In-situ monitoring soil freeze-thaw device and method for measuring soil carbon loss based on the device
A carbon loss, freezing and thawing technology, applied in measurement devices, soil material testing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as the inability to monitor the contribution of carbon emissions from specific soil layers, the inability to truly reflect the soil freezing and thawing process, etc., to achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
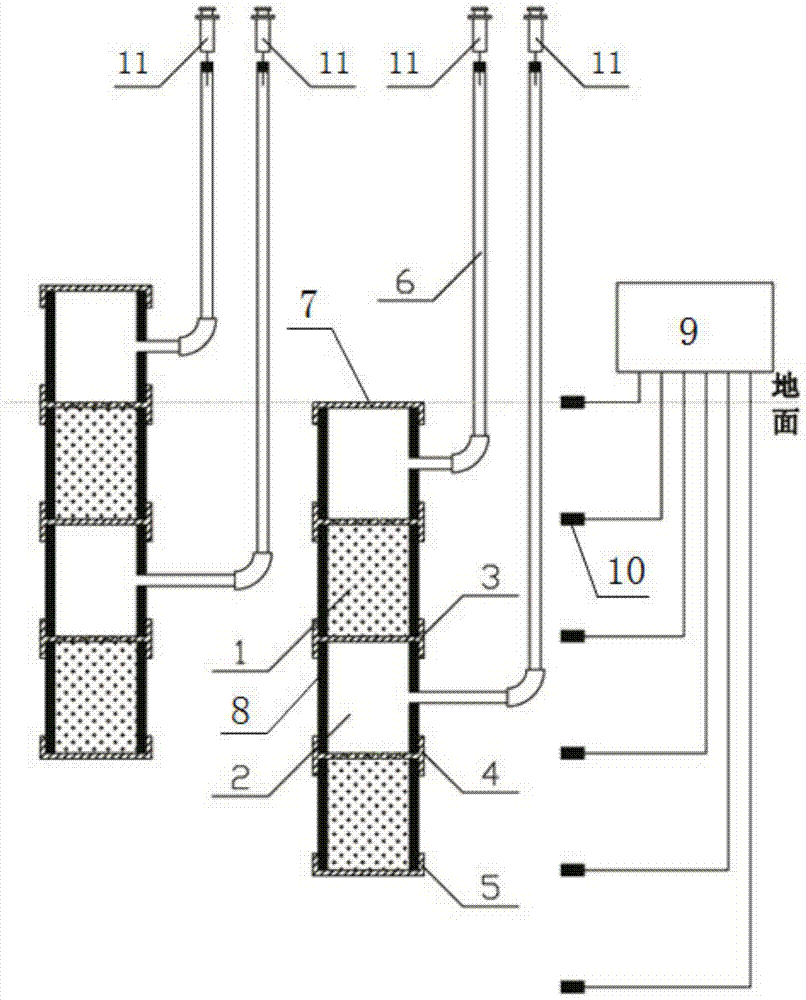
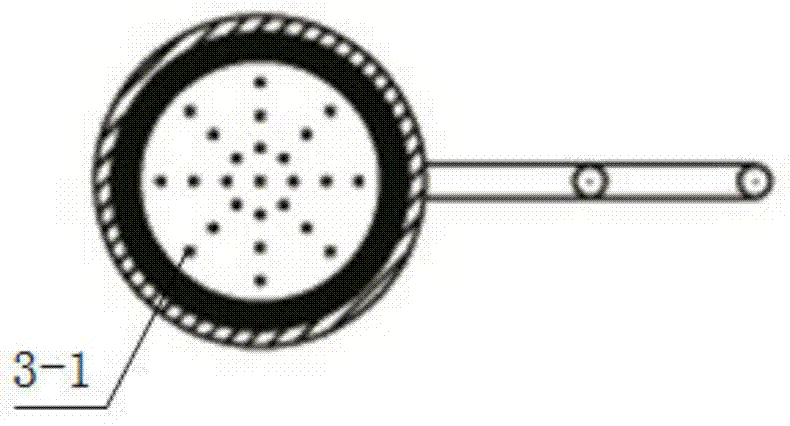
[0020] Specific embodiment 1: The in-situ monitoring soil freeze-thaw device in this embodiment includes a freeze-thaw column, a temperature monitor 9 and an air duct 6, wherein the freeze-thaw column consists of a rubber sleeve 3, a top cover 7, a bottom cover 5 and a plurality of circular tubes body 8, the longitudinal section of the rubber sleeve 3 is "H" shaped, the central axes of a plurality of circular tube bodies 8 are overlapped to form a long tube body, and the top cover 7 and the bottom cover 5 are respectively added to the two ends of the long tube body, The horizontal rubber plates of the rubber sleeves 3 are used to alternately form the soil column chamber 1 and the gas buffer chamber 2 between the round pipe bodies 8, and a plurality of air holes 3- 1. One end of the air duct 6 communicates with the gas buffer chamber 2, and the other end of the air duct 6 extends above the ground surface. Multiple temperature probes 10 are connected to the temperature monitor 9 ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0022] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that the height of the soil column chamber 1 is 10-15 cm.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0023] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that the material of the circular tube body 8 and the airway tube 6 is hard plastic.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com