Autonomous navigation and automatic charging method for service robot in bank hall environment
A service robot and autonomous navigation technology, applied in the field of autonomous navigation and automatic charging of service robots, can solve the problems of inability to realize human-computer interaction, waste of resources, and complicated operation methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1. An autonomous navigation method for a service robot facing a bank hall environment.
[0030] Step S1: When it is necessary to deploy a robot in a new bank hall, first use the host computer remote control robot to scan each area of the hall to construct the map. The specific steps are as follows:
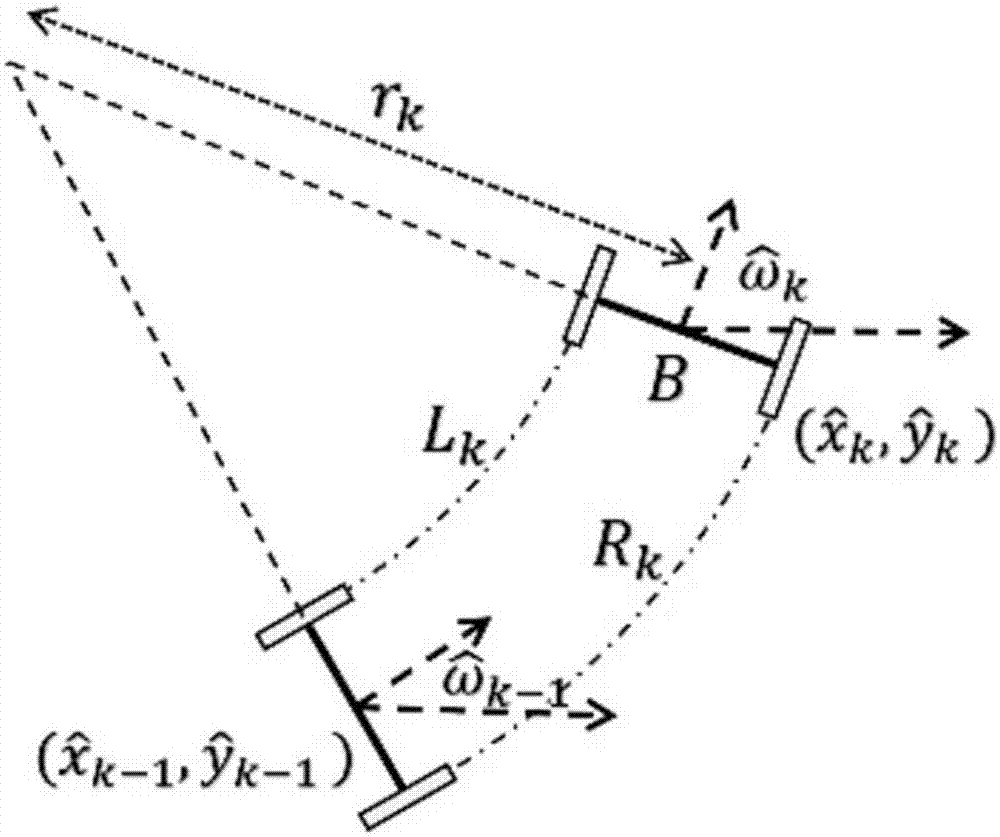
[0031] A): The robot is equipped with a laser sensor, a monocular camera, an RGB-D camera, a wheel odometer, an ultrasonic sensor, and an inertial measurement unit. The autonomous navigation system collects sensor information, and the wheel odometer module obtains a rough real-time attitude of the robot through dead reckoning. The two-wheel differential steering model is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the dead reckoning process of the two-wheel differential model is expressed as
[0032]
[0033]
[0034] where V k is the real-time motion rate of the robot; the visual odometer is based on the feature matching of the front and rear frames of stereo visio...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Embodiment 2. A method for automatic charging, positioning and navigation of a robot.
[0052] Step S1, continuously monitor the battery voltage, and when the voltage is lower than the threshold, use the method in Embodiment 1 to guide the robot to the front of the charging pile.
[0053] Step S2, collect the image through the image sensor, extract the visual sign placed on the charging pile in the image, set P i =[X i Y i Z i ] T , i=1,2,3,4 are the coordinates of the four vertices of the image logo in its own coordinate system, p i =[u i v i ] T , i = 1, 2, 3, 4 After image recognition, the four vertices of the image logo are corresponding points in the image, for P i The points are calculated through the pinhole camera model to obtain the image projection points, and the objective function is optimized After obtaining the transformation matrix of the robot relative to the image mark, the distance d=|t| between the robot and the image mark can be obtain...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com