Method for Raising Bat Moth Larvae by Soil Stratification
A technique for bat moth larvae and soil stratification, which is applied in animal husbandry and other fields, and can solve problems such as poor growth and low larval survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
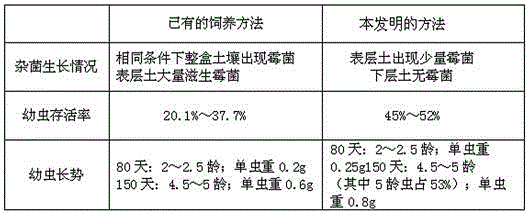
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] In the method for rearing bat moth larvae in layers of the present embodiment 1 soil: use a 40cm × 30cm × 14cm insect raising box to raise; use 100 ℃ normal pressure steam full sterilization 10 hours after the aseptic soil is used as insect raising soil; use ClO 2 The sterilized fresh feed is used as larvae feed; 100-200 worm eggs are put in each box, and 1-2 kg of feed is put in (that is, the feeding ratio of worm ovum feed is 10g of feed for each worm egg), and the completed larvae The rearing box was placed in a sterile environment with a humidity of 60% to 80%, a temperature of 7°C to 18°C, and a dark environment for rearing.
[0019] In the present embodiment 1, the soil for raising insects adopts the method of four-layer gradient humidity stratification, and the method of four-layer gradient humidity stratification is:
[0020] Evenly cover the bottom of the insect rearing box with insect rearing soil with a humidity of 45% to 50% and a thickness of 2cm;
[0021...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The method for cultivating bat moth larvae in layered soil in Example 2 is basically the same as in Example 1, except that the soil for raising insects adopts the method of three-layer gradient humidity layering.
[0026] The method of three-layer gradient humidity stratification is:
[0027] Evenly cover the bottom of the insect rearing box with insect rearing soil with a humidity of 40% to 45% and a thickness of 2cm;
[0028] Evenly spread the larvae feed on the insect breeding soil with a humidity of 40% to 45%, and cover with 3-4cm of insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40% (the insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40% will After the feed is completely covered, it is about 2cm higher than the feed layer);
[0029] Place bat moth larva eggs evenly on the insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40%, and cover with an insect breeding soil with a humidity of 30% to 35% and a thickness of 2cm.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The method for rearing bat moth larvae in layered soil in the present embodiment 3 is basically the same as in embodiment 1, except that the soil for raising insects adopts the method of two-layer gradient humidity layering.
[0032] The method of two-layer gradient humidity stratification is:
[0033] Evenly cover the bottom of the insect rearing box with insect rearing soil with a humidity of 35% to 40% and a thickness of 3cm;
[0034] Evenly spread the larvae feed on the insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40%, and cover with 3-4cm of insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40% (the insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40% will After the feed is completely covered, it is about 2cm higher than the feed layer);
[0035] Place bat moth larva eggs evenly on the insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40%, and cover with insect breeding soil with a humidity of 35% to 40% and a thickness of 2cm;
[0036] Cover the insect breeding soil w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com