Method and platform for predicating teleoperation of robot
A prediction method and robot technology, applied in the field of robots, can solve the problems of not fully reflecting the operation of the robot, no compensation for the real-time operation information of the robot, and no on-site sensor signals.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
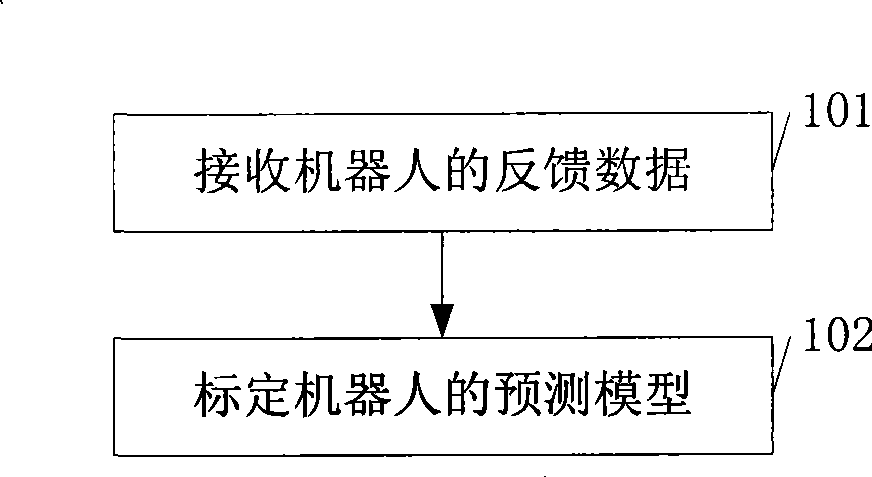
[0022] see figure 1 , an embodiment of the present invention provides a robot teleoperation prediction method, including:
[0023] Step 101: receiving feedback data from the robot;
[0024] Step 102: Use the feedback data to calibrate the predictive model of the robot.
[0025] Concretely include in step 101:
[0026] Receive the joint angle data and pose data of the robot;
[0027] The joint angle data is specifically the angle of each joint angle of the robot in each degree of freedom direction, which is obtained by real-time measurement when the robot is running; the robot runs for one cycle, and each joint angle forms a joint angle angle-time in each direction of each degree of freedom. curve;
[0028] The pose data is specifically the position data and attitude data of the robot, which is obtained by real-time detection when the robot is running; the position data is the projection of the center of gravity of the robot on each coordinate axis of the three-dimensional ...
Embodiment 2
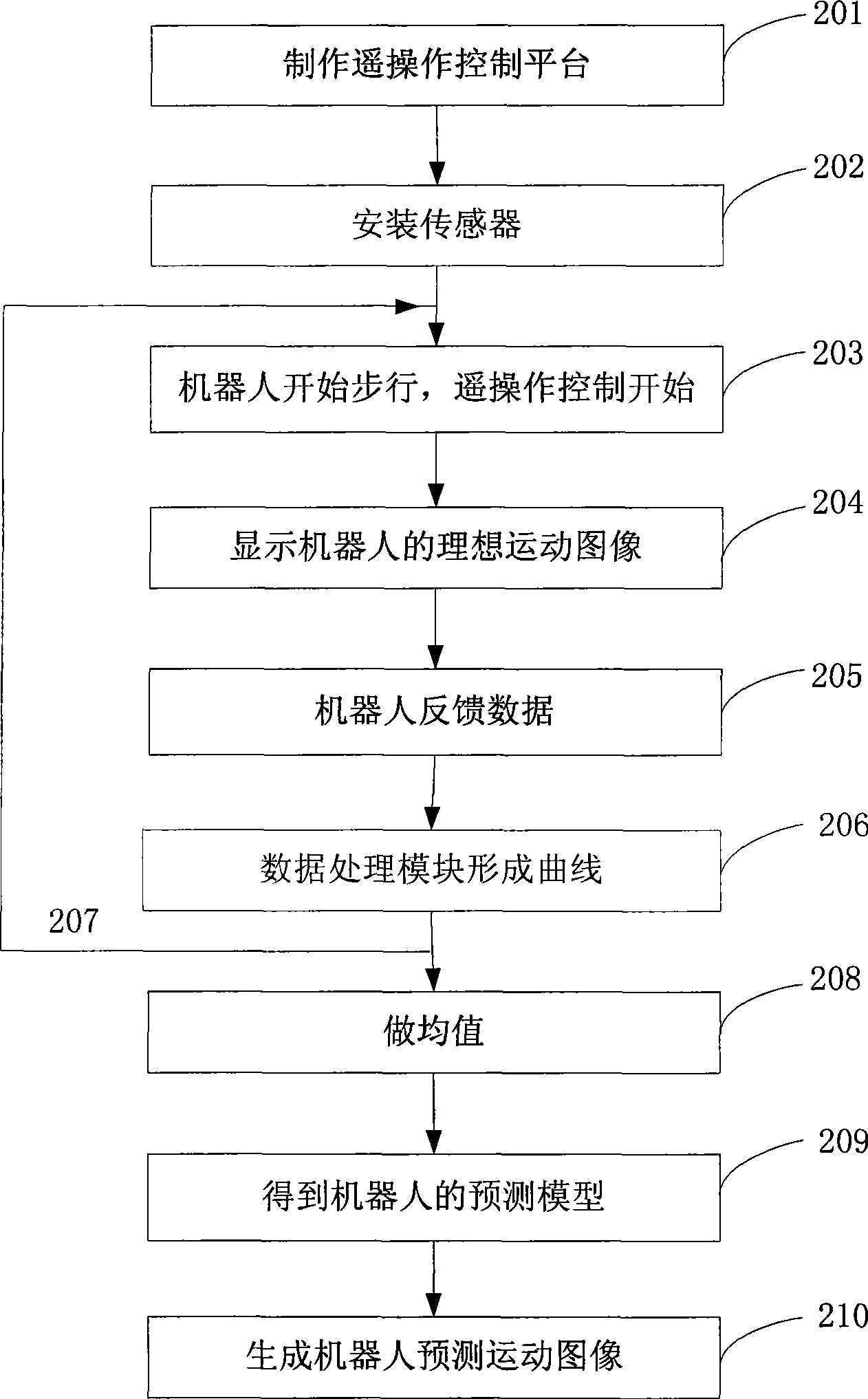
[0046] In this embodiment, taking the walking of a humanoid robot as an example, the robot teleoperation prediction method is described in detail:
[0047] The walking process of the robot is divided into three gait states, namely:
[0048] Step state 1: feet side by side upright;
[0049] Step state 2: left foot in front and right foot behind;
[0050] Step state 3: Right foot in front and left foot behind.
[0051] The above 3 gait states can be transformed into 6 gait patterns:
[0052] Gait mode 1: the left foot starts to walk as state 1 -> state 2;
[0053] Gait mode 2: the right foot starts to walk as state 1 -> state 3;
[0054] Gait mode 3: step forward with the left foot to state 3 -> state 2;
[0055] Gait mode 4: Stepping forward with the right foot is state 2 -> state 3;
[0056] Gait mode 5: the left foot retracts to state 3 -> state 1;
[0057] Gait pattern 6: The right foot retracts to state 2 -> state 1.
[0058] The above six gait patterns can be combi...
Embodiment 3
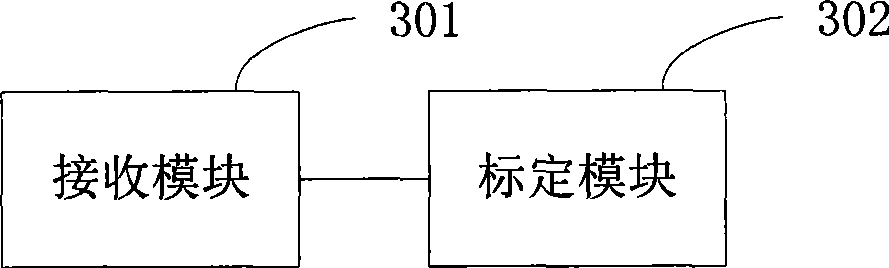
[0091] see image 3 , the embodiment of the present invention provides a teleoperation prediction platform, including:
[0092] Receiving module 301, for receiving the feedback data of robot;
[0093] The calibration module 302 is configured to calibrate the predictive model of the robot by using the feedback data.
[0094] The receiving module 301 is specifically used for:
[0095] Receive the joint angle data and pose data of the robot;
[0096] The joint angle data is specifically the angle of each joint angle of the robot in each degree of freedom direction, which is obtained by real-time measurement when the robot is running; the robot runs for one cycle, and each joint angle forms a joint angle angle-time in each direction of each degree of freedom. curve;
[0097] The pose data is specifically the position data and attitude data of the robot, which is obtained by real-time detection when the robot is running; the position data is the projection of the center of grav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com