Multi-level significance map scanning
A technology of internal scanning and effective coefficients, which is applied in image communication, television, electrical components, etc., and can solve the problems of high computational intensity and expensive memory access operations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
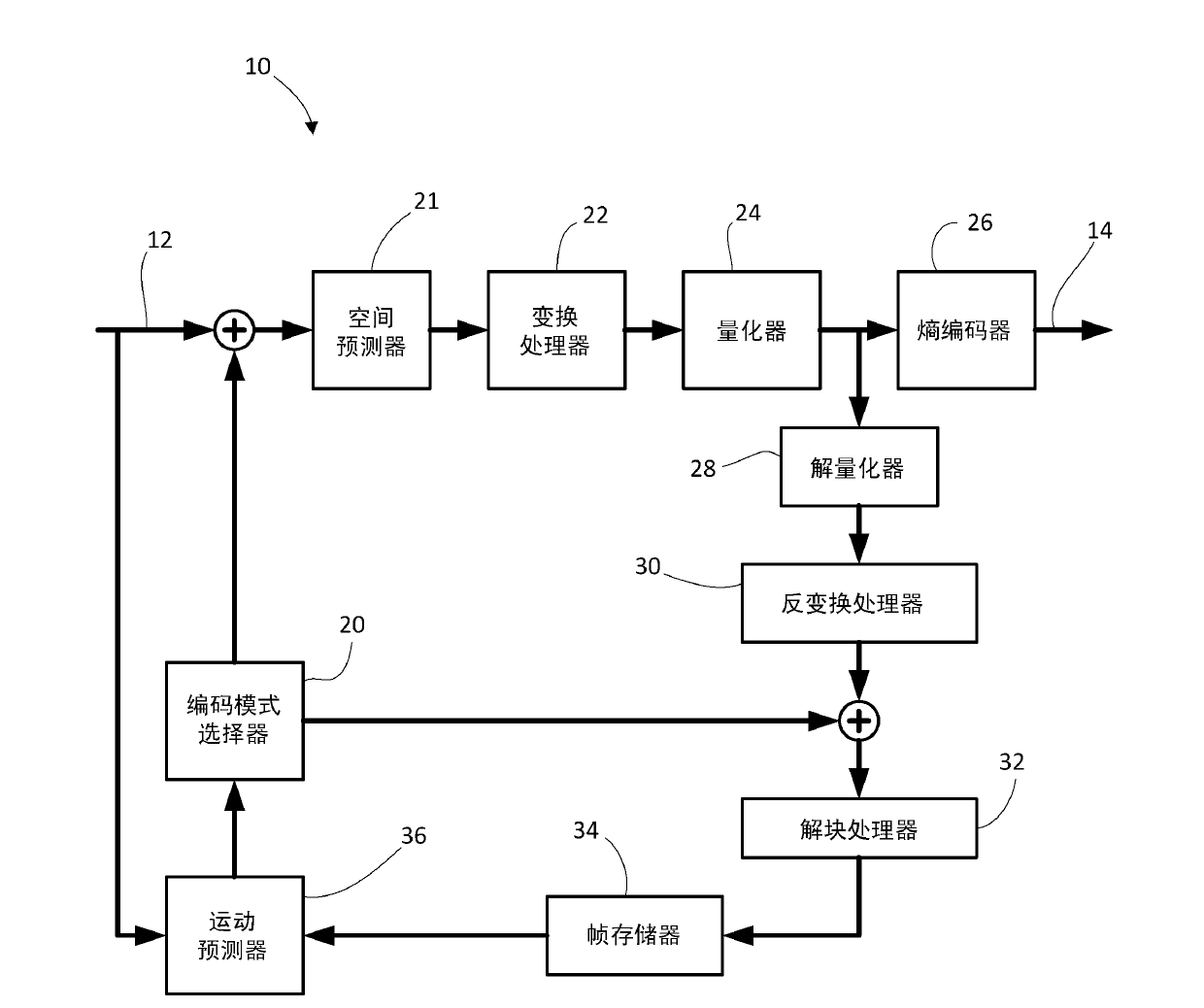
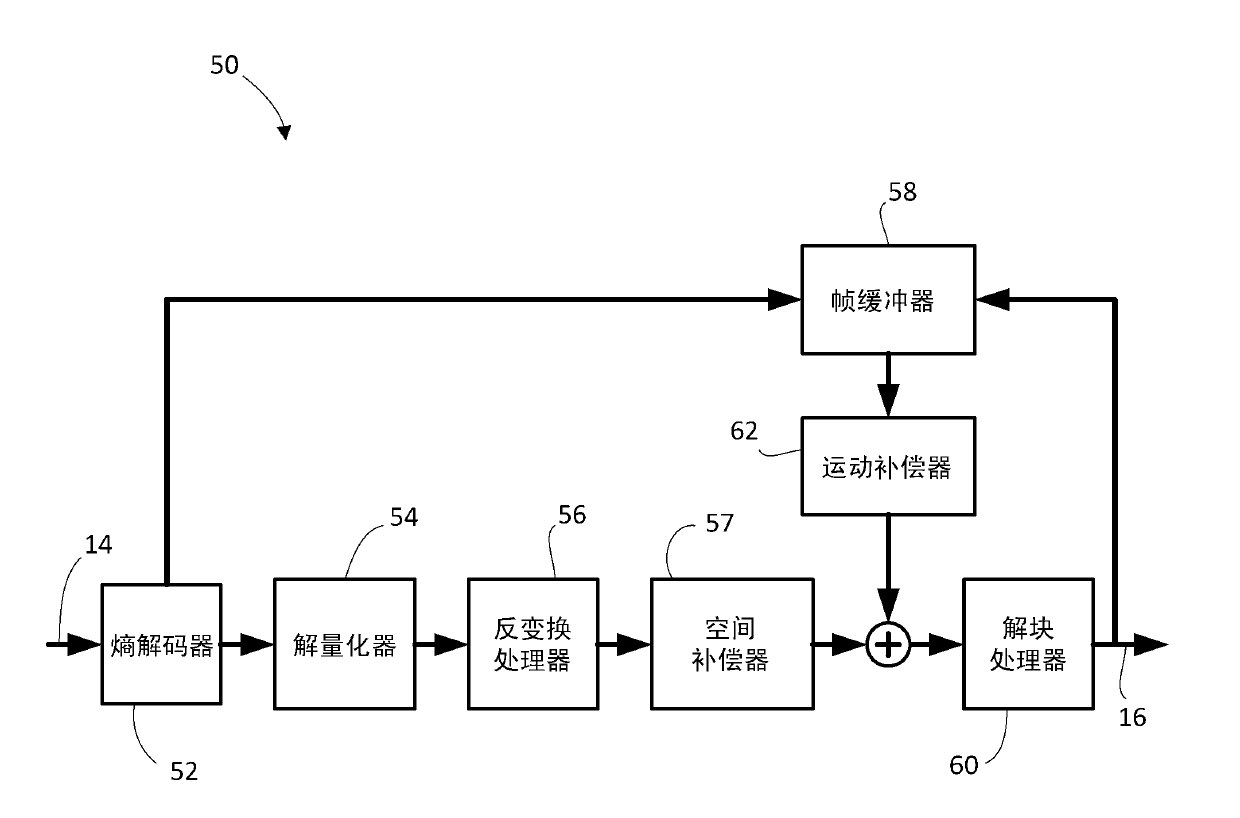
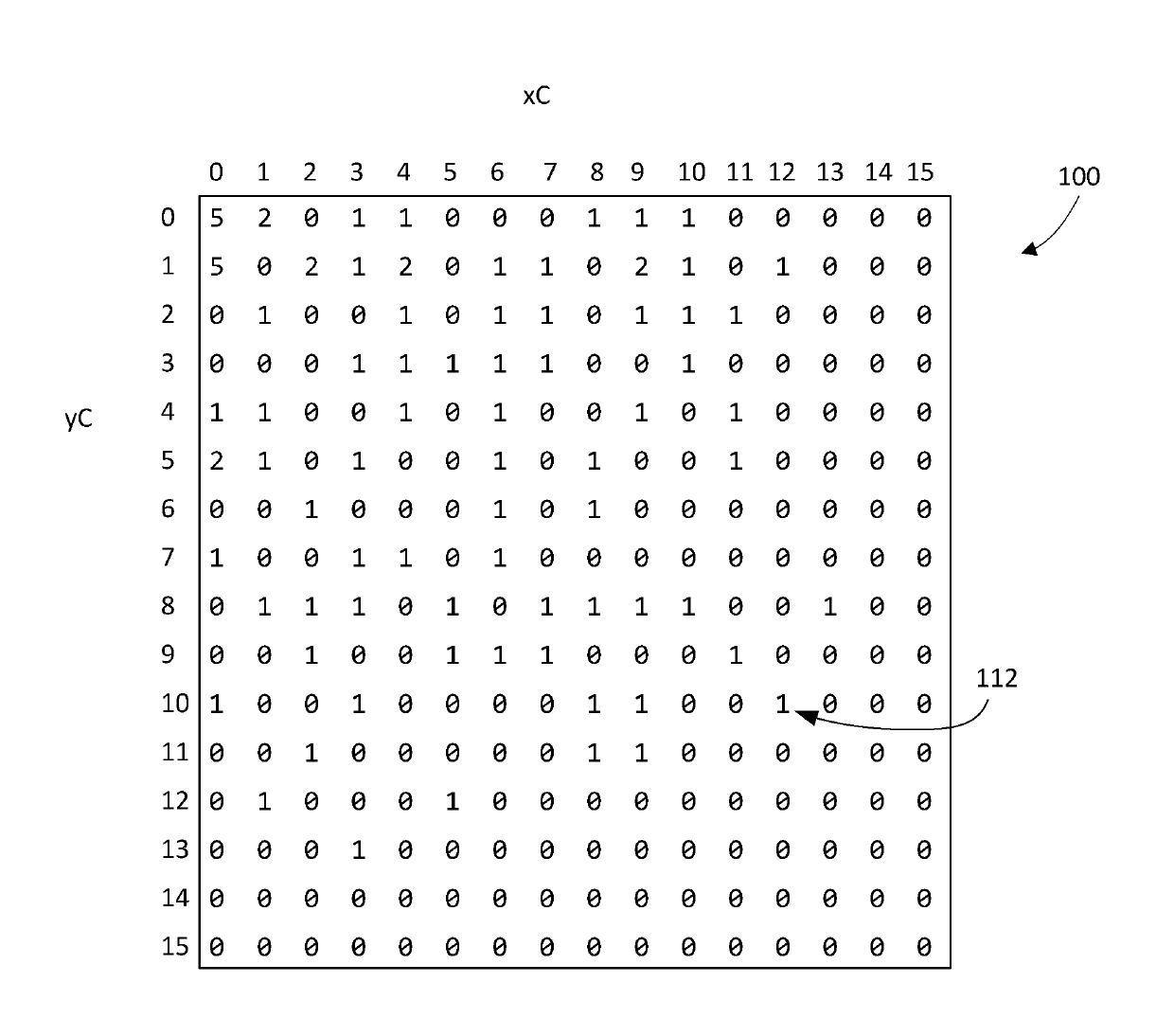
[0035]In the following description, some example embodiments are described with reference to the H.264 standard for video coding and / or the developing HEVC standard. Those skilled in the art should understand that the present application is not limited to H.264 or HEVC, but is applicable to other video coding / decoding standards, including possible future standards, multi-view coding standards, scalable video coding standards, and reconfigurable The configured video encoding standard.
[0036] In the following description, the terms frame, picture, slice, tile and rectangular slice group are used somewhat interchangeably when referring to video or images. Those skilled in the art will recognize that, in the case of the H.264 standard, a frame may contain one or more slices. It will also be recognized that, depending on the specific requirements or terminology of the applicable image or video coding standard, some encoding / decoding operations are performed on a frame-by-frame b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com