Energy Efficient Transmission of Content Over Wireless Connections
A content-efficient technology for energy-efficient transmission that can solve the problem of consuming the total power consumption of smartphones and draining the battery of smartphones
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0032] Example 2 - Environment for energy efficient delivery of content
[0033] figure 1 is a block diagram depicting an example environment 100 for implementing the energy efficient transfer techniques described herein. The example environment 100 includes a first computing device 110 and a second computing device 130 . For example, the first computing device 110 may be a battery-powered mobile device such as a smartphone, tablet, or laptop. The first computing device implements one or more of the energy efficient transmission techniques described herein, such as adaptive switching and / or low power mode. The second computing device 130 may be a device connected to a display 150, such as a high-definition television. Alternatively, second computing device 130 may be integrated with display 150 .
[0034] The first computing device 110 includes a radio station 120 (eg, a Wi-Fi station). The second computing device 130 also includes a radio station 140 (eg, a Wi-Fi station...
example 3
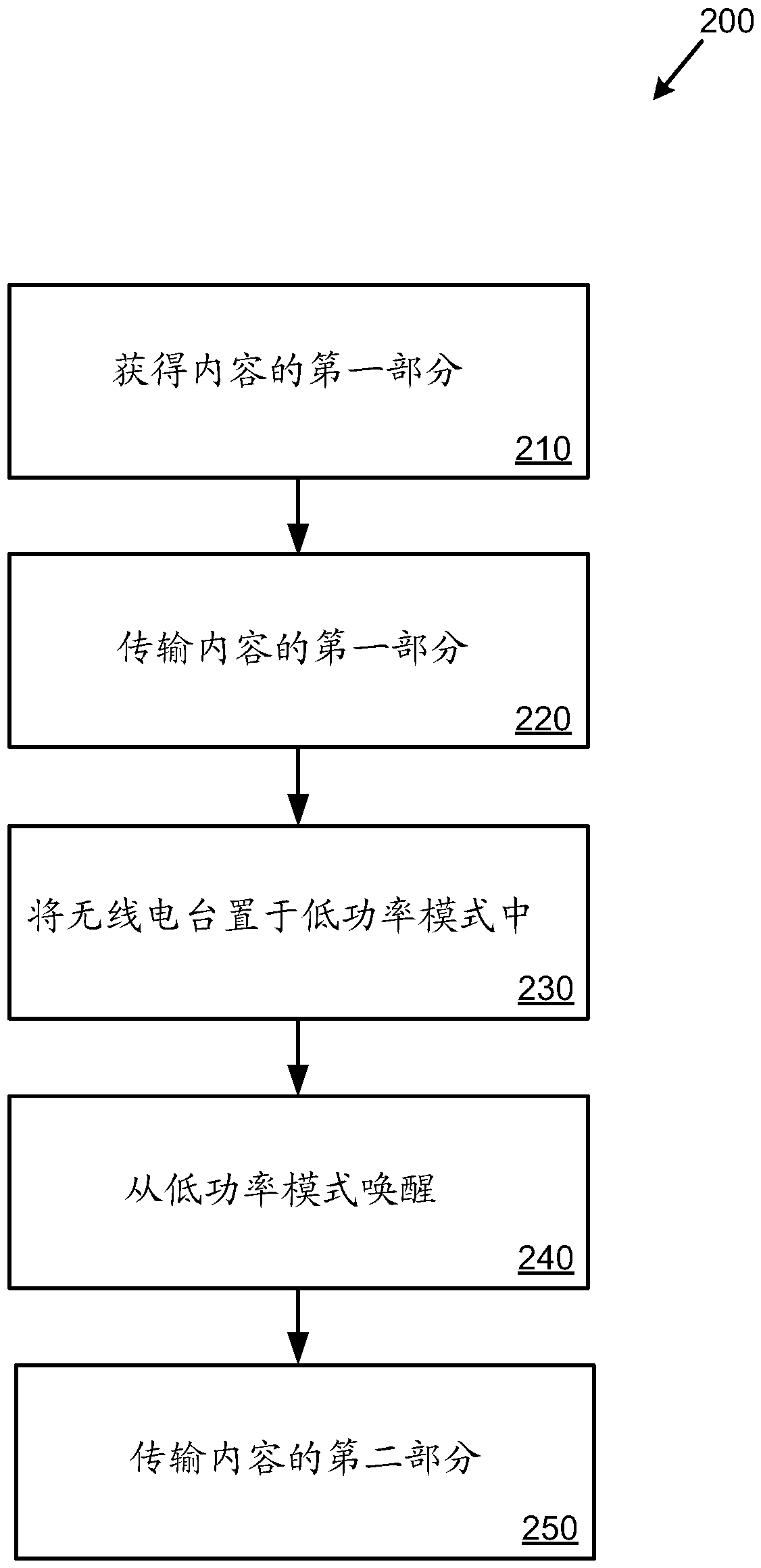
[0039] Example 3 - Energy Efficient Delivery of Content
[0040] In any of the examples herein, portions of content (eg, portions of video or audio files, web page content, slide presentation content, etc.) can be transmitted in an energy efficient manner. For example, a radio station may be placed in a low power mode between portions of transmitted content.
[0041] figure 1 is a flowchart of an example method 100 for energy-efficient transmission of content. Method 100 may be performed at least in part by a first computing device that includes a wireless station (eg, a Wi-Fi station). At 110, a first portion of content is obtained. For example, the first portion of content may be a segment of content of a certain size or duration (eg, a 5 or 10 second portion of content).
[0042] At 120, the first portion of the content is transmitted to the second computing device for playback (eg, display) by the second computing device. For example, a second computing device may be ...
example 4
[0050] Example 4 - Adaptive switching for energy efficient delivery of content
[0051]In any of the examples herein, adaptive switching may be performed to enable energy efficient transmission of content. For example, one or more portions of content (e.g., one or more segments of a video and / or audio file) may be transmitted in a mirrored Local decoding and display and encoding of displayed content, wireless transmission of encoded displayed content to a second computing device (eg, television), and simultaneous (or near-simultaneous) display by the second computing device. One or more other portions of content (e.g., one or more other sections of a video and / or audio file) may be transferred to a second device for decoding and display without decoding and display by the first computing device. show. The first computing device may enter a low power mode when other portions of the content have been transferred (eg, between transferring other portions, or between transferring...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com