A Method of Flow Simulation in Complex Fractured Reservoirs
A complex fracture and flow simulation technology, applied in the direction of earthwork drilling and production, wellbore/well components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to simulate multiphase flow, large gap between fracture grid and bedrock grid scale, and complex small-scale mapping relationship question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056] The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for simulating the flow of complex fractured reservoirs.
[0057] In order to make the above objects, features and advantages of the present invention more comprehensible, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
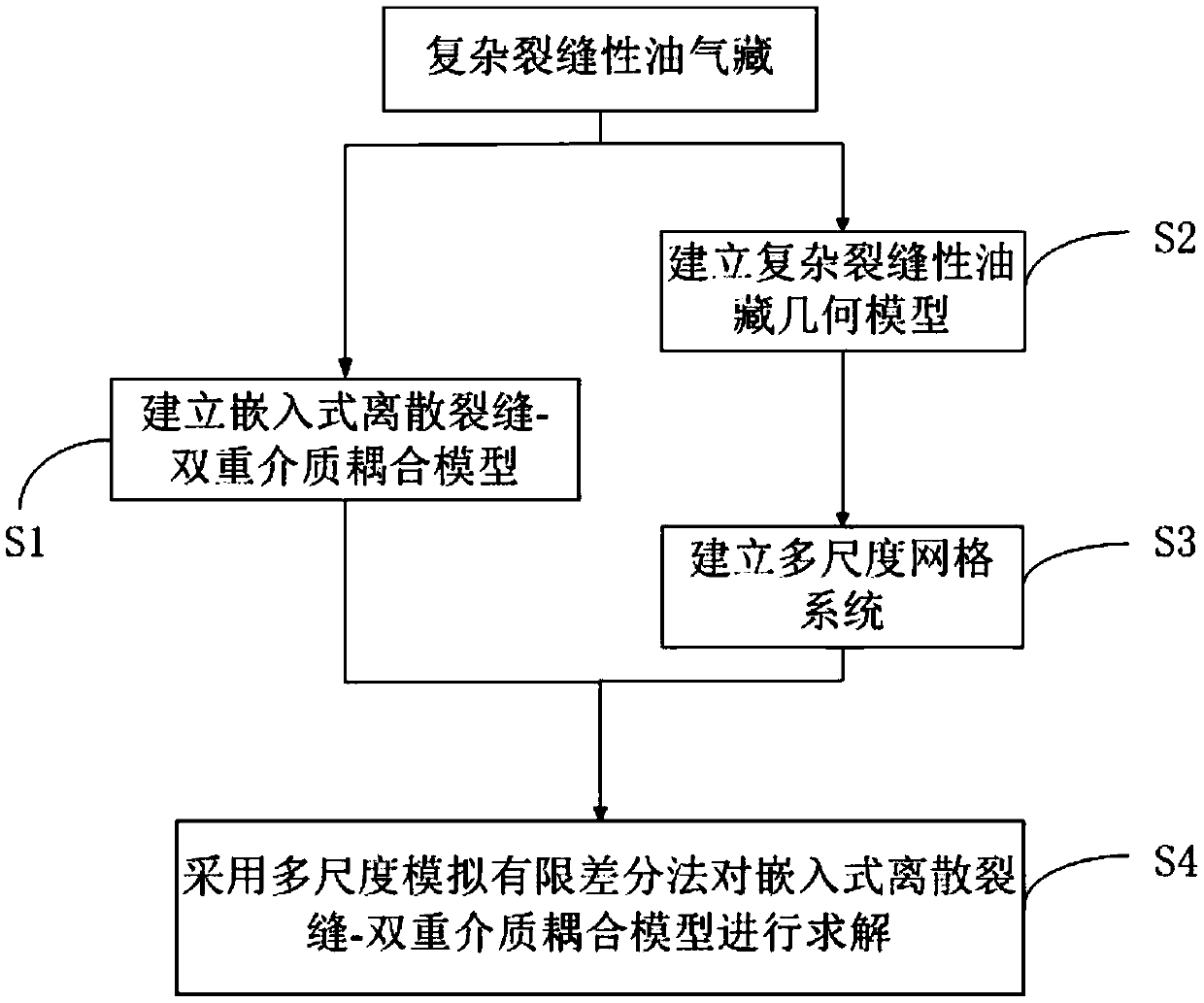
[0058] Such as figure 1 As shown, as an implementable method, a method for flow simulation of complex fractured reservoirs includes the following steps:
[0059] S1. Establish an embedded discrete fracture-dual medium coupling model according to the seepage characteristics of micro-fractures and large fractures;
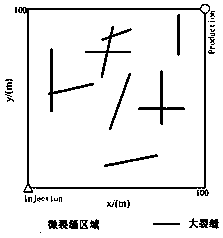
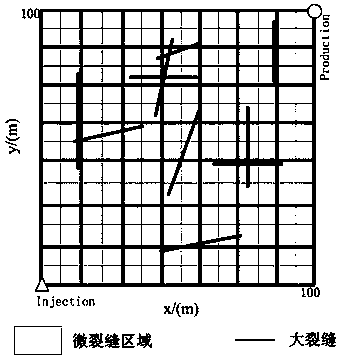
[0060] S2. According to the actual geological data of fractured oil and gas reservoirs, determine the distribution of large fractures, hydraulic fractures and micro-fractures in the oil and gas reservoirs, and establish a geometric model of complex fractured reservoirs; Figure 4 As shown, the g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com