Design of curved fiber paths for composite laminates
A composite material and laminate technology, which is applied in the design field of curved fiber paths for composite laminates, can solve the problems of low design efficiency, high cost of thickness accumulation, and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
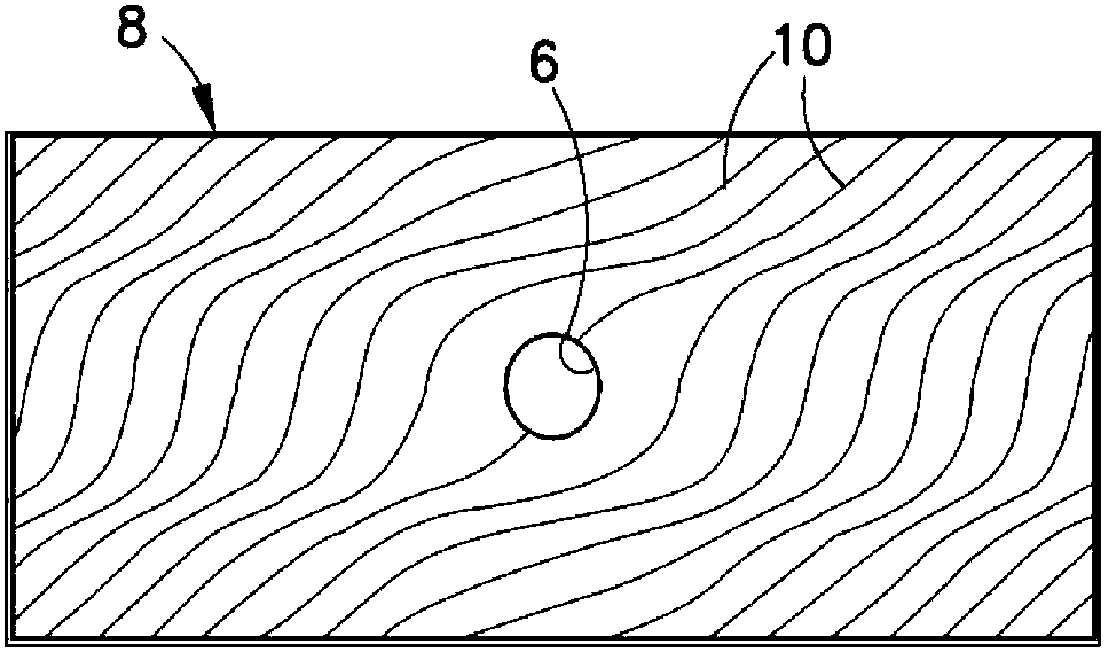
[0044] The following disclosure is the result of the development and validation of an optimization process for the design and analysis of variable stiffness composite skins. In the course of this work, the potential feasibility and weight reduction of fiber steering for laminated structures was investigated.
[0045] The design process disclosed here allows loads to be steered by steering fibers. Conventional laminates carry in-plane loads around the cut by transferring the load between the plies (eg, from 0° ply to ±45° ply). Loads can be carried more efficiently around cuts when fibers are allowed to follow curved paths within the ply. The challenge in designing laminates with steered fibers is to efficiently describe the manufacturable fiber paths. A potential outcome is a reduction in weight and cost of the final fabricated structure.
[0046] For conventional plies on flat panels, the fiber paths are all described by the ply angle. For conventional laminates, the ply ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap