How to Improve Heat Seal Strength in LDPE Packaging?
JUN 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDPE Heat Seal Background and Objectives
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has been a cornerstone material in the packaging industry since its introduction in the 1930s. Its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and excellent barrier properties have made it a preferred choice for various packaging applications. The heat sealing capability of LDPE is particularly crucial, as it allows for the creation of secure, airtight packaging that protects contents from external contaminants and extends shelf life.
The evolution of LDPE heat sealing technology has been driven by increasing demands for packaging performance, efficiency, and sustainability. Early heat sealing methods were often inconsistent and prone to failure, leading to product spoilage and waste. As the packaging industry grew, so did the need for stronger, more reliable seals that could withstand the rigors of transportation, storage, and handling.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards improving heat seal strength while simultaneously addressing environmental concerns. This has led to the development of thinner films that maintain or exceed the performance of their thicker predecessors, reducing material usage and environmental impact. Additionally, there is a growing interest in enhancing the recyclability and biodegradability of LDPE packaging without compromising seal integrity.
The primary objective in improving heat seal strength in LDPE packaging is to enhance the overall performance and reliability of the packaging system. This involves optimizing the seal strength to resist various stresses, including mechanical forces, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to different environmental conditions. Achieving this goal requires a multifaceted approach that considers material properties, sealing equipment, process parameters, and quality control measures.
Another critical objective is to improve the consistency of heat seals across different production batches and varying environmental conditions. This consistency is essential for maintaining product quality and safety, particularly in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, where packaging integrity is paramount. Researchers and industry professionals are exploring advanced sealing technologies, innovative LDPE formulations, and precise control systems to achieve more uniform and dependable seals.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing heat sealing solutions that align with sustainable packaging initiatives. This includes creating stronger seals that allow for the use of thinner films, thereby reducing material consumption and waste. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the compatibility of LDPE heat seals with recycling processes, contributing to the circular economy goals of the packaging industry.
As we look to the future, the objectives for improving heat seal strength in LDPE packaging continue to evolve. The industry is moving towards more intelligent and adaptive sealing systems that can automatically adjust to variations in material properties and environmental conditions. There is also a push for the integration of nanotechnology and smart materials to create next-generation heat seals with enhanced strength, flexibility, and functionality.
The evolution of LDPE heat sealing technology has been driven by increasing demands for packaging performance, efficiency, and sustainability. Early heat sealing methods were often inconsistent and prone to failure, leading to product spoilage and waste. As the packaging industry grew, so did the need for stronger, more reliable seals that could withstand the rigors of transportation, storage, and handling.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards improving heat seal strength while simultaneously addressing environmental concerns. This has led to the development of thinner films that maintain or exceed the performance of their thicker predecessors, reducing material usage and environmental impact. Additionally, there is a growing interest in enhancing the recyclability and biodegradability of LDPE packaging without compromising seal integrity.
The primary objective in improving heat seal strength in LDPE packaging is to enhance the overall performance and reliability of the packaging system. This involves optimizing the seal strength to resist various stresses, including mechanical forces, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to different environmental conditions. Achieving this goal requires a multifaceted approach that considers material properties, sealing equipment, process parameters, and quality control measures.
Another critical objective is to improve the consistency of heat seals across different production batches and varying environmental conditions. This consistency is essential for maintaining product quality and safety, particularly in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, where packaging integrity is paramount. Researchers and industry professionals are exploring advanced sealing technologies, innovative LDPE formulations, and precise control systems to achieve more uniform and dependable seals.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing heat sealing solutions that align with sustainable packaging initiatives. This includes creating stronger seals that allow for the use of thinner films, thereby reducing material consumption and waste. Additionally, efforts are being made to improve the compatibility of LDPE heat seals with recycling processes, contributing to the circular economy goals of the packaging industry.
As we look to the future, the objectives for improving heat seal strength in LDPE packaging continue to evolve. The industry is moving towards more intelligent and adaptive sealing systems that can automatically adjust to variations in material properties and environmental conditions. There is also a push for the integration of nanotechnology and smart materials to create next-generation heat seals with enhanced strength, flexibility, and functionality.
Market Analysis for Enhanced LDPE Packaging
The market for enhanced LDPE packaging, particularly with improved heat seal strength, is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global LDPE packaging market is projected to expand at a steady rate, with a particular focus on innovations that enhance package integrity and performance.
Consumer goods and food packaging sectors are the primary drivers of this market growth. As consumers become more conscious of product freshness and safety, there is a growing demand for packaging solutions that offer superior sealing capabilities. This trend is particularly evident in the food industry, where extended shelf life and prevention of contamination are crucial factors.
The e-commerce boom has also contributed to the increased demand for robust LDPE packaging. With more products being shipped directly to consumers, there is a need for packaging that can withstand the rigors of transportation while maintaining product integrity. Enhanced heat seal strength in LDPE packaging addresses this challenge by reducing the risk of package failure during transit.
Sustainability concerns are shaping market dynamics as well. While LDPE is not biodegradable, improvements in heat seal strength can lead to the use of thinner films, potentially reducing overall plastic consumption. This aligns with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly packaging solutions and regulatory pressures to minimize plastic waste.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key market for enhanced LDPE packaging, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance packaging solutions for premium products.
The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts to improve heat seal strength without compromising other desirable properties of LDPE, such as flexibility and clarity. Major players in the packaging industry are investing in advanced technologies and materials to gain a competitive edge in this growing market segment.
Market analysts predict that the demand for enhanced LDPE packaging with improved heat seal strength will continue to rise in the coming years. This growth is expected to be fueled by advancements in polymer science, increasing adoption of flexible packaging, and the need for cost-effective solutions that ensure product protection throughout the supply chain.
Consumer goods and food packaging sectors are the primary drivers of this market growth. As consumers become more conscious of product freshness and safety, there is a growing demand for packaging solutions that offer superior sealing capabilities. This trend is particularly evident in the food industry, where extended shelf life and prevention of contamination are crucial factors.
The e-commerce boom has also contributed to the increased demand for robust LDPE packaging. With more products being shipped directly to consumers, there is a need for packaging that can withstand the rigors of transportation while maintaining product integrity. Enhanced heat seal strength in LDPE packaging addresses this challenge by reducing the risk of package failure during transit.
Sustainability concerns are shaping market dynamics as well. While LDPE is not biodegradable, improvements in heat seal strength can lead to the use of thinner films, potentially reducing overall plastic consumption. This aligns with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly packaging solutions and regulatory pressures to minimize plastic waste.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key market for enhanced LDPE packaging, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and changing consumer lifestyles. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-performance packaging solutions for premium products.
The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing research and development efforts to improve heat seal strength without compromising other desirable properties of LDPE, such as flexibility and clarity. Major players in the packaging industry are investing in advanced technologies and materials to gain a competitive edge in this growing market segment.
Market analysts predict that the demand for enhanced LDPE packaging with improved heat seal strength will continue to rise in the coming years. This growth is expected to be fueled by advancements in polymer science, increasing adoption of flexible packaging, and the need for cost-effective solutions that ensure product protection throughout the supply chain.
Current Challenges in LDPE Heat Sealing
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) packaging is widely used in various industries due to its flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. However, the heat sealing process, crucial for package integrity, faces several challenges that impact the overall strength and reliability of LDPE packaging.
One of the primary challenges in LDPE heat sealing is achieving consistent seal strength across different production batches. Variations in material properties, such as thickness and molecular weight distribution, can lead to inconsistencies in seal quality. This variability often results in weak spots or incomplete seals, compromising the package's barrier properties and shelf life.
Temperature control during the heat sealing process presents another significant challenge. LDPE has a relatively narrow temperature window for optimal sealing, and even slight deviations can result in inadequate fusion or material degradation. Maintaining precise temperature control across the entire sealing surface, especially in high-speed production environments, remains a persistent issue for manufacturers.
The presence of contaminants on the sealing surface is a common problem that affects seal strength. Dust, moisture, or product residues can interfere with the fusion process, creating weak points or channels for potential leakage. Ensuring a clean sealing environment and developing effective cleaning protocols are ongoing challenges in LDPE packaging production.
Seal geometry and pressure distribution also play critical roles in seal strength. Uneven pressure application or improper seal design can lead to inconsistent sealing patterns, reducing overall package integrity. Optimizing seal bar design and pressure distribution systems to accommodate various package shapes and sizes remains a complex engineering challenge.
The impact of packaging contents on seal strength is another area of concern. Some products, particularly those with high fat or oil content, can migrate to the sealing area during storage or transportation, potentially weakening the seal over time. Developing sealing technologies that are resistant to product interference is an ongoing research focus in the industry.
Environmental factors, such as humidity and ambient temperature, can significantly affect the heat sealing process and subsequent seal strength. Fluctuations in these conditions can alter the material properties of LDPE, making it challenging to maintain consistent sealing parameters across different production environments and geographic locations.
Lastly, the increasing demand for sustainable packaging solutions presents new challenges in LDPE heat sealing. As manufacturers explore bio-based or recycled LDPE alternatives, they must adapt sealing technologies to accommodate these materials' unique properties while maintaining or improving seal strength.
One of the primary challenges in LDPE heat sealing is achieving consistent seal strength across different production batches. Variations in material properties, such as thickness and molecular weight distribution, can lead to inconsistencies in seal quality. This variability often results in weak spots or incomplete seals, compromising the package's barrier properties and shelf life.
Temperature control during the heat sealing process presents another significant challenge. LDPE has a relatively narrow temperature window for optimal sealing, and even slight deviations can result in inadequate fusion or material degradation. Maintaining precise temperature control across the entire sealing surface, especially in high-speed production environments, remains a persistent issue for manufacturers.
The presence of contaminants on the sealing surface is a common problem that affects seal strength. Dust, moisture, or product residues can interfere with the fusion process, creating weak points or channels for potential leakage. Ensuring a clean sealing environment and developing effective cleaning protocols are ongoing challenges in LDPE packaging production.
Seal geometry and pressure distribution also play critical roles in seal strength. Uneven pressure application or improper seal design can lead to inconsistent sealing patterns, reducing overall package integrity. Optimizing seal bar design and pressure distribution systems to accommodate various package shapes and sizes remains a complex engineering challenge.
The impact of packaging contents on seal strength is another area of concern. Some products, particularly those with high fat or oil content, can migrate to the sealing area during storage or transportation, potentially weakening the seal over time. Developing sealing technologies that are resistant to product interference is an ongoing research focus in the industry.
Environmental factors, such as humidity and ambient temperature, can significantly affect the heat sealing process and subsequent seal strength. Fluctuations in these conditions can alter the material properties of LDPE, making it challenging to maintain consistent sealing parameters across different production environments and geographic locations.
Lastly, the increasing demand for sustainable packaging solutions presents new challenges in LDPE heat sealing. As manufacturers explore bio-based or recycled LDPE alternatives, they must adapt sealing technologies to accommodate these materials' unique properties while maintaining or improving seal strength.
Existing Heat Seal Strength Solutions
01 Polymer blends for improved heat seal strength
Blending LDPE with other polymers such as LLDPE, HDPE, or metallocene catalyzed polyethylene can enhance the heat seal strength of packaging films. These blends often provide a better balance of properties, including improved seal strength and lower seal initiation temperatures.- Polymer blends for improved heat seal strength: Blending LDPE with other polymers such as LLDPE, HDPE, or metallocene catalyzed polyethylene can enhance the heat seal strength of packaging films. These blends often provide a better balance of properties, including improved seal strength and lower seal initiation temperatures.
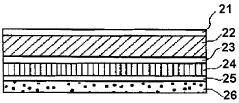
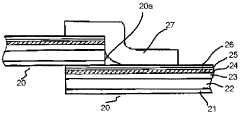
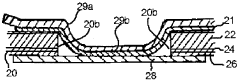
- Multilayer film structures for enhanced sealing: Developing multilayer film structures with specific seal layers can significantly improve heat seal strength. These structures often incorporate a low melting point sealant layer combined with structural layers to optimize both sealing performance and overall film properties.
- Surface treatment and coatings: Applying surface treatments or coatings to LDPE packaging can enhance heat seal strength. Techniques such as corona treatment, plasma treatment, or the application of heat-sealable coatings can improve the surface energy and sealability of the film.
- Optimization of sealing parameters: Fine-tuning sealing parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dwell time can significantly impact heat seal strength. Proper optimization of these factors can lead to improved seal integrity and overall packaging performance.
- Additives and modifiers for seal strength enhancement: Incorporating specific additives or modifiers into LDPE formulations can improve heat seal strength. These may include tackifiers, plastomers, or other specialty additives designed to enhance sealing properties without compromising other film characteristics.
02 Multilayer film structures for enhanced sealing
Developing multilayer film structures with specific seal layers can significantly improve heat seal strength. These structures often incorporate a low melting point polymer as the sealant layer, combined with structural layers for overall film performance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface treatment and coatings
Applying surface treatments or coatings to LDPE packaging can enhance heat seal strength. Techniques such as corona treatment, plasma treatment, or the application of heat-sealable coatings can improve the surface energy and sealability of the film.Expand Specific Solutions04 Optimization of sealing parameters
Fine-tuning sealing parameters such as temperature, pressure, and dwell time can significantly impact heat seal strength. Proper optimization of these factors can lead to improved seal integrity without compromising the LDPE film structure.Expand Specific Solutions05 Additives for improved seal performance
Incorporating specific additives into LDPE formulations can enhance heat seal strength. These may include tackifiers, plasticizers, or compatibilizers that can improve the sealing properties of the polymer without significantly altering its other characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in LDPE Packaging Industry
The heat seal strength improvement in LDPE packaging is a competitive field in the mature packaging industry. The market is substantial, driven by the widespread use of LDPE in various sectors. Major players like ExxonMobil Chemical, Dow Global Technologies, and Chevron Phillips Chemical are at the forefront of technological advancements. These companies, along with others such as Japan Polyethylene Corp. and SABIC Global Technologies, are investing in R&D to enhance heat seal properties. The technology's maturity is evident, but ongoing innovations focus on improving performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Smaller specialized firms like Coating Excellence International and Toray Plastics (America) are also contributing to advancements in this area.
ExxonMobil Chemical Patents, Inc.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil has pioneered the development of Exceed™ XP performance polymers, which offer exceptional heat seal strength for LDPE packaging. Their technology focuses on molecular design to create resins with a unique balance of long and short chain branching[3]. This structure allows for improved seal initiation temperatures and overall seal strength. ExxonMobil's approach also includes the development of metallocene catalysts that enable precise control over polymer architecture, resulting in enhanced sealing properties[4]. They have further innovated by creating blends of different polyethylene grades to optimize both seal strength and film toughness. Their research extends to co-extrusion techniques that allow for tailored seal layers in multi-layer film structures.
Strengths: Excellent seal initiation at lower temperatures, high seal strength retention at elevated temperatures. Weaknesses: May require specialized processing conditions and potentially higher raw material costs.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow has developed advanced LDPE resins specifically designed for heat seal applications. Their ELITE™ AT polymer technology combines enhanced seal strength with improved hot tack performance[1]. This technology utilizes a unique molecular architecture that allows for lower sealing temperatures while maintaining excellent package integrity. Dow's approach involves optimizing the polymer structure to create a broader sealing window, which improves processability on packaging lines. Additionally, they have introduced additives that enhance the heat seal strength without compromising other film properties[2]. Their research also focuses on developing multi-layer film structures that optimize the heat seal layer while maintaining overall package performance.
Strengths: Broad sealing window, improved hot tack, and compatibility with high-speed packaging lines. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for optimal performance and potentially higher material costs.
Innovative Heat Seal Technologies
Low density polyethylene with enhanced hot tack strength and adhesion-to-metal by the addition of ionomers
PatentWO2021022010A1
Innovation
- A polymer blend comprising at least 90% LDPE and 1-10% ionomer, specifically an ethylene acid copolymer with neutralized carboxylic acid salts, is developed to enhance hot tack strength and adhesion to metal substrates, with the ionomer improving molecular interactions and diffusion at the interface.
Laminated packaging material for paper container
PatentWO2000044632A1
Innovation
- A packaging material comprising a thermoplastic layer, a paper layer, and a barrier layer, with an innermost thermoplastic layer made of linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) having specific molecular weight distribution and melting properties, enhancing sealability and preventing leakage while maintaining quality.
Environmental Impact of LDPE Packaging
The environmental impact of LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) packaging is a critical consideration in the context of improving heat seal strength. While LDPE offers excellent sealing properties, its widespread use in packaging has significant environmental implications that must be addressed.
LDPE packaging contributes to plastic pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature. When improperly disposed of, it can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, leading to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and natural ecosystems. This accumulation poses threats to wildlife, particularly marine life, as animals may ingest or become entangled in plastic debris.
The production of LDPE packaging also has environmental consequences. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as raw materials and energy sources. This dependence contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources. Additionally, the production of LDPE involves the use of various chemicals and additives, some of which may have harmful effects on the environment if not properly managed.
Recycling LDPE packaging presents challenges due to contamination issues and the need for specialized recycling facilities. While LDPE is technically recyclable, the actual recycling rates remain low in many regions. This low recycling rate means that a significant portion of LDPE packaging ends up in landfills or incineration facilities, further exacerbating environmental concerns.
Efforts to improve heat seal strength in LDPE packaging may have both positive and negative environmental implications. On one hand, stronger seals can lead to more durable packaging, potentially reducing the need for excessive material use and minimizing food waste. This could result in a net positive environmental impact by reducing overall resource consumption and waste generation.
However, the pursuit of stronger heat seals may also lead to the incorporation of additional additives or the use of more complex multi-layer structures. These modifications could potentially make the packaging more difficult to recycle or increase its environmental footprint during production. It is crucial to balance the benefits of improved seal strength with the potential environmental trade-offs.
To address these environmental concerns, research into more sustainable alternatives is ongoing. Biodegradable and compostable materials are being explored as potential replacements for traditional LDPE packaging. Additionally, efforts to improve recycling technologies and infrastructure are underway to increase the recycling rates of LDPE packaging.
In conclusion, while improving heat seal strength in LDPE packaging is important for product protection and shelf life, it is equally crucial to consider and mitigate the environmental impact of these materials. A holistic approach that balances performance improvements with environmental sustainability is essential for the future of packaging technology.
LDPE packaging contributes to plastic pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature. When improperly disposed of, it can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, leading to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and natural ecosystems. This accumulation poses threats to wildlife, particularly marine life, as animals may ingest or become entangled in plastic debris.
The production of LDPE packaging also has environmental consequences. The manufacturing process relies heavily on fossil fuels, both as raw materials and energy sources. This dependence contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources. Additionally, the production of LDPE involves the use of various chemicals and additives, some of which may have harmful effects on the environment if not properly managed.
Recycling LDPE packaging presents challenges due to contamination issues and the need for specialized recycling facilities. While LDPE is technically recyclable, the actual recycling rates remain low in many regions. This low recycling rate means that a significant portion of LDPE packaging ends up in landfills or incineration facilities, further exacerbating environmental concerns.
Efforts to improve heat seal strength in LDPE packaging may have both positive and negative environmental implications. On one hand, stronger seals can lead to more durable packaging, potentially reducing the need for excessive material use and minimizing food waste. This could result in a net positive environmental impact by reducing overall resource consumption and waste generation.
However, the pursuit of stronger heat seals may also lead to the incorporation of additional additives or the use of more complex multi-layer structures. These modifications could potentially make the packaging more difficult to recycle or increase its environmental footprint during production. It is crucial to balance the benefits of improved seal strength with the potential environmental trade-offs.
To address these environmental concerns, research into more sustainable alternatives is ongoing. Biodegradable and compostable materials are being explored as potential replacements for traditional LDPE packaging. Additionally, efforts to improve recycling technologies and infrastructure are underway to increase the recycling rates of LDPE packaging.
In conclusion, while improving heat seal strength in LDPE packaging is important for product protection and shelf life, it is equally crucial to consider and mitigate the environmental impact of these materials. A holistic approach that balances performance improvements with environmental sustainability is essential for the future of packaging technology.
Quality Control in Heat Sealing Process
Quality control in the heat sealing process is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable packaging performance, particularly when aiming to improve heat seal strength in LDPE packaging. Effective quality control measures involve a combination of process monitoring, equipment calibration, and rigorous testing protocols.
One of the primary aspects of quality control in heat sealing is maintaining precise control over the sealing parameters. This includes monitoring and adjusting the sealing temperature, pressure, and dwell time. Variations in these parameters can significantly impact seal strength. Implementing automated process control systems can help maintain consistency and reduce human error.
Regular calibration and maintenance of heat sealing equipment are essential for quality control. This includes checking and adjusting heating elements, pressure bars, and cooling systems. Worn or misaligned components can lead to inconsistent seal quality. Establishing a preventive maintenance schedule and keeping detailed records of equipment performance can help identify potential issues before they affect seal strength.
Material quality control is another critical factor. Incoming LDPE film should be inspected for thickness uniformity, surface defects, and contamination. Variations in film properties can affect seal integrity. Implementing a robust supplier quality management system and conducting regular audits can help ensure consistent raw material quality.
In-process quality checks are vital for early detection of sealing issues. This may involve visual inspection of seals, periodic destructive testing, and the use of inline seal integrity testing equipment. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or vision systems, can provide real-time feedback on seal quality without compromising packaging.
Statistical process control (SPC) techniques can be employed to monitor seal strength trends over time. By collecting and analyzing data on seal strength, manufacturers can identify process drift, cyclical variations, or other patterns that may indicate the need for corrective action. SPC charts and other analytical tools can help visualize trends and set appropriate control limits.
Establishing clear quality standards and acceptance criteria for heat seal strength is essential. This includes defining minimum seal strength requirements, allowable variation ranges, and specific testing methods. Regular training of operators and quality control personnel ensures consistent application of these standards across production shifts.
Implementing a robust traceability system allows for quick identification and isolation of potentially affected products in case of seal quality issues. This system should track key process parameters, raw material lots, and equipment settings for each production run.
By implementing comprehensive quality control measures throughout the heat sealing process, manufacturers can significantly improve the consistency and reliability of seal strength in LDPE packaging. This not only enhances product quality but also reduces waste, improves efficiency, and ultimately contributes to better overall packaging performance.
One of the primary aspects of quality control in heat sealing is maintaining precise control over the sealing parameters. This includes monitoring and adjusting the sealing temperature, pressure, and dwell time. Variations in these parameters can significantly impact seal strength. Implementing automated process control systems can help maintain consistency and reduce human error.
Regular calibration and maintenance of heat sealing equipment are essential for quality control. This includes checking and adjusting heating elements, pressure bars, and cooling systems. Worn or misaligned components can lead to inconsistent seal quality. Establishing a preventive maintenance schedule and keeping detailed records of equipment performance can help identify potential issues before they affect seal strength.
Material quality control is another critical factor. Incoming LDPE film should be inspected for thickness uniformity, surface defects, and contamination. Variations in film properties can affect seal integrity. Implementing a robust supplier quality management system and conducting regular audits can help ensure consistent raw material quality.
In-process quality checks are vital for early detection of sealing issues. This may involve visual inspection of seals, periodic destructive testing, and the use of inline seal integrity testing equipment. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or vision systems, can provide real-time feedback on seal quality without compromising packaging.
Statistical process control (SPC) techniques can be employed to monitor seal strength trends over time. By collecting and analyzing data on seal strength, manufacturers can identify process drift, cyclical variations, or other patterns that may indicate the need for corrective action. SPC charts and other analytical tools can help visualize trends and set appropriate control limits.
Establishing clear quality standards and acceptance criteria for heat seal strength is essential. This includes defining minimum seal strength requirements, allowable variation ranges, and specific testing methods. Regular training of operators and quality control personnel ensures consistent application of these standards across production shifts.
Implementing a robust traceability system allows for quick identification and isolation of potentially affected products in case of seal quality issues. This system should track key process parameters, raw material lots, and equipment settings for each production run.
By implementing comprehensive quality control measures throughout the heat sealing process, manufacturers can significantly improve the consistency and reliability of seal strength in LDPE packaging. This not only enhances product quality but also reduces waste, improves efficiency, and ultimately contributes to better overall packaging performance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!