Offline Data Validation Verification Method
A technology of data validity and verification method, which is applied in the field of offline data validity verification, can solve problems such as system misjudgment, and achieve the effect of preventing repeated recharging and preventing wrong recharging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
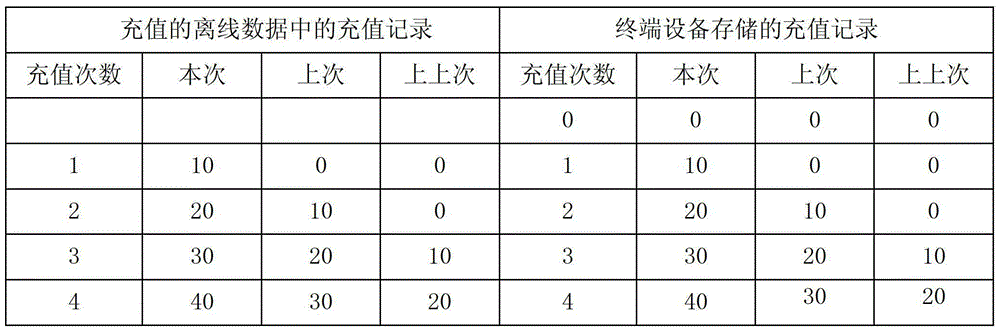
[0018] Table 1 Comparison of recharge records with a difference of 0 recharge times
[0019]
[0020] As shown in Table 1, the offline data validity verification method includes the following steps:
[0021] The difference between the recharge times stored in the recharge offline data packet and the recharge times stored in the terminal device, the difference between the recharge times stored in the terminal device is 0, the default offline data of this recharge, the offline data of the last recharge and the previous The offline data of the last recharge is all 0. When the recharge times in the recharge offline data package is 1, its current, last, and last offline data are 10, 0, 0, and the recharge times in the terminal device The offline data of this time, the last time, and the last time are 1, which are 10, 0, and 0. It can be seen that the offline data of the two are the same, so they will not be processed.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Table 2 Comparison of recharge records with a difference of 1 in recharge times
[0024]
[0025] As shown in Table 2, the offline data validity verification method includes the following steps:
[0026] S1. Make a difference between the number of recharge times stored in the recharge offline data packet and the number of recharge times stored in the terminal device. If the number of recharge times differs by 1, proceed to step S2;
[0027] S2. Compare the last recharge offline data and last recharge offline data in the recharge offline data packet with the current recharge offline data and last recharge offline data stored in the terminal device: when the recharge offline data packet When the number of times is 3, its current, last, and last offline data are: 30, 20, 10, and when the number of recharges in the terminal device is 2, its current, last, and last offline data It is 20, 10, 0. It can be seen that the offline data of this recharge stored in the terminal ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Table 3 Comparison of recharge records with a difference of 2 recharge times
[0030]
[0031] Offline data validity verification method, it comprises the following steps:
[0032] S1. Make a difference between the number of recharge times stored in the recharge offline data packet and the number of recharge times stored in the terminal device: the difference between the number of recharge times is 2, and proceed to step S3;
[0033] S3, comparing the offline data of the last recharge in the recharge offline data packet with the offline data of this recharge stored in the terminal: when the recharge times in the recharge offline data packet is 3, its current and last time , The last offline data is: 30, 20, 10, and when the number of recharges in the terminal device is 1, its current, last, last offline data are 10, 0, 0, it can be seen that the terminal storage The offline data of this recharge is the same as the offline data of the previous recharge in the recharg...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap