A Dynamic Modeling Method for Smooth Particles with Solid Structure
A technology of dynamic modeling and solid structure, applied in the field of materials, it can solve the problems of insufficient completeness of the derivative of the SPH approximate function, poor SPH accuracy, unstable motion, etc. Stability phenomenon and the effect of saving computing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] This embodiment provides a solid structure smooth particle dynamics modeling method. Taking the two-dimensional planar solid structure as an example, the following describes in detail how to use the SPH method to establish the dynamic model of the solid structure and solve the stress deformation and related physical information of the planar structure.
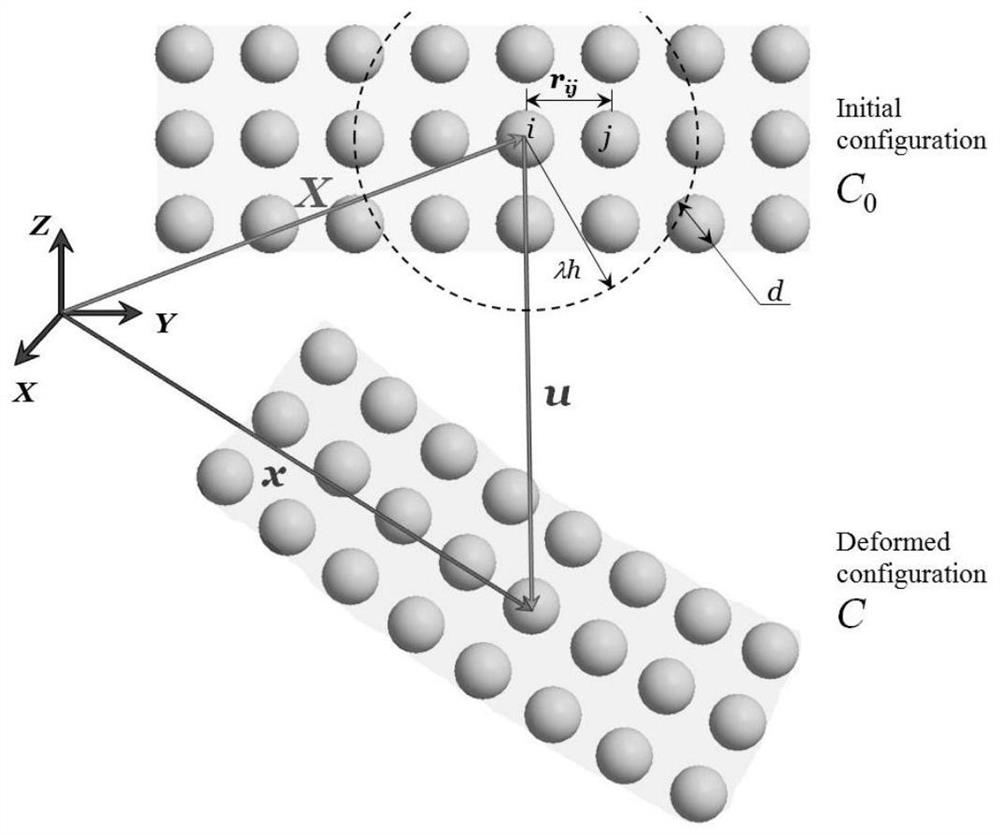
[0071] Step 1: Discretize the planar solid structure into SPH particles, each particle carries at least one kind of the same physical information, such as density, velocity, stress, strain, velocity, etc. figure 1 A schematic diagram of the SPH discrete particles of the planar solid structure provided by an embodiment of the present invention in a deformed state, from figure 1 The SPH discrete particle structure of the solid structure can be seen.
[0072] Step 2: In the deformed state, in order to solve the spatial point x i Deformation occurred at , according to the formula (1) to calculate x i Correction mode for ...
Embodiment 2
[0108] In this embodiment, a dynamic modeling method for solid structure smooth particles is provided. On the basis of the above method, the deformation acceleration of particles is further calculated. The method provided in this embodiment also includes:
[0109] Step 5: Calculate Lagrangian strain and Euler strain according to formula (4) and formula (5):
[0110]
[0111] ε=F -T EF -1 (5)
[0112] Among them, E represents Lagrangian strain, ε represents Euler strain;
[0113] Step 6: Calculate the Cauchy stress according to the plane stress assumption of formula (6):
[0114]
[0115] Among them, σ represents the Cauchy stress;
[0116] Step 7: According to the formula (7), convert the Cauchy stress to the initial undeformed configuration to obtain the first Piola-Kirchhoff stress:
[0117] P=JσF -T (7)
[0118] Among them, P represents the first Piola-Kirchhoff stress, J=|F|, which is the Jacobian determinant;
[0119] Step 8: According to formula (8), calcu...
Embodiment 3
[0131] This embodiment provides a solid structure smooth particle dynamics modeling method, wherein the planar solid structure is an isotropic cantilever arm. Figure 5 Force diagram of an isotropic cantilever beam provided by an embodiment of the present invention. The left end of the beam is fixed and a downward force is applied to the right end. The length, width and height of the beam are 100mm, 1mm and 10mm respectively. Material elastic modulus E = 210GPa, Poisson's ratio υ = 0.3.
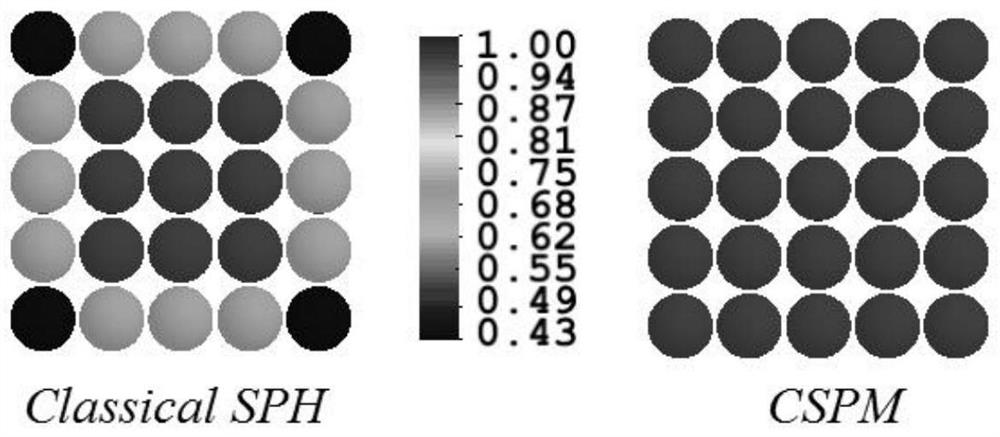
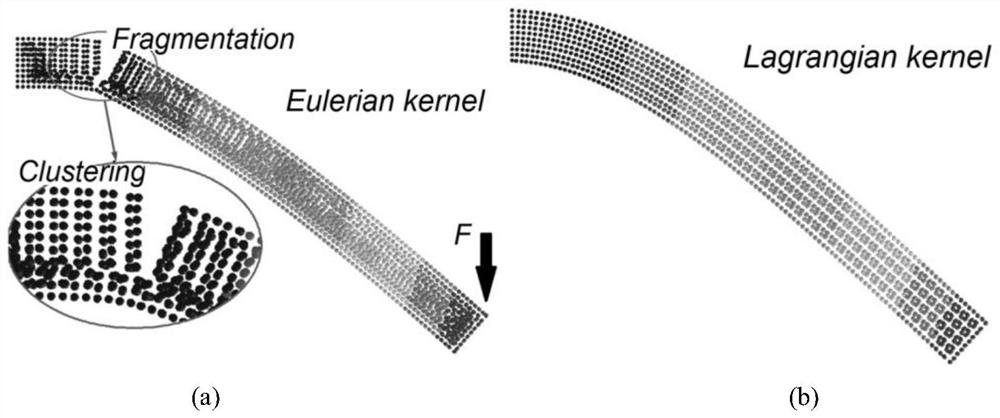
[0132] Using the solid structure smooth particle dynamics modeling method provided in Embodiment 1, the planar structure is discretized into 100×10 SPH particles, and the correction of the derivative of the smooth function at the midpoint C of the free edge of the suspended end is calculated according to formula (1) mode, and then solve the deflection of the middle point C of the free side at the right end under different forces. The calculation results are compared with Timoshenko's analy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Poisson's ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com