Large scale topographical map surveying and mapping method utilizing rotating TIN (triangulated irregular network) and distance and included angle dual-weight interpolation method
A technique of scale and interpolation, applied in the field of geographic information systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0115] Specific implementation mode 1: the following combination Figure 8 to Figure 13 This embodiment will be described in detail. This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0116] 1. The mapping scale is 1:500, the distance between topographic fragments is 15m, and the distance between topographic fragments is 30m as the side length of the basic square.
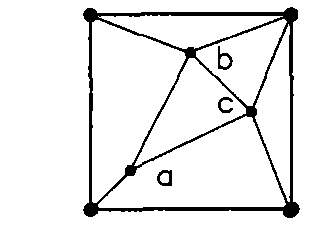
[0117] 2. Arrange a surveying and mapping point at each of the four vertices of the basic square, and arrange three surveying and mapping points scattered in the basic square, see the schematic figure 1 , The plane coordinates of the four vertices are (0, 0), (30, 0), (30, 30) and (0, 30), point a is (9, 9), point b is (12, 22.5) , Point c is (24,12), the above three points a, b, and c are connected to form a triangle, the above three internal surveying points are connected to form a triangle, and then a vertex is selected from the four vertices of the basic square, and the distance between the vertex and the The sum of t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
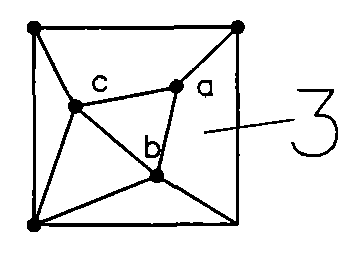
[0194] Specific embodiment two; see schematic figure 1 To indicate Image 6 , The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is: in step 2, the three surveying points scattered in the basic square are a(6,6), b(15,24), c(24, 15); Other steps are the same as the first embodiment.
[0195] Compared with the first embodiment, the first embodiment has better dispersion along the trend and trend of the surveying points in the basic unit; this embodiment has better dispersion along the trend and trend of the surveying points in the supporting unit; 2. The length between two adjacent surveying and mapping points in the surveying and mapping network is reduced compared to the first embodiment, and it is reduced within the range of 0.43 to 0.67 times the side length of the basic square.
specific Embodiment approach 3
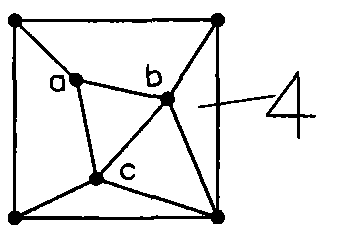
[0196] Specific implementation mode three: see Figure 14 to Figure 19 The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is: in step two, one surveying point is arranged at each of the four vertices of the basic square, and three surveying points are scattered in the basic square, and the above three internal points are connected to form a triangle , And then arrange a surveying and mapping point at the right midpoint of the basic square, adding up to the surveying and mapping points on the four vertices of the basic square and the three surveying and mapping points scattered in the basic square for a total of eight surveying and mapping points. Signal Figure 14 The eight surveying and mapping points are (0, 0), (30, 0), (30, 30), (0, 30), a(8.31, 13.62), b(15, 24), c(20.37, 6 ), d(30, 15). Connect the surveying point at the midpoint on the right of the square to the two surveying points of the nearest triangle inside, respectively, and place the two vertices of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com