Design method and device of synchronization access sequence
A design method and auxiliary synchronization sequence technology, applied in the field of communication, to achieve the effect of meeting the synchronization requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
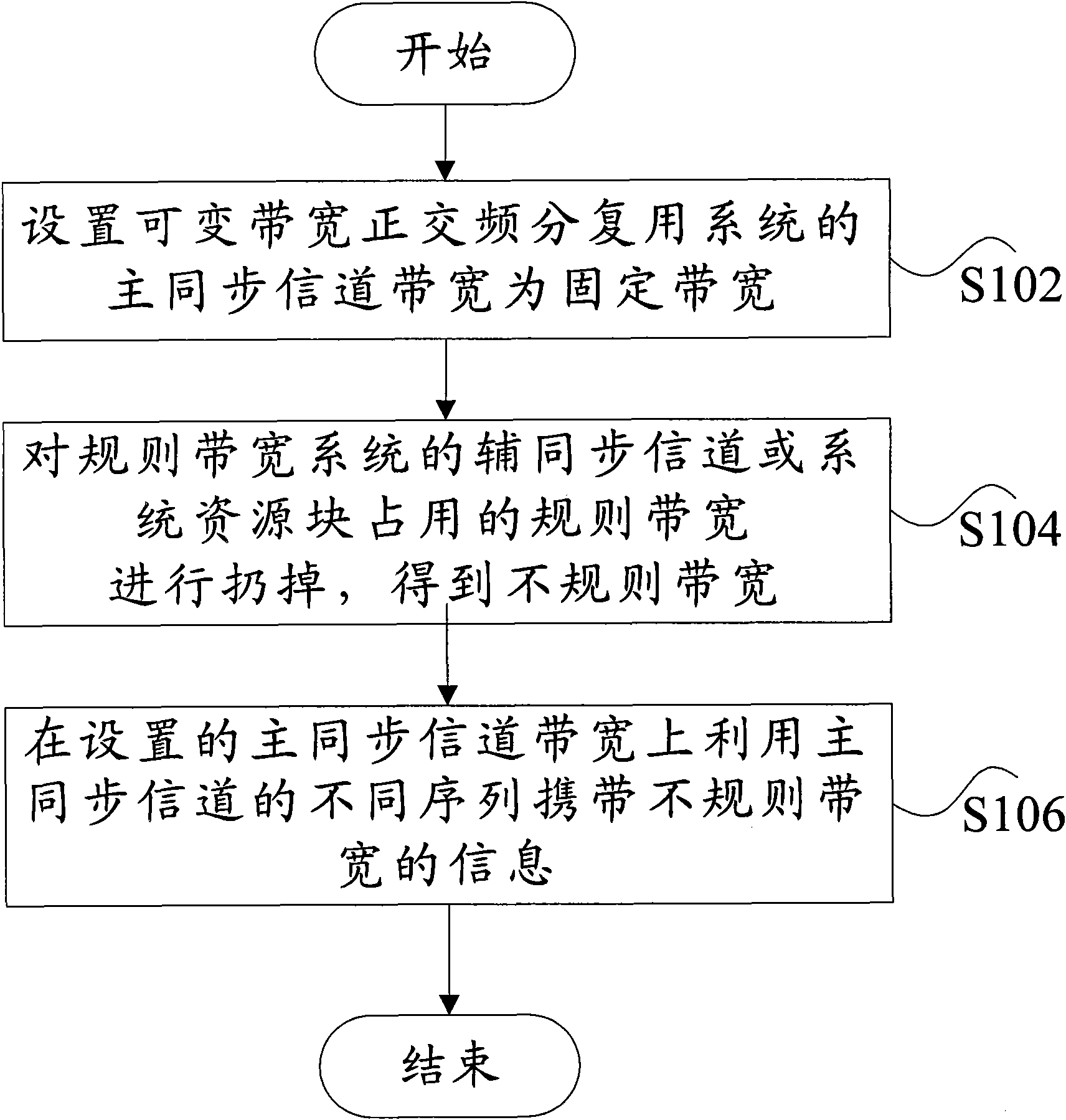
[0062] The first implementation of the variable bandwidth synchronization channel sequence design method is: performing dropping design in units of synchronization sequence sub-blocks. Combine below Figure 4 This implementation is described.
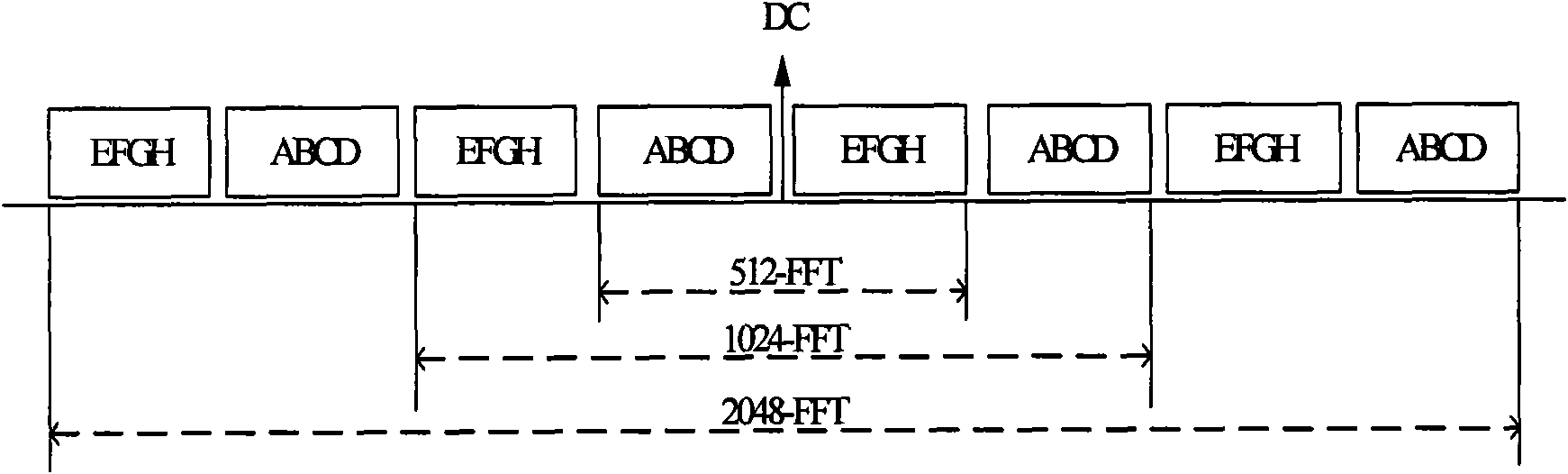
[0063] Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the corresponding relationship between the sub-blocks of the secondary synchronization sequence and the resource sub-bands of the regular bandwidth (5, 10MHz) 16m system according to the embodiment of the present invention, as shown in Figure 4 As shown, the DC carrier (Direct Current, DC for short) is used to illustrate, since the SA sequence adopts a scalable design, that is, 5MHz uses 8 sub-blocks {ABCDEFGH}, and each sub-block occupies 54 sub-carriers. In order to support the irregular bandwidth between 5MHz and 10MHz, the subcarriers of the 10MHz system are dropped from both sides in the form of subblocks, such as Figure 4 In the 10MHz system, two sub-blocks are discarded on both s...
Embodiment 2
[0072] The second implementation of the variable bandwidth synchronous channel sequence design method is: taking sub-band as a unit of dropping design.
[0073] According to the 16-system resource mapping method, the available sub-carriers of 5MHZ are divided into 6 sub-bands, and each sub-band occupies 72 sub-carriers. If will Figure 4 In the 10MHz system, two sub-bands are discarded on both sides of the 12 sub-bands, and then Image 6 The non-standard bandwidth of , whose bandwidth is 7.2MHz, at this time, the Sub-block set of SA is S1={H, A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, A}.
[0074] Similarly, when different numbers of sub-blocks are discarded, the series of non-standard bandwidths shown in Table 3 below are obtained.
[0075] Therefore, when dropping in units of sub-bands, the possible bandwidth series, system resource blocks (subbands) and corresponding SA sub-block sets are:
[0076] Table 3 Non-standard bandwidth series
[0077] The sub-band contained in the irregul...
Embodiment 3
[0082] The third implementation of the variable bandwidth synchronous channel sequence design method is: combining SAsub-block and resource mapping subband size dropping design.
[0083] In this method, the variable bandwidth selects the series design that is closest to the post-dropping bandwidth of the SA sub-block and resource mapping subband size and the non-standard bandwidth, so it is also called a hybrid dropping design.
[0084] At this time, the bandwidth (number of subcarriers) occupied by the system broadcast information channel and the bandwidth (number of subcarriers) occupied by the SA may be different. When the terminal initially accesses, the bandwidth information carried by the PA, that is, the bandwidth information carried by the system broadcast information channel The occupied bandwidth (number of subcarriers) or the bandwidth occupied by SA (number of subcarriers), to determine the bandwidth occupied by SA, first detect the CellID information carried by SA,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com