Three-Dimensional Display with Motion Parallax
A motion parallax and parallax technology, applied in image communication, equipment, stereo system, etc., can solve problems such as fatigue and discomfort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
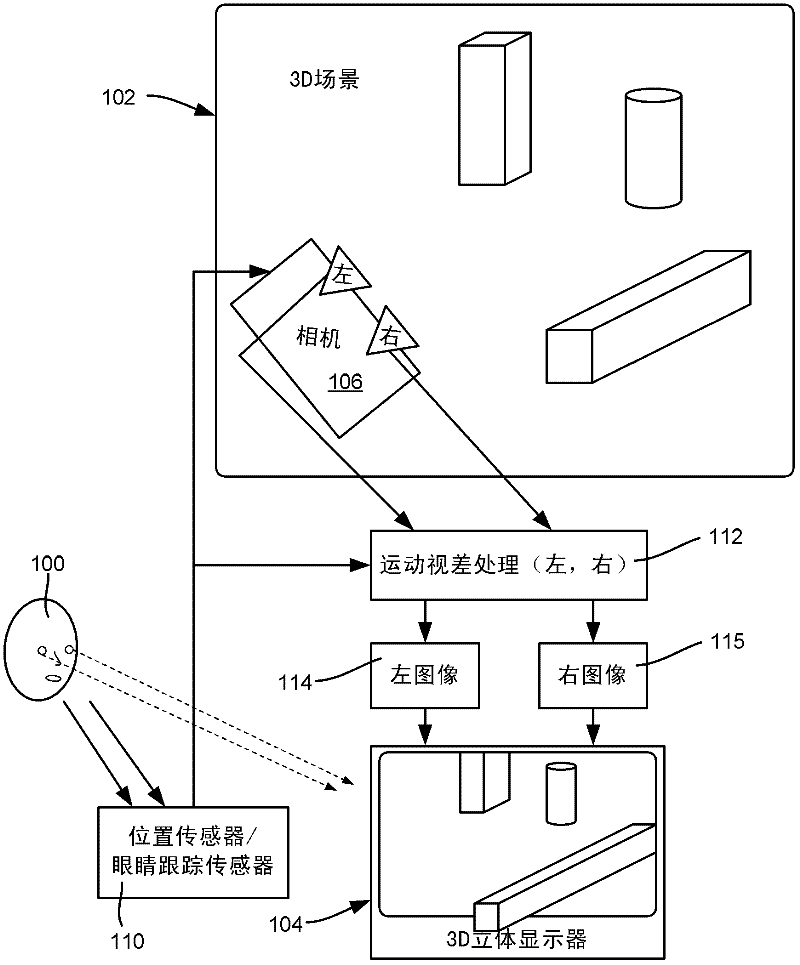
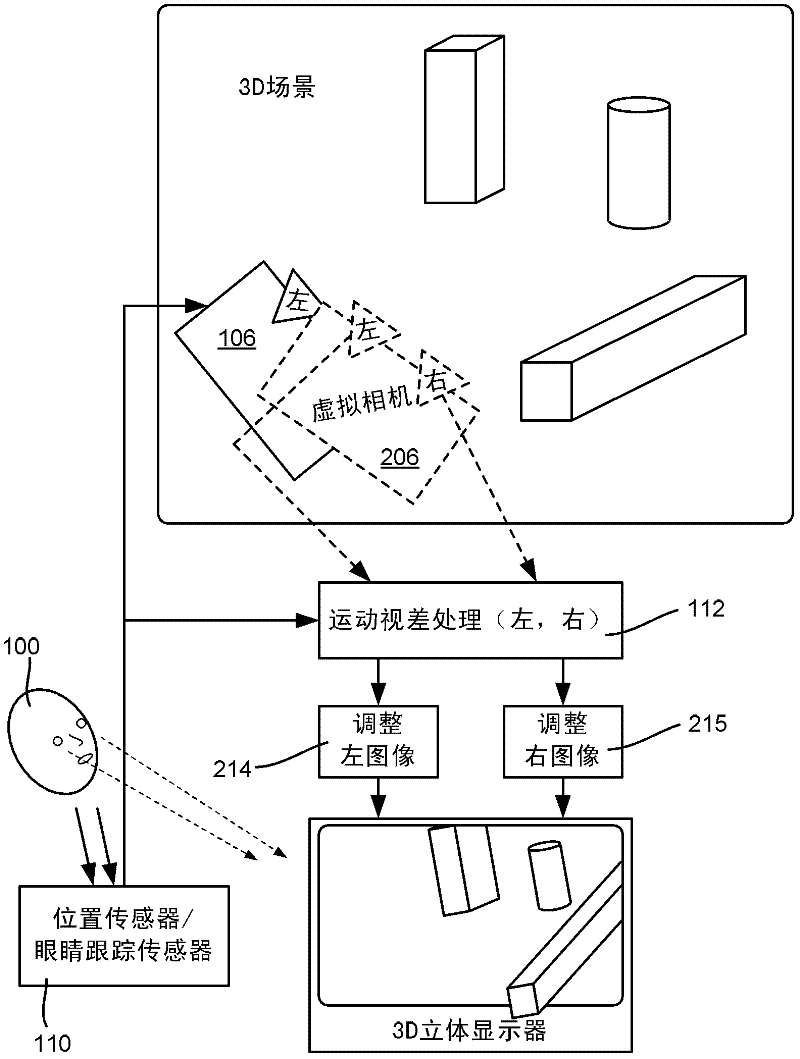
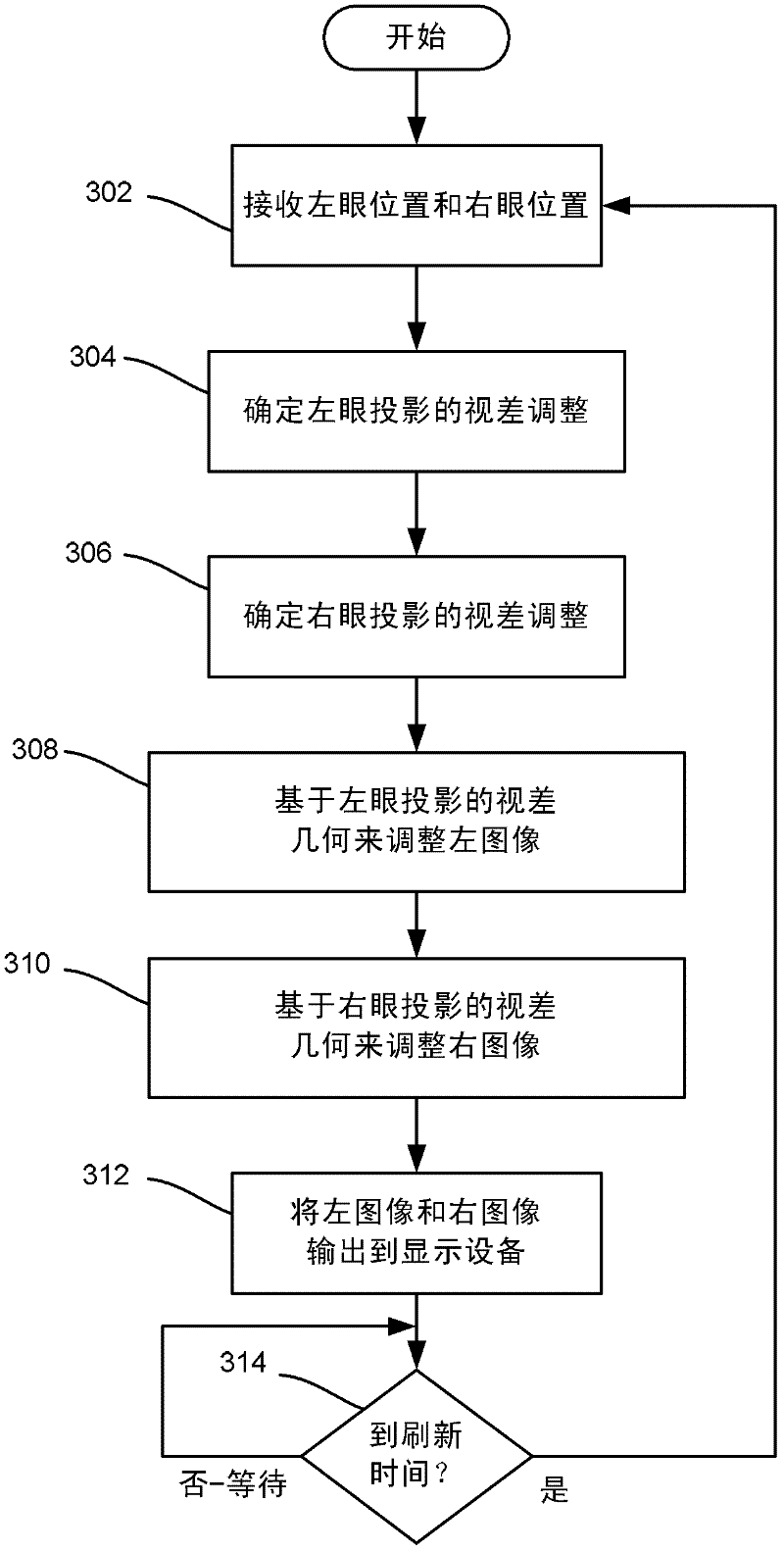
[0018] Aspects of the invention generally relate to a hybrid stereoscopic image / motion parallax system that uses stereoscopic 3D vision technology to present a different image to each eye, combined with motion parallax technology to adjust the left and right images for the position of the viewer's eyes . In this way, the viewer receives both stereoscopic and parallax cues as the viewer moves while viewing the 3D scene, which tends to result in greater visual comfort / less fatigue for the viewer. To this end, the position of each eye (or eyeglass lens, as described below) can be tracked directly or via estimation. A 3D image of the scene is presented to each eye in real time using perspective projection computed from the viewer's point of view, providing parallax cues.
[0019] It should be understood that any examples herein are non-limiting. Thus, the invention is not limited to any specific embodiment, aspect, concept, structure, function or example described herein. Rathe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com