Method for treating highly saline atrazine production waste water
A treatment method and technology for producing wastewater, which are applied in natural water body treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. The effect of eliminating evaporation process, low energy consumption and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 The high-salt production wastewater produced by atrazine has a salt content of 12%, TOC 6000mg / L, and COD 16200mg / L. The wastewater first enters the reactor, and compounds cyanuric acid, sulfuric acid and diatomaceous earth are added thereto , react with the organic matter in the wastewater to form a precipitate, such as hydrolysis and complexation, and filter to remove the precipitate in the wastewater. After the treatment, the TOC of the wastewater is 1800mg / L, and the COD is 100mg / L, and then the DK nanofiltration membrane is used for nanofiltration separation. The filtered wastewater TOC is 500mg / L and COD is 1260mg / L, and then the wastewater is adsorbed with powdered activated carbon. After adsorption, the wastewater TOC is 8.3mg / L and COD is 22mg / L.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2 A treatment method for atrazine high-salt production wastewater is to remove organic matter in atrazine wastewater by reaction, filtration, nanofiltration, and activated carbon adsorption, so that the wastewater reaches the level of chlor-alkali factory brine after treatment. requirements, or meet national emission standards.
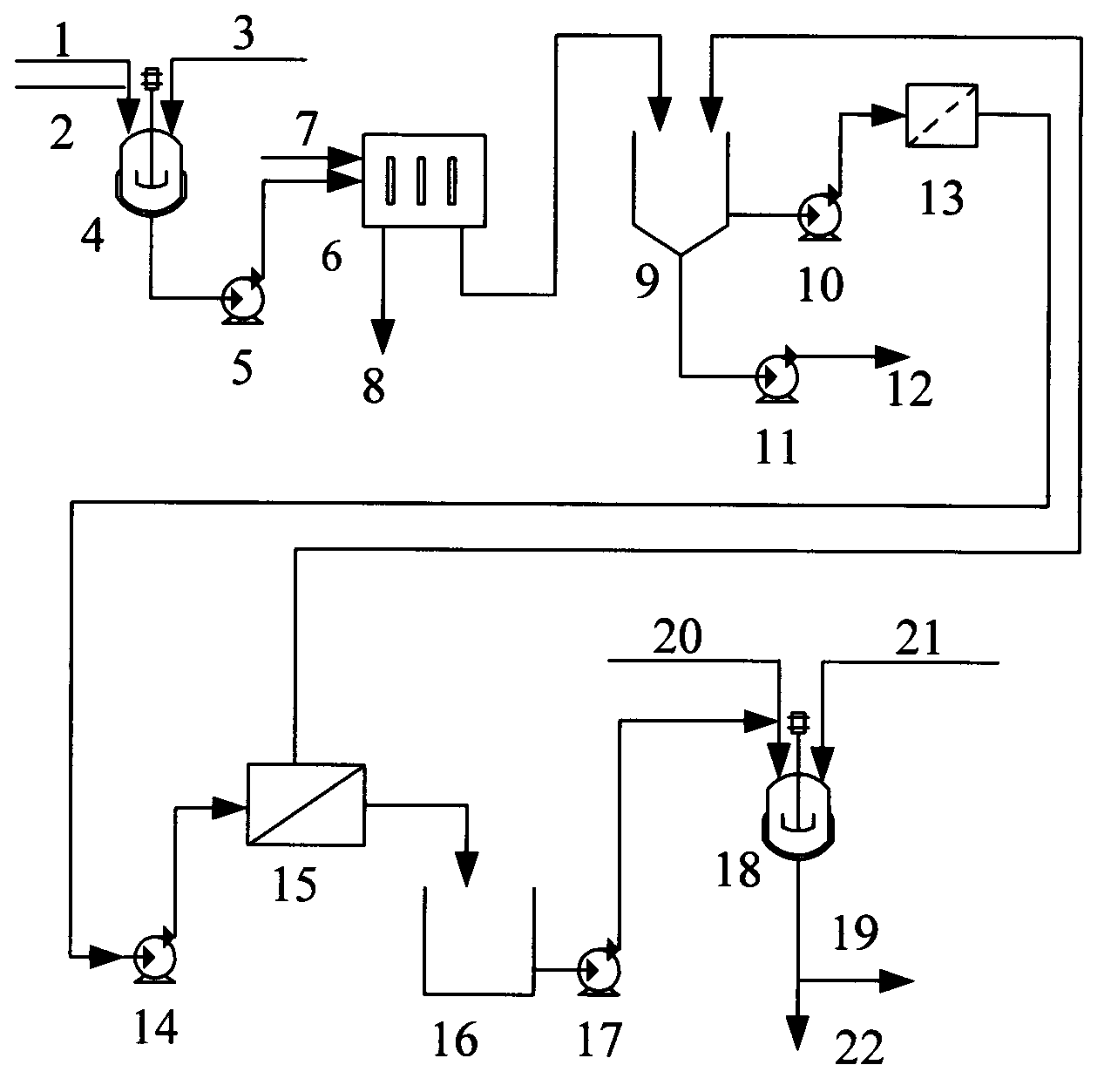
[0034] Fig. 1 is a schematic flow chart of atrazine high-salt production wastewater treatment of the present invention, using this process to take out high-salt production wastewater from the atrazine production process, with a salt content of 15%, TOC 6500mg / L, COD 17500mg / L, first enter the reactor, add compound cyanuric acid amide, hydrochloric acid, perlite to the waste water, and react with the organic matter in the waste water to hydrolyze and complex to form a precipitate, and filter to remove the precipitate in the waste water. After the reaction and precipitation, the wastewater TOC is 2200mg / L, COD 5960mg / L, and then enters...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com