Constructs for expressing herbicide tolerance genes, related plants, and related trait combinations
A technology of transgenic plants and herbicides, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, plant products, genetic engineering, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
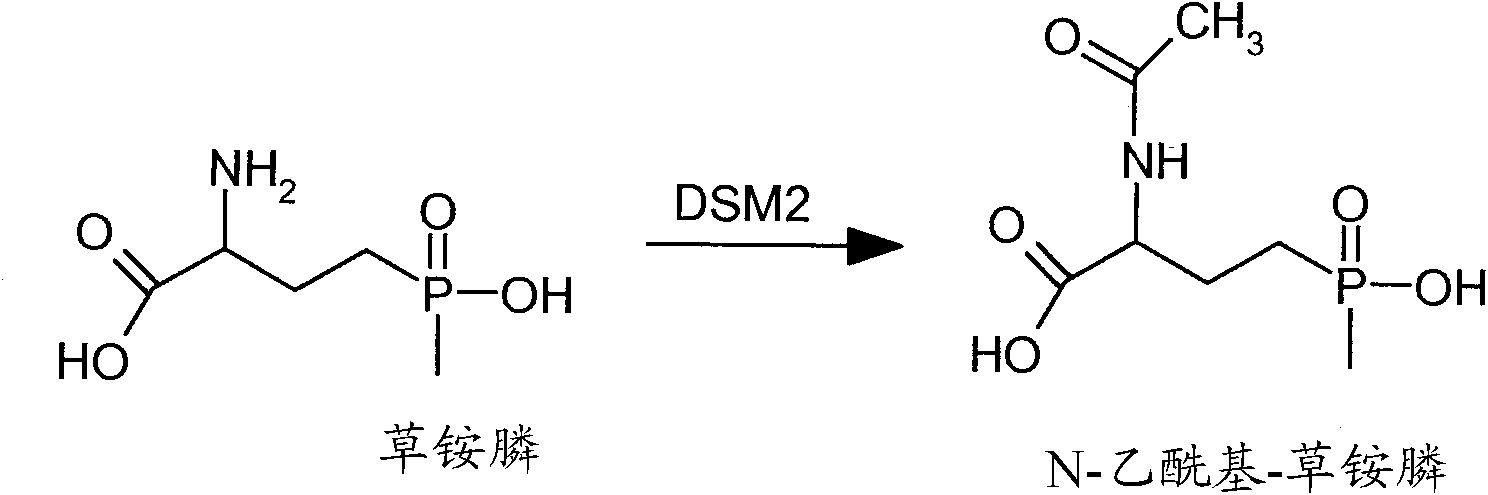
[0110] Example 1. Method for identifying genes that confer glufosinate-ammonium resistance in plants
[0111] As a method for identifying genes possessing herbicide-degrading activity in planta or cell culture, current public databases such as NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) can be mined. To start the process, one must have an identified functional gene sequence encoding a protein with the desired characteristics (ie, phosphinothricin acetyltransferase). This protein sequence was then used as input to the BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) (Altschul et al., 1997) algorithm for comparison against stored available NCBI protein sequences. Using default settings, this search returned more than 100 homologous protein sequences at different levels. These range from high identity (85-98%) to very low identity (23-32%) at the amino acid level. Traditionally, only sequences with high homology would be expected to retain similar properties to the input sequ...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2. Optimization of sequences for expression in plants and bacteria
[0114] 2.1- Background
[0115] In order to obtain higher levels of expression of heterologous genes in plants, it may be preferable to reengineer the protein coding sequences of said genes so that they are expressed more efficiently in plant cells. Maize is one such plant in which the heterologous protein coding region can preferably be redesigned prior to transformation to increase the expression level of the gene and the level of the encoded protein in the plant. Therefore, an additional step in the design of genes encoding bacterial proteins is the reengineering of heterologous genes for optimal expression. See, for example, Kawabe et al. (2003), "Patterns of Codon Usage Bias in Three Dicot and Four Monocot Plant Species," Genes Genet. Syst., pp. 343-352; and Ikemura et al. (1993), "Plant Molecular Biology Labfax", Croy , ed., Bios Scientific Publishers Ltd., p.3748), and all relevant ref...
Embodiment 3
[0132] Example 3. Cloning of Transformation Vectors
[0133] 3.1 - Construction of a binary plasmid containing DSM-2 (v2)
[0134] The DSM-2 (v2) codon-optimized gene of the coding sequence (DASPICO45) was cut with restriction enzymes BbsI (New England Biolabs, Inc., Beverly MA, Cat. No. R0539s) and SacI (New England Biolabs, Inc., Cat. No. R0156s) . The resulting fragment was ligated into pDAB773 at the corresponding restriction sites NcoI (New England Biolabs, cat# R0193s) and Sad. Positive colonies were identified by restriction enzyme digestion. The resulting clone contains Rb7MAR v3 / / At Ubi10 Promoter v2 / / Gene of Interest / / Atu Orf 13'UTR v3. The plasmid containing DSM-2 (v2) as the gene of interest was labeled pDAB3774.
[0135] The Rb7MAR v3 / / AtUbi10 Promoter v2 / / Gene of Interest / / Atu Orf13'UTRv3 expression cassette was cloned as an AgeI (New England Biolabs, Inc., Cat. No. R0552s) restriction fragment into the binary vector pDAB3736. This expression cassette was cl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com