Vibration control device
A technology for control devices and vehicles, which is applied to control devices, battery/fuel cell control devices, power devices, etc., can solve problems such as unstable vehicle conditions, and achieve the effect of suppressing influences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
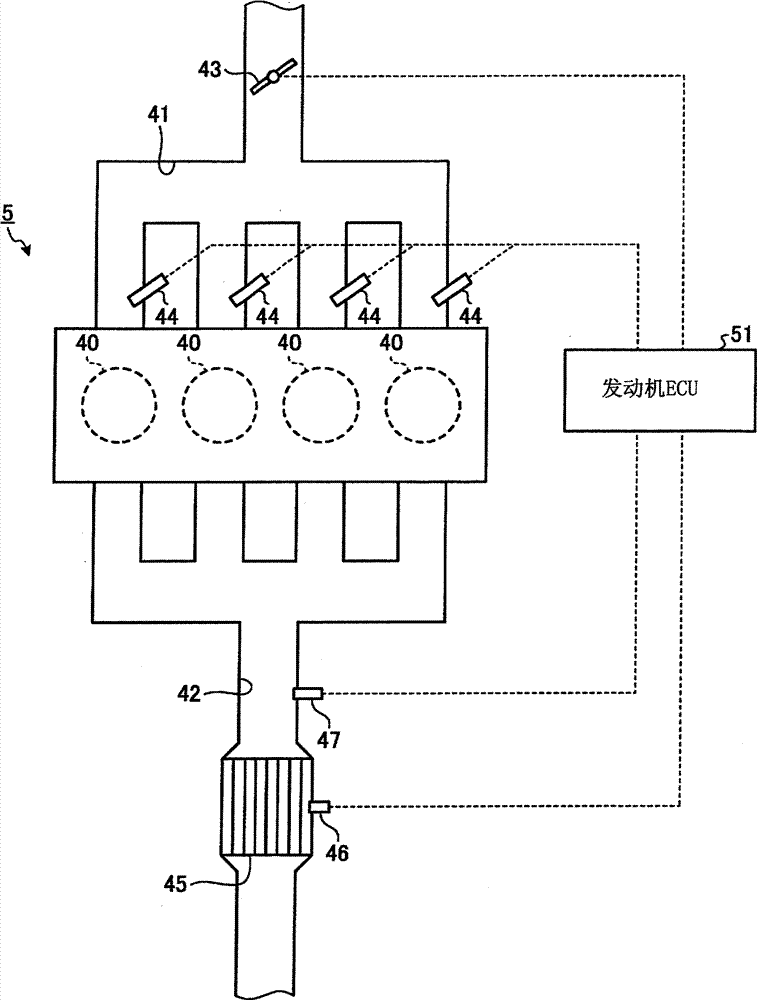
[0081] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of main parts of a vehicle provided with the vibration damping control device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In the following description, the traveling direction when the vehicle 1 normally travels is referred to as the front, and the direction opposite to the traveling direction is referred to as the rear. In addition, the sprung vibration in the following description refers to the vibration generated on the vehicle body via the suspension due to the input from the road surface to the wheels of the vehicle, for example, vibration of frequency components in the vicinity of 1 to 4 Hz, more specifically 1.5 Hz. The sprung vibration of the vehicle includes a component in the pitch direction or the jump direction (up-down direction) of the vehicle. In addition, sprung vibration damping refers to a technique for suppressing the above-mentioned sprung vibration of the vehicle.
[0082] figure 1 The shown vehicle 1 is...
Embodiment 2
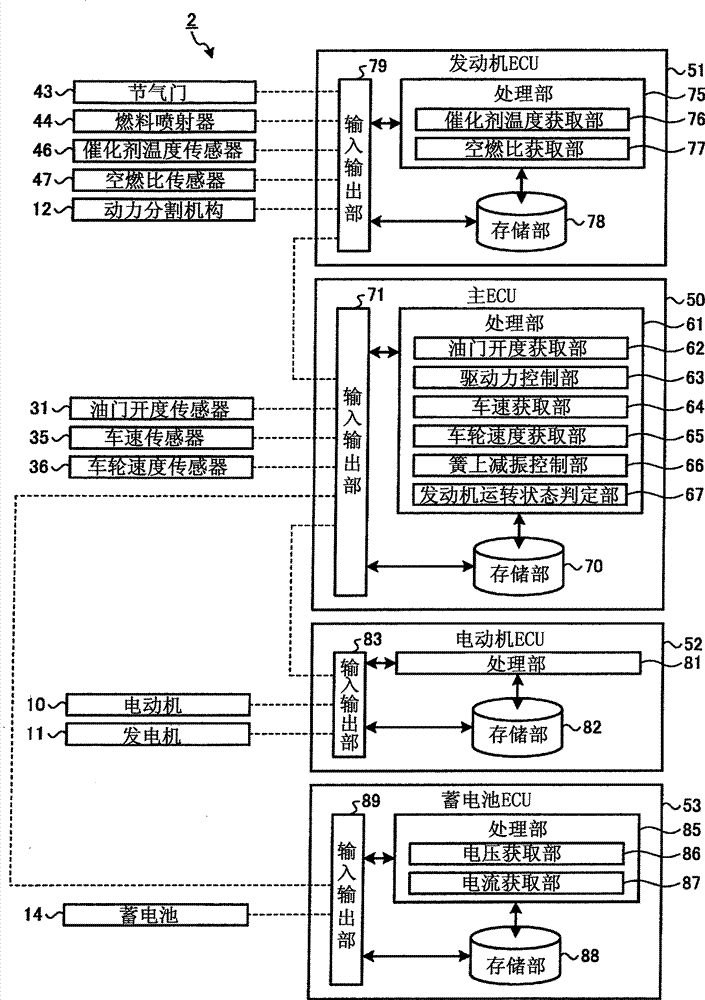
[0123] The vibration damping control device 90 of the second embodiment has substantially the same configuration as the vibration damping control device 2 of the first embodiment, but is characterized by including the voltage of the battery 14 as the execution condition of the sprung vibration damping. The other configurations are the same as those in Embodiment 1, so descriptions thereof are omitted, and the same reference numerals are attached. Figure 5 It is a configuration diagram of main parts of the vibration damping control device of the second embodiment. Regarding the vibration damping control device 90 of the second embodiment, similar to the vibration damping control device 2 of the first embodiment, whether the engine 5 is started or stopped is used to determine whether to prohibit the sprung vibration damping control. In the vibration damping control device 90 of 2, the voltage of the battery 14 is also used in the judgment of whether to prohibit the sprung vibra...
Embodiment 3
[0139] The vibration damping control device 100 of the third embodiment has substantially the same configuration as the vibration damping control device 2 of the first embodiment, but has a disadvantage in that it determines whether to execute the sprung vibration damping based on the presence or absence of the catalyst 45 warm-up request. feature. The other configurations are the same as those in Embodiment 1, so descriptions thereof are omitted, and the same reference numerals are attached. Figure 8 It is a configuration diagram of main parts of the vibration damping control device of the third embodiment. The vibration damping control device 100 of the third embodiment uses whether or not there is a request to warm up the catalyst 45 in determining whether to prohibit the sprung vibration damping control. Therefore, in the vibration damping control device 100 of Embodiment 3, the processing unit 61 of the main ECU 50 has an accelerator opening acquisition unit 62, a drivi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com