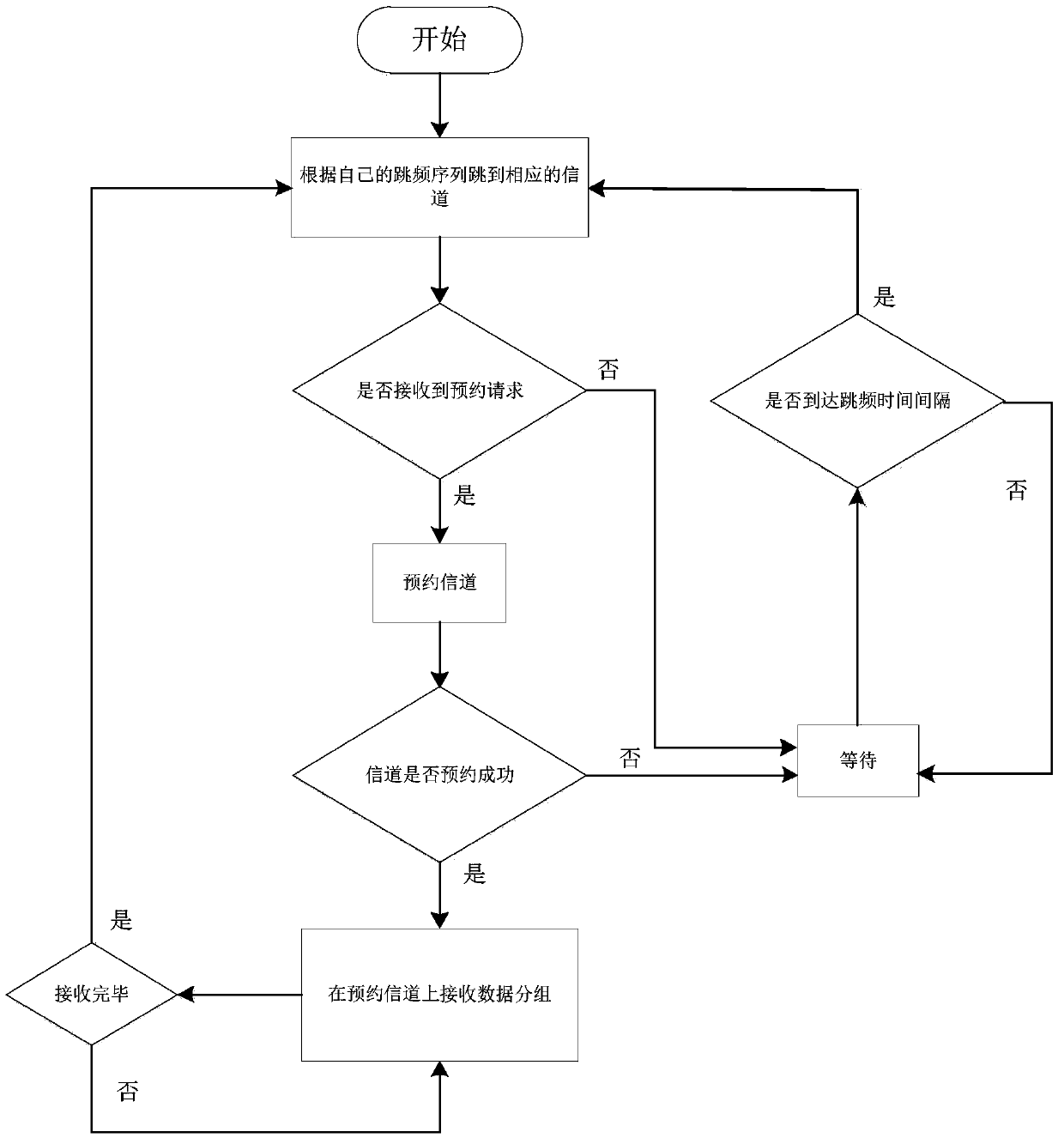
A Frequency Hopping Communication Method for Cognitive Wireless Networks Supporting Node Priority
A cognitive wireless network and node support technology, applied in the field of communication interaction mechanism design, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish communication priority levels, low communication transmission performance, and large channel load
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
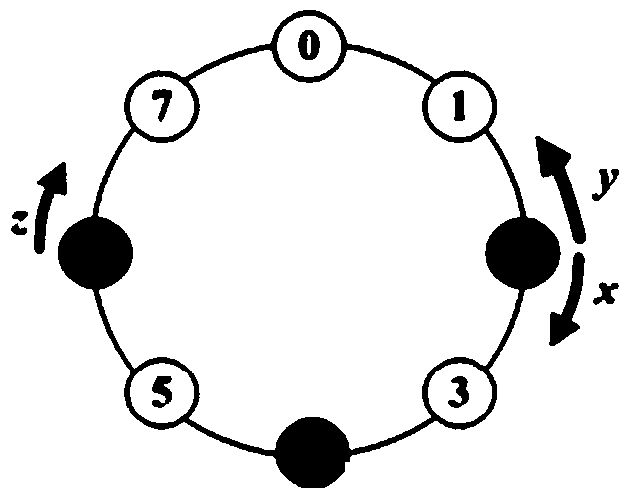
[0048] Examples of generation algorithm for cognitive sending and receiving frequency hopping sequence supporting node priority
[0049] When the total number of authorized channels is N=8, since the integer 8 has only two non-1 true factors 4 and 2, the cognitive frequency hopping communication mechanism supporting node priority proposed by the present invention can support up to 2 node priorities. Level, namely M=2. Among them, the time interval for the low-priority sending and receiving nodes to achieve 2 consecutive convergences is q 1 = 4 time slots, and the time interval for high-priority sending and receiving nodes to achieve 2 consecutive convergences is q 2 = 2 time slots.
[0050] According to the restriction conditions, the channel interval r for a single frequency hopping of the low-priority cognitive sending node 1,s Can be set to r 1,s =1, and the channel interval r of the single frequency hopping of the low-priority cognitive receiving node 1,t Can be set to r 1,t = ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Examples of existing cognitive transmission and reception frequency hopping sequence generation algorithms that do not support node priority
[0069] The existing cognitive transmit and receive frequency hopping sequences are obtained based on a priority-insensitive synchronization frequency hopping sequence generation algorithm. In this algorithm, the number of authorized channels N must be an even number, and each transmit frequency hopping sequence Is the following N 2 Periodic repetition of / 2 element sequence:
[0070] {b i +0modulo N,b i +1 modulo N,…,b i +N-1modulo N,(b i +2)+0 modulo N,(b i +2)+1modulo N,…,(b i +2)+N-1 modulo N,…,(b i +N-2)+0modulo N,(b i +N-2)+1 modulo N,…,(b i +N-2)+N-1 modulo N}, where b i , I∈[1,N / 2], represents the frequency hopping sequence Where the initial channel is located, and satisfies b 1 = B 2 =...=b N / 2 modulo 2.
[0071] At the same time, each received frequency hopping sequence ψ i Is a sequence of N elements {a i modulo N,a i -1mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com