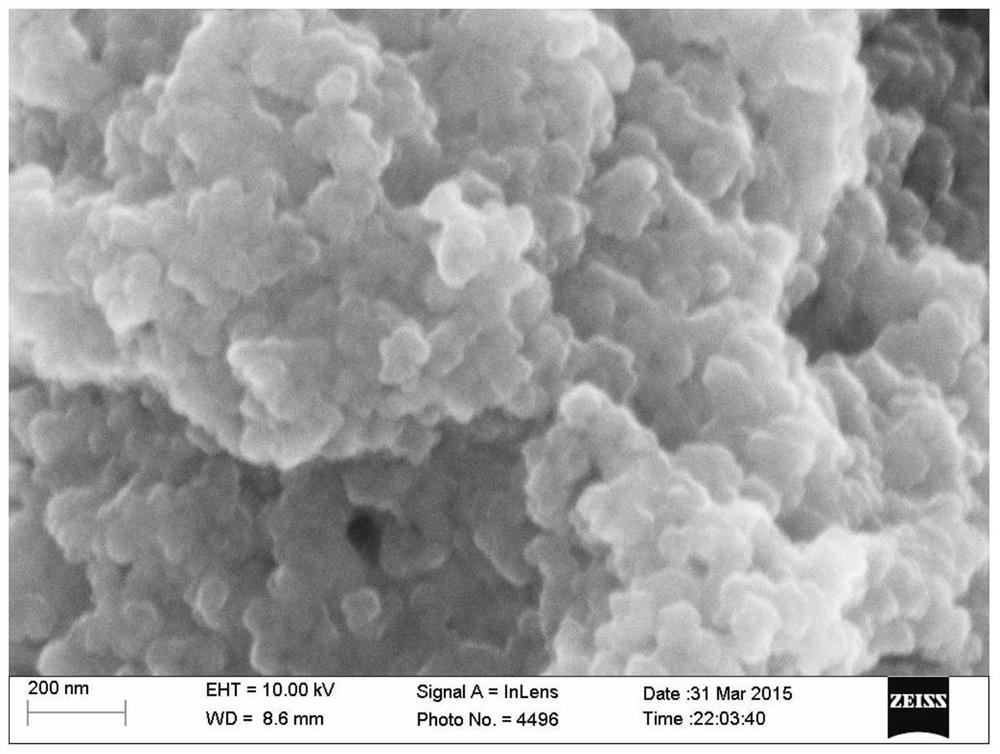
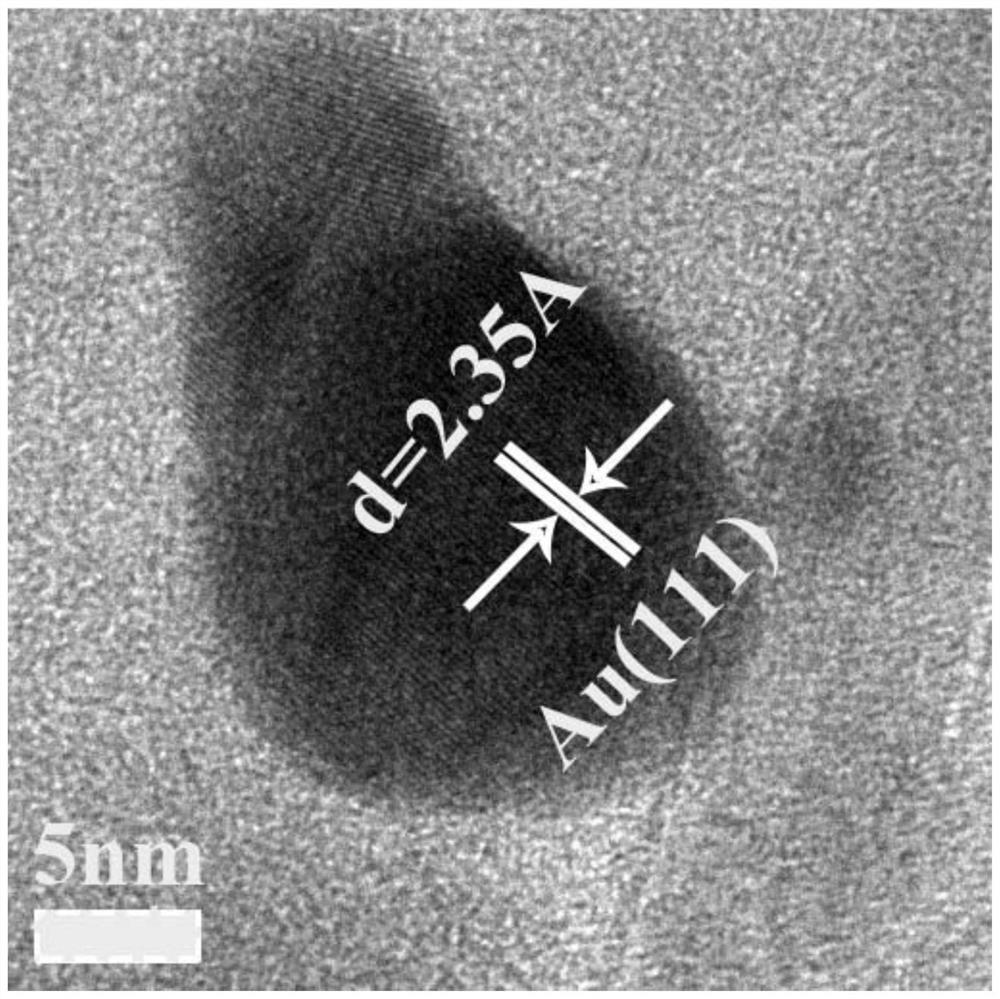
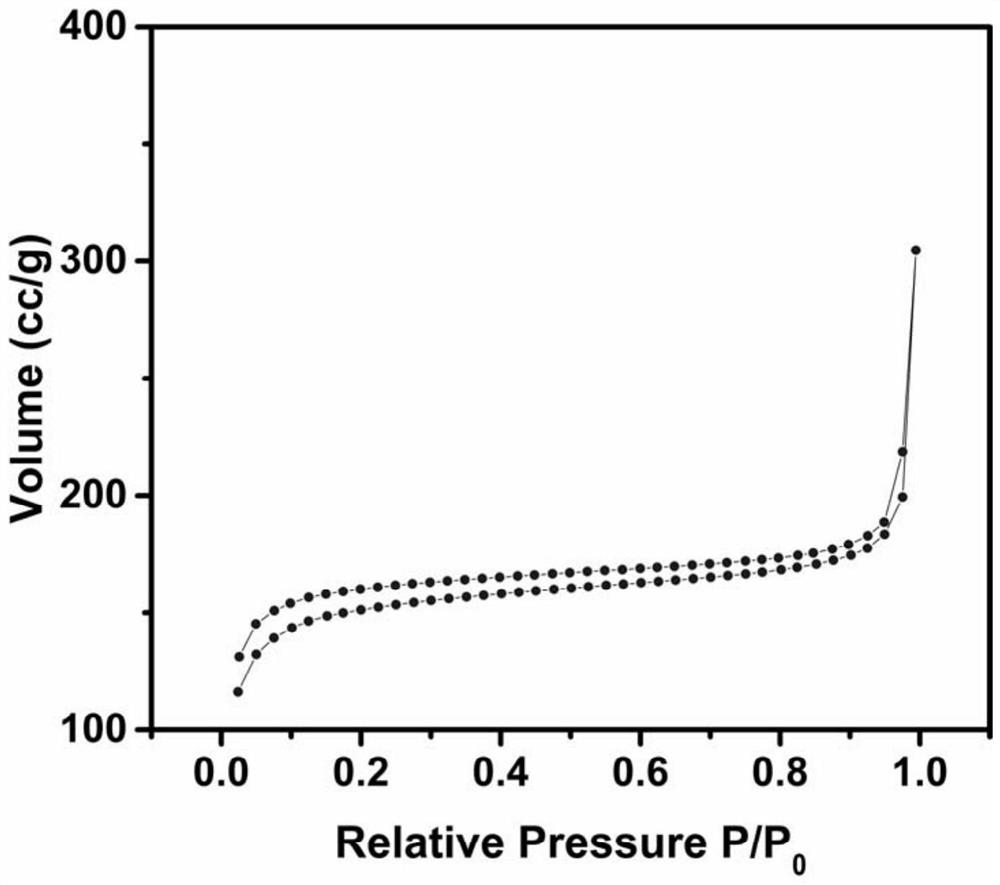
A method for synthesizing precious metal MOFs composites
A composite material and precious metal technology, which is used in the field of synthesizing precious metal MOFs composite materials, can solve the problems of blocking pores, affecting catalytic activity, MOFs structure and pore collapse, and achieves the effects of high yield, short synthesis cycle and few steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for synthesizing precious metal MOFs composite materials that the present embodiment relates to, the content of described method is: dissolving 4.8g of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate in 50mL of water, and dissolving 0.77g of sodium hydroxide in 24mL 0.71 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate was weighed and dissolved in 10 mL of water. The three are quickly mixed and added, stirred and mixed quickly, and aged at room temperature for 24 hours. Dissolve 1g of chloroauric acid powder in 100mL of aqueous solution to configure chloroauric acid solution. Add 1mL of chloroauric acid solution to the above solution, and stir for 30 minutes. Weigh 5.064 g of trimesic acid powder, and dissolve it in 224 mL of ethanol to form a homogeneous solution. The ethanol solution was mixed with the above solution and stirred for 24 hours. Subsequently, the reaction product was centrifuged at 6,000 rpm for 30 minutes to collect samples, redispersed in an appropriate amount of ethanol, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A kind of method for synthesizing precious metal MOFs composite material that present embodiment relates to, the content of described method is:
[0055] Dissolve 8.234 g of ferrous chloride dihydrate in 100 mL of water, dissolve 1.54 g of sodium hydroxide in 48 mL of water, and dissolve 1.421 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate in 20 mL of water. The three are quickly mixed and added, stirred and mixed quickly, and aged at room temperature for 3 hours. Dissolve 1 g of potassium chloroplatinate powder in 100 mL of aqueous solution to prepare a potassium chloroplatinate solution. Take 5 mL of potassium chloroplatinate solution and add it to the above solution, and stir for 30 minutes. Weighed 10.12 g of trimesic acid powder and dissolved it in 450 mL of ethanol to form a homogeneous solution. The ethanol solution was mixed with the above solution and stirred for 6 hours. Subsequently, the reaction product was filtered with a quantitative filter paper with a pore size of 1-3...
Embodiment 3
[0057] A kind of method for synthesizing precious metal MOFs composite material that present embodiment relates to, the content of described method is:
[0058] Dissolve 5.74 g of cobalt chloride hexahydrate in 50 mL of water, 0.77 g of sodium hydroxide in 24 mL of water, and 0.71 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate in 10 mL of water. The three were quickly mixed and added, stirred and mixed evenly, and aged at room temperature for 6 hours. Dissolve 1 g of palladium chloride powder in 100 mL of aqueous solution to prepare a palladium chloride solution. Take 1 mL of palladium chloride solution and add to the above solution, and stir for 30 minutes. Weigh 5.064 g of trimesic acid powder, and dissolve it in 224 mL of ethanol to form a homogeneous solution. The ethanol solution was mixed with the above solution and stirred for 12 hours. Subsequently, the reaction product was centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 30 minutes to collect a sample, which was redispersed in an appropriate amount of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com