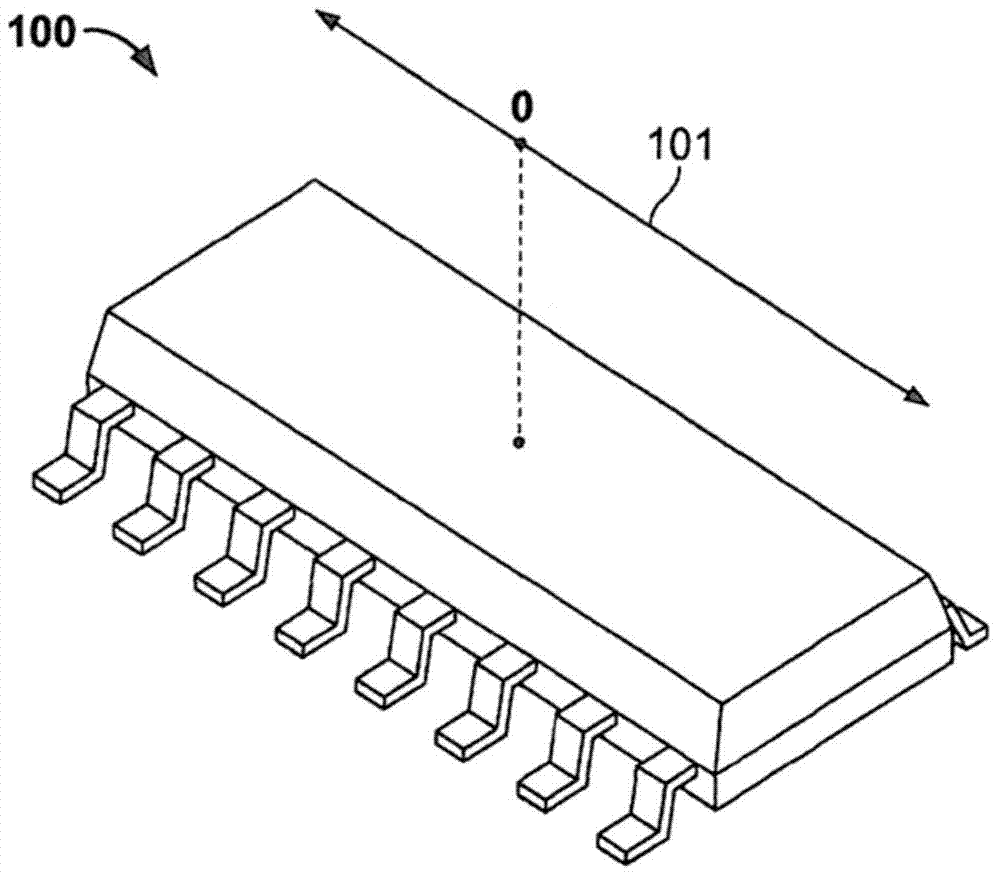
Displacement sensor for contactlessly measuring a position by means of a plurality of magnetic field sensors arranged in series
A technology of magnetic field sensor and displacement sensor, applied in the field of displacement sensor, which can solve the problems of large variation of measurement error and low precision
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
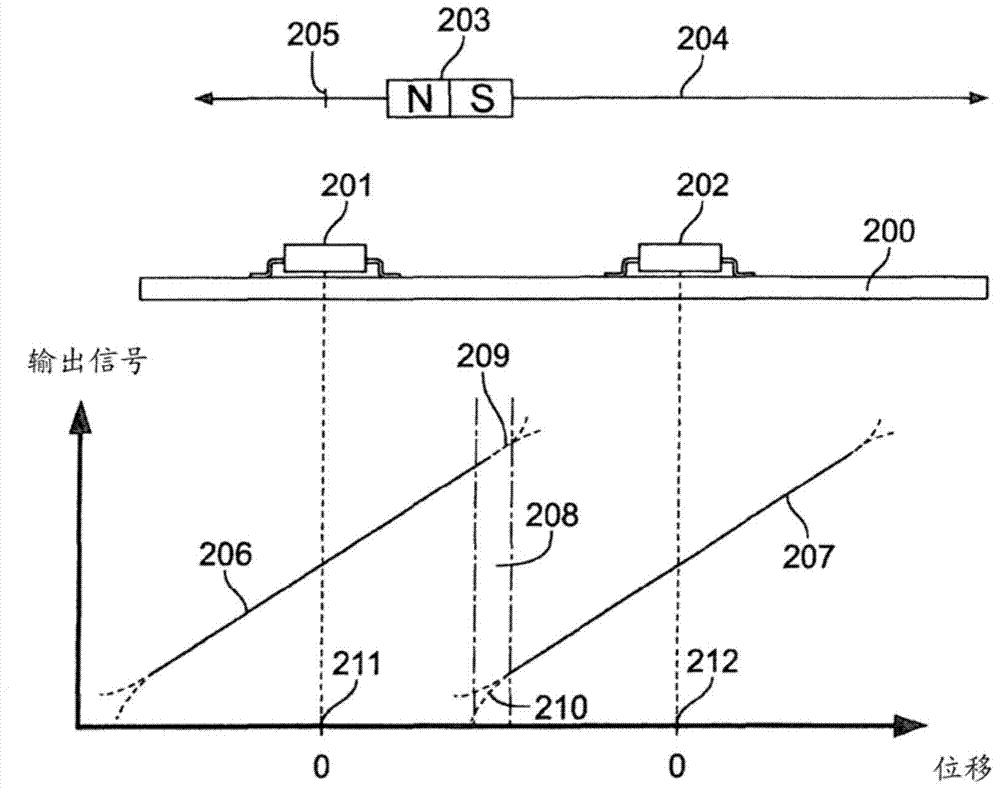
[0042] image 3 A displacement sensor arrangement according to the invention is shown. Two 3D Hall sensors 201 and 202 arranged in series are mounted in a fixed position on the printed circuit board 200 and a magnet 203 , preferably a permanent magnet, is displaceable along a movement axis 204 relative to the two Hall sensors. The N / S axis of the magnet 203 is oriented parallel to the axis of motion 204 . However, this orientation is not strictly necessary. In principle, it is also possible to carry out the invention if the N / S axes of the magnets have a different orientation, eg transverse to said axis of motion.
[0043] Magnets are available from image 3 The reference point 205 shown is shifted. The 3D Hall sensor with the magnet arranged in close proximity detects at least two orthogonal magnetic field components and produces an output signal exte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com