned torso trajectory or target state. Wherein, the torso force includes the torso force in different directions. Usually, the force on the torso is a six-dimensional vector, including forces in X, Y, and Z directions and moments in X, Y, and Z directions.
[0062] For a r...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Please refer to Figure 5 , based on the method of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, this embodiment proposes a multi-legged robot joint control device 10, including:
[0125] The information acquisition module 110 is configured to acquire the current trunk posture and trunk force of the multi-legged robot, and each joint angle of each supporting leg, wherein the trunk stress includes the trunk's stress in different directions.
[0126] A mapping matrix construction module 120, configured to construct a mapping matrix from the trunk force to the expected plantar support force of all support legs according to the trunk pose, the force on the trunk and the joint angles of each supporting leg .
[0127] The target prioritization module 130 is configured to perform target prioritization on the force of the torso in different directions to obtain several priority targets, determine a weight matrix for each priority target and based on the mapping matrix and the The weight ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com