Self-compensating laser tracker
A laser tracker and self-compensation technology, applied in the direction of instruments, optics, optical components, etc., can solve problems such as cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011] Reference will now be made in detail to the exemplary embodiments, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings.
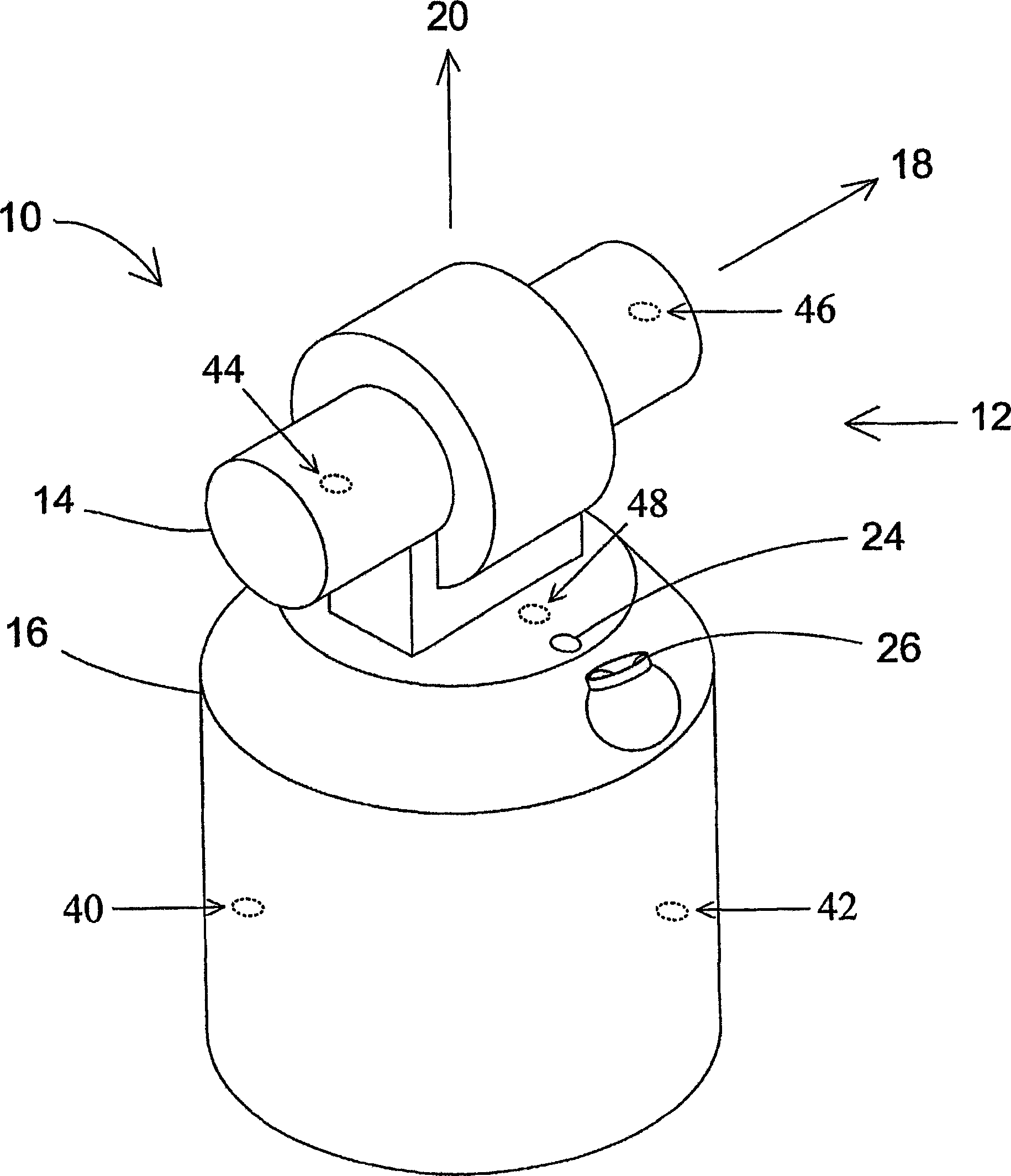
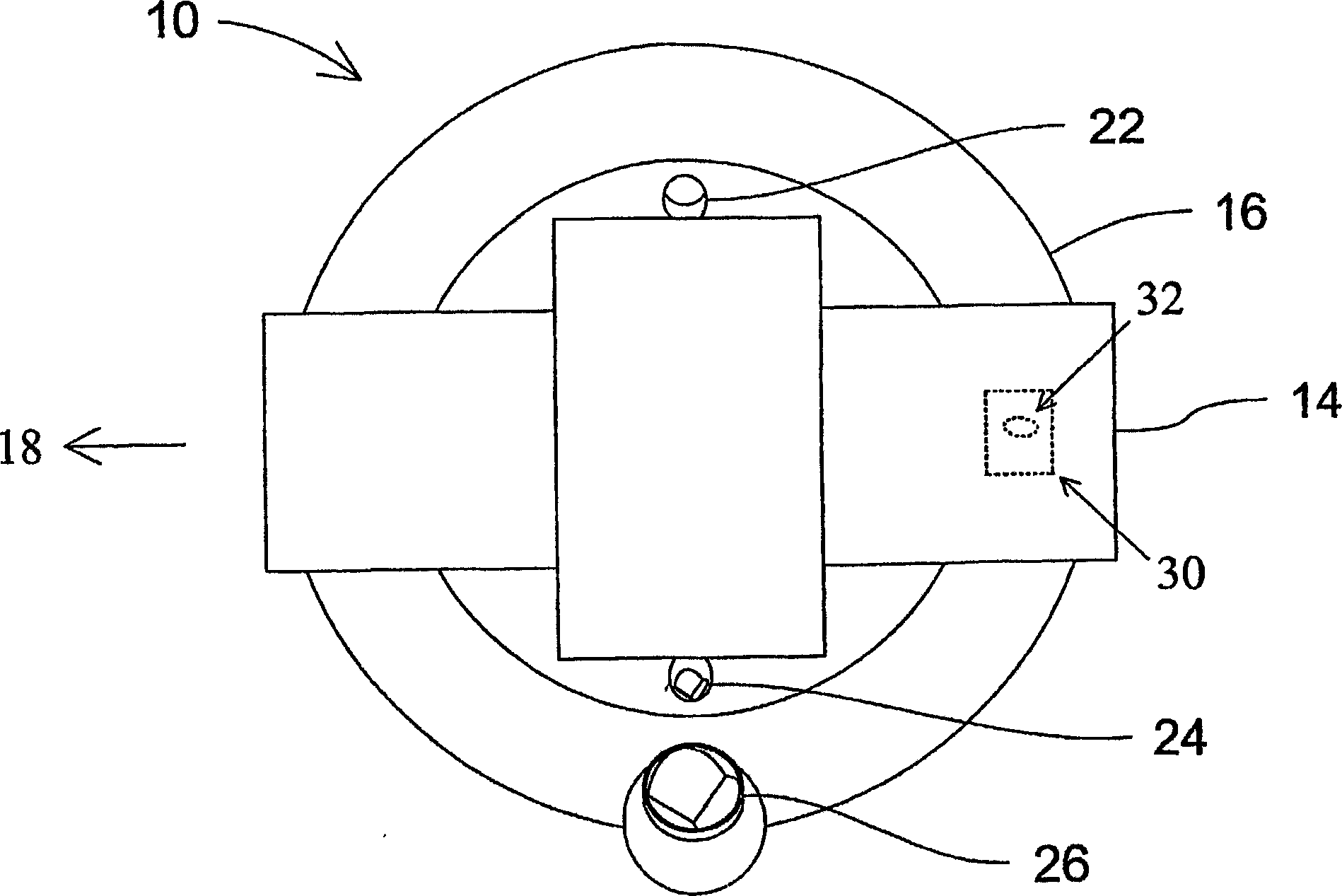
[0012] An exemplary gimbal beam steering mechanism 12 of the laser tracker 10 is as figure 1 As shown, it includes an apex rotation mount 14 mounted on an azimuth rotation base 16, and the apex and azimuth mechanical axes 18, 20 rotate to direct the laser beam in the desired direction. For clarity and simplicity, this type of gimbal mechanism 12 is used in the following discussion. However, other types of universal joints can also be used, and the techniques described here can be applied to these other types of universal joints as well.
[0013] Self-compensation with built-in tracker targets
[0014] An exemplary self-compensation method provides a method of determining four payload parameters TX, TY, RX, and RY that describe the position and orientation of the laser beam relative to the gimbal point of the tracker. The gimbal point is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com