Crank mechanism in particular for a weighing sensor on a balance working on the electromagnetic force compensation principle
A technology of weighing sensor and lever transmission, which is applied in the field of lever transmission device of the weighing sensor of the scale working according to the principle of electromagnetic force compensation, which can solve the problems of high spring constant, poor rigidity, adverse effects on measurement accuracy, etc., Achieve high transmission ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
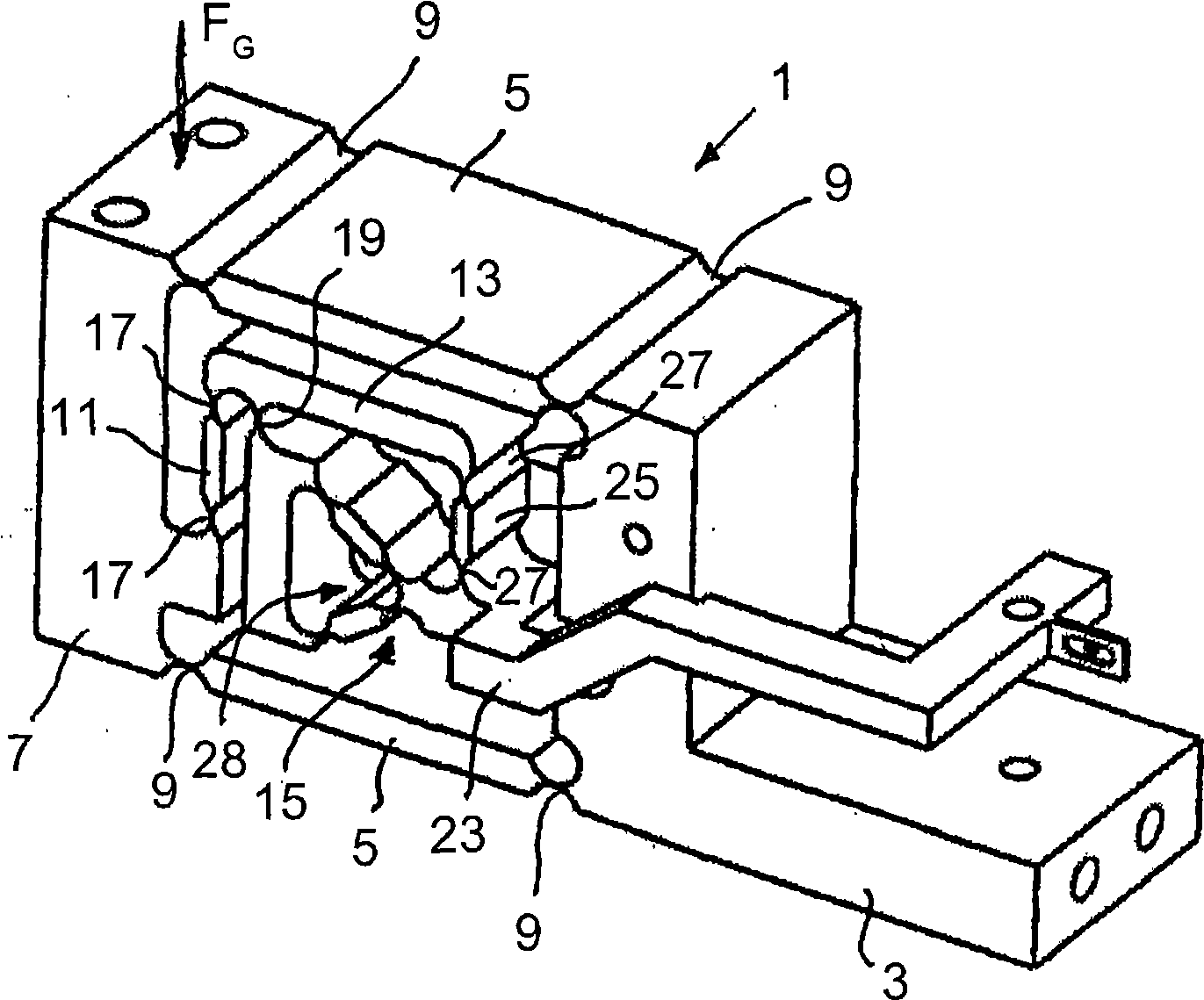
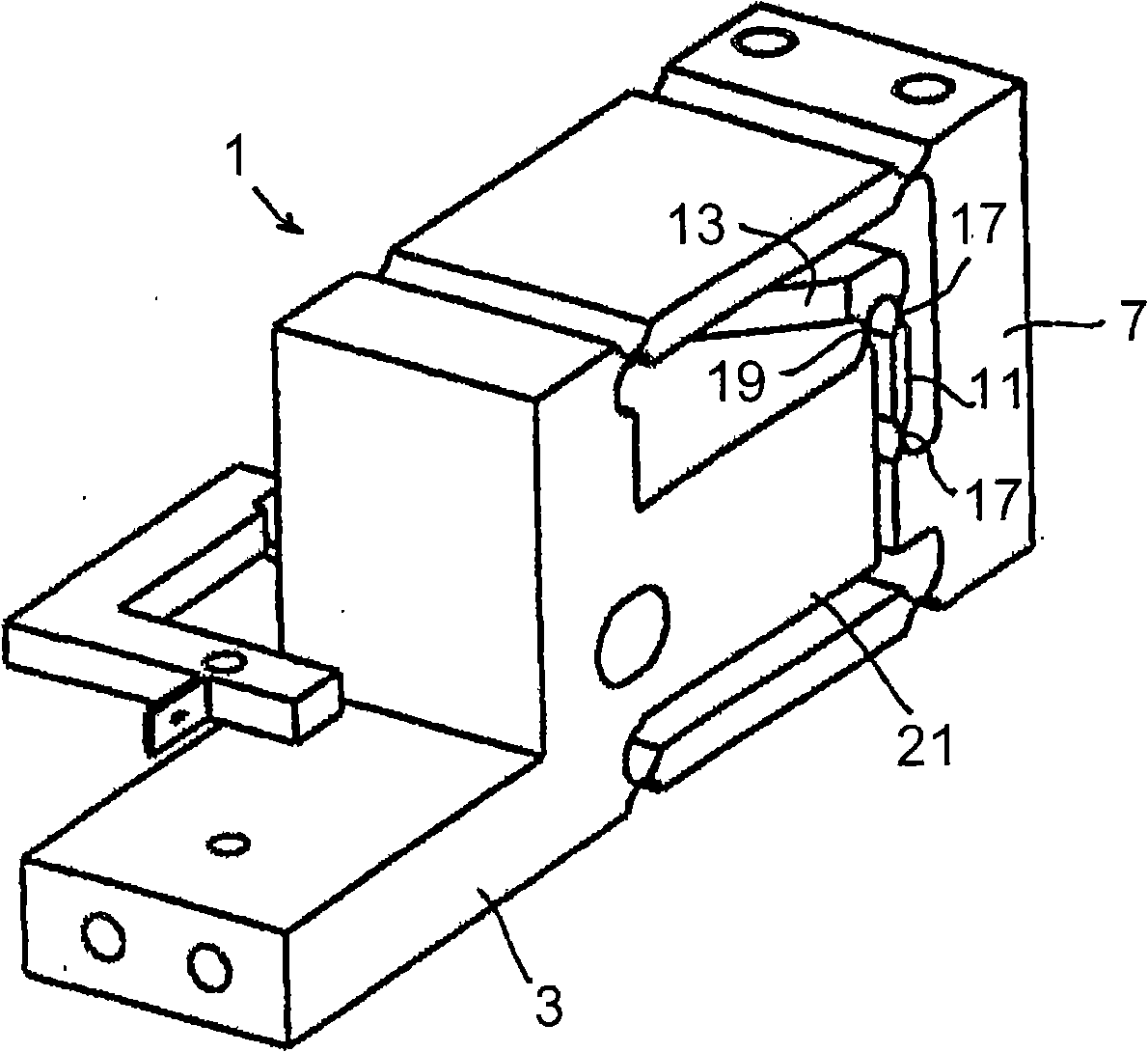
[0041] figure 1 The load cell 1 shown is of one-piece construction. In this embodiment, it is produced, for example, by machining a block of material, in particular milling and drilling. The load cell 1 comprises a body 3 which can be fixedly mounted, for example, in a housing of a scale. The main body 3 is connected to the carrier 7 via two parallel arms or parallel rods 5 , wherein the arms 5 are respectively connected to the stationary main body 3 and the carrier 7 by means of elastically deformable hinges 9 . The carrier 7 can be connected to a receiving device for items to be weighed (not shown).
[0042] The gravitational force FG acting on the carrier 7 causes a deflection of the parallel bars 5 and a movement of the carrier 7 towards the direction of gravity.
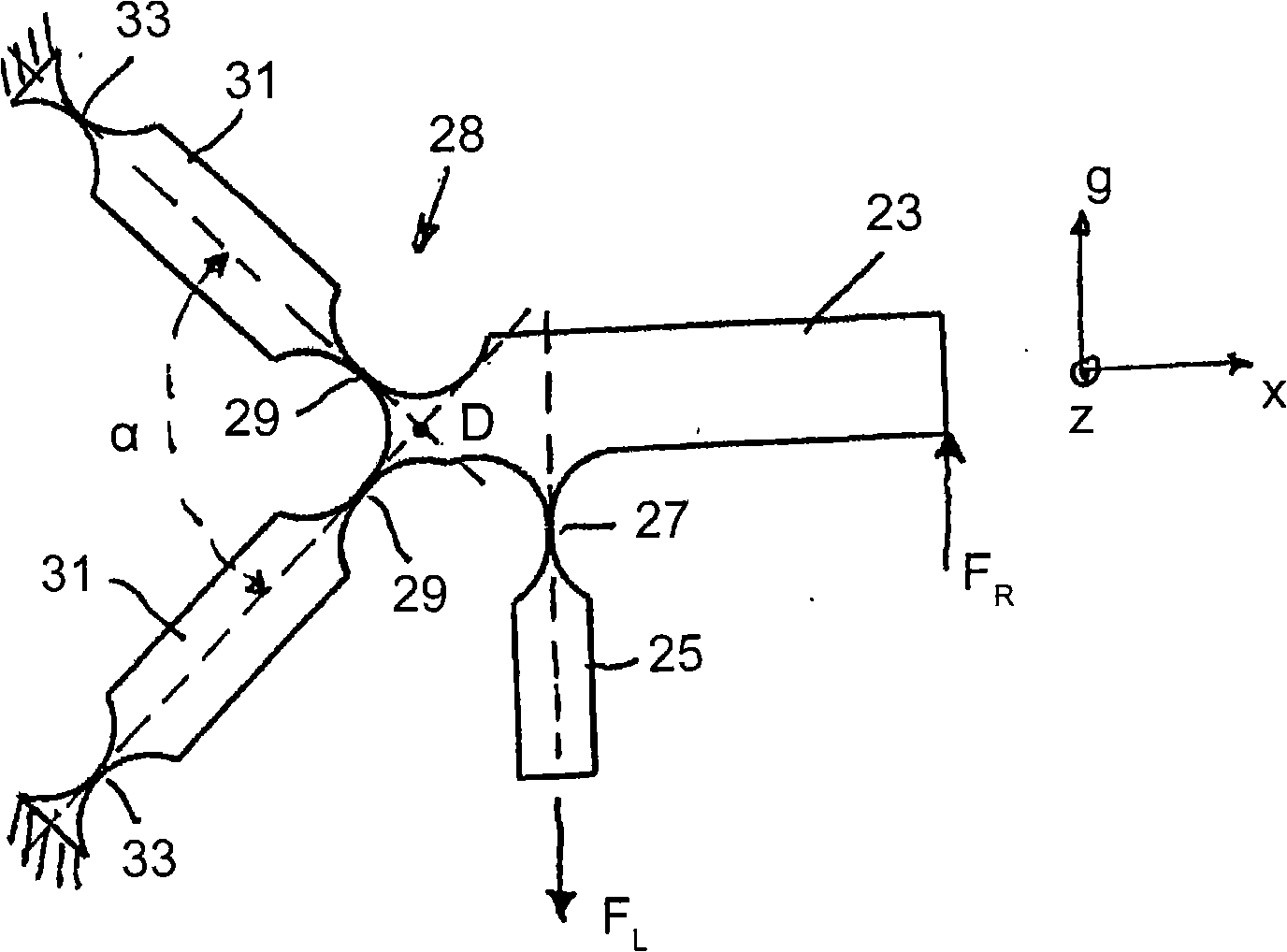
[0043] The carrier part 7 is connected via a connecting part 11 to the short lever arm of a first lever 13 of a two-stage lever transmission 15 . This connection in turn takes place via an elastically deform...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com