Image pickup unit and image pickup display system
A technology of an imaging device and a photoelectric conversion device, which is applied in the field of X-ray imaging technology, can solve problems such as leakage current, shot noise, and image quality degradation, so as to reduce the influence of shot noise, improve imaging quality, and suppress current leakage Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0044] structure
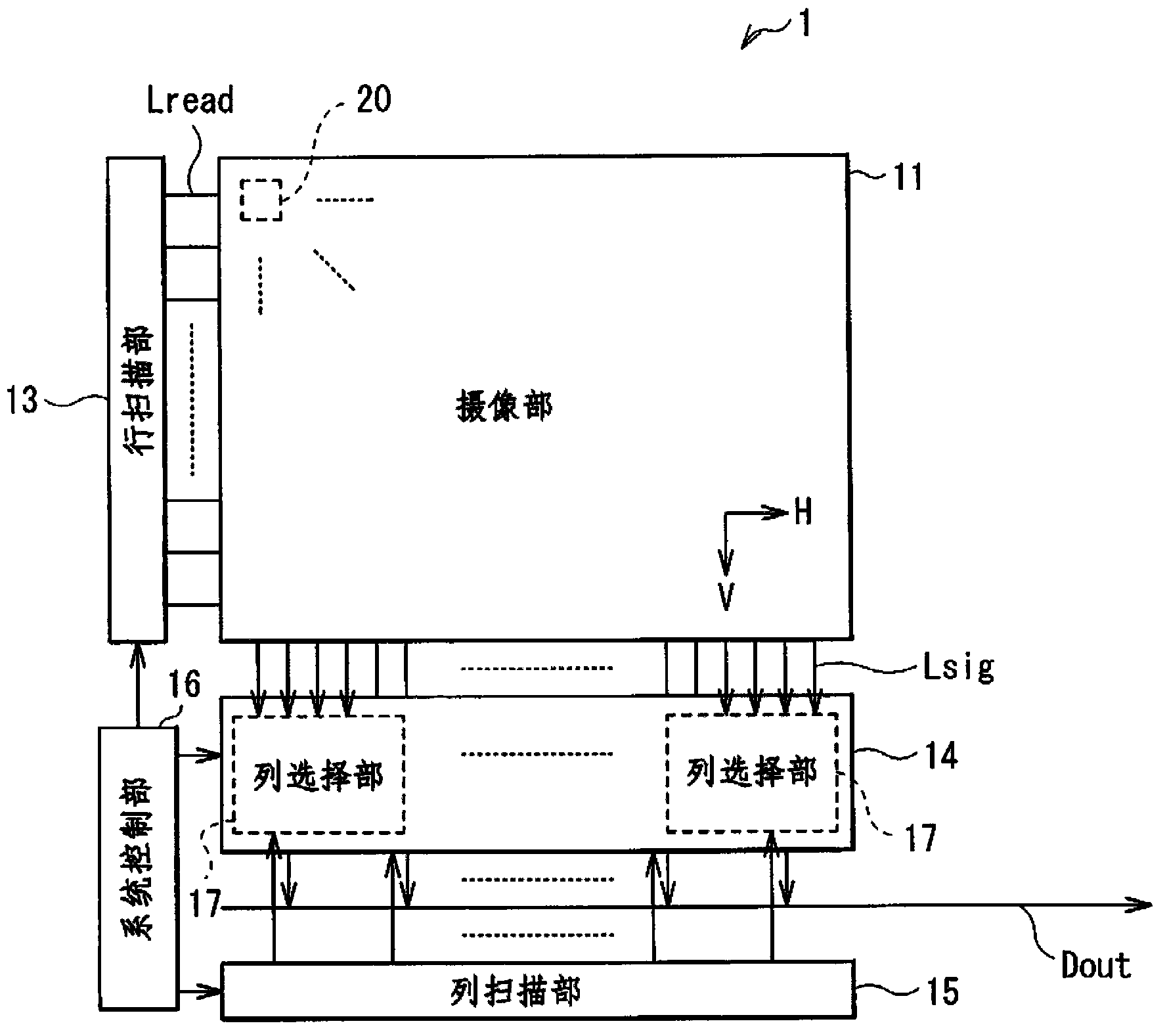
[0045] figure 1 The overall block configuration of the imaging device (imaging device 1 ) of the embodiment of the present invention is shown. The imaging device 1 reads information of an object (acquires an image of the object) based on incident light (imaging light). The imaging device 1 includes an imaging unit 11 , a row scanning unit 13 , an A / D converting unit 14 , a column scanning unit 15 , and a system control unit 16 .
[0046] camera department 11
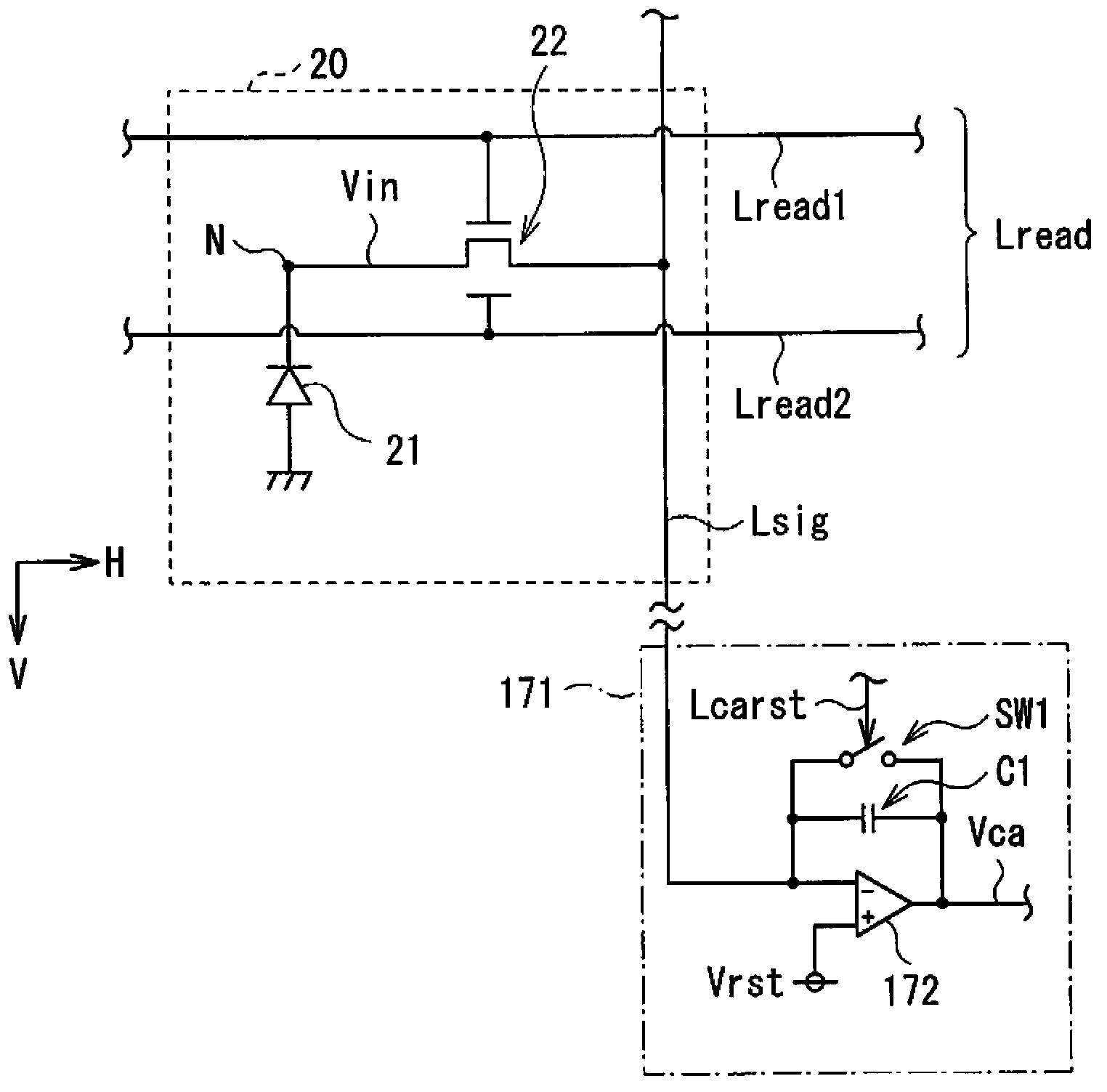
[0047] The imaging unit 11 generates an electrical signal depending on incident light (imaging light). In the imaging section 11, pixels (imaging pixels, unit pixels) 20 can be two-dimensionally arranged in a row-column pattern (matrix pattern), and each pixel 20 has a photoelectric conversion device (photoelectric conversion device 21 described below), a photoelectric The conversion means generates photoelectric charges having a charge amount corresponding to the amount of imaging light, and inter...
example 1-1
[0080] Image 6 A cross-sectional structure of a transistor (transistor 22A) of Modification Example 1-1 is shown. Like the transistor 22 in the above-mentioned embodiment of the present invention, a transistor 22A and a photoelectric conversion device 21 are provided in each pixel 20 of the imaging unit 11 of the above-mentioned imaging device 1 . In the transistor 22A of this modified example, the gate electrodes 120A and 120B are arranged to face each other with the semiconductor layer 126 arranged therebetween, and the LDD layers 126b1 and 126b2 may be formed adjacent to the source side and the channel layer 126a in the semiconductor layer 126 . Both ends 126e1 and 126e2 on the drain side. In this configuration, like the configurations of the above-described embodiments of the present invention, the transistor 22A also has a non-overlapping region d2 corresponding to the drain-side end 126e2 of the channel layer 126a.
[0081] However, the transistor 22A of the present m...
example 1-2
[0085] Figure 8 A cross-sectional structure of the transistor (transistor 22B) of Modification Example 1-2 is shown. Like the transistor 22 in the above-described embodiment of the present invention, a transistor 22B and a photoelectric conversion device 21 are provided in each pixel 20 of the imaging unit 11 of the imaging device 1 described above. In the transistor 22B of the present modified example, the gate electrodes 120A and 120B are arranged to face each other with the semiconductor layer 126 arranged therebetween. Like the above-described embodiments of the present invention, the transistor 22B has a non-overlapping region d2 corresponding to the drain-side end 126e2 of the channel layer 126a.
[0086] However, in the transistor 22B of the present modification example, in the semiconductor layer 126 , the LDD layer 126 b 2 is formed adjacent to only the end portion 126 e 2 on the drain side of the channel layer 126 a. Figure 9 An example of the planar layout confi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com