Strategies for Isocyanate Regulatory Compliance Excellence
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Regulations and Compliance Objectives
Isocyanates have been a critical component in various industries, particularly in the production of polyurethanes, for decades. However, their potential health hazards have led to increasing regulatory scrutiny worldwide. The primary objective of isocyanate regulations is to protect workers and consumers from exposure to these potentially harmful chemicals while ensuring the continued use of these valuable materials in industrial applications.
Regulatory bodies across the globe, including the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the European Union, have established comprehensive guidelines for the safe handling, use, and disposal of isocyanates. These regulations aim to minimize exposure risks through stringent workplace controls, personal protective equipment requirements, and proper training protocols.
Compliance objectives for organizations dealing with isocyanates typically focus on several key areas. First and foremost is the implementation of robust safety measures to prevent worker exposure. This includes engineering controls such as ventilation systems, enclosed processes, and automated handling equipment. Additionally, companies must establish comprehensive training programs to educate employees about the risks associated with isocyanates and proper handling procedures.
Another crucial compliance objective is the development and maintenance of detailed documentation and record-keeping systems. This includes safety data sheets, exposure monitoring records, and incident reports. Such documentation not only aids in regulatory compliance but also serves as a valuable tool for continuous improvement of safety protocols.
Environmental considerations also play a significant role in isocyanate regulations. Companies must adhere to strict guidelines regarding the storage, transportation, and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials to prevent environmental contamination. This often involves implementing spill prevention and response plans, as well as utilizing specialized containment and treatment technologies.
As regulatory requirements continue to evolve, organizations must stay abreast of changes and adapt their compliance strategies accordingly. This may involve regular audits of existing processes, investing in new technologies, and collaborating with industry partners and regulatory bodies to develop best practices.
Ultimately, the goal of isocyanate regulatory compliance is to strike a balance between protecting human health and the environment while allowing for the continued use of these versatile chemicals in industrial applications. By prioritizing safety, implementing robust control measures, and fostering a culture of compliance, organizations can navigate the complex regulatory landscape surrounding isocyanates and achieve excellence in their operations.
Regulatory bodies across the globe, including the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) in the European Union, have established comprehensive guidelines for the safe handling, use, and disposal of isocyanates. These regulations aim to minimize exposure risks through stringent workplace controls, personal protective equipment requirements, and proper training protocols.
Compliance objectives for organizations dealing with isocyanates typically focus on several key areas. First and foremost is the implementation of robust safety measures to prevent worker exposure. This includes engineering controls such as ventilation systems, enclosed processes, and automated handling equipment. Additionally, companies must establish comprehensive training programs to educate employees about the risks associated with isocyanates and proper handling procedures.
Another crucial compliance objective is the development and maintenance of detailed documentation and record-keeping systems. This includes safety data sheets, exposure monitoring records, and incident reports. Such documentation not only aids in regulatory compliance but also serves as a valuable tool for continuous improvement of safety protocols.
Environmental considerations also play a significant role in isocyanate regulations. Companies must adhere to strict guidelines regarding the storage, transportation, and disposal of isocyanate-containing materials to prevent environmental contamination. This often involves implementing spill prevention and response plans, as well as utilizing specialized containment and treatment technologies.
As regulatory requirements continue to evolve, organizations must stay abreast of changes and adapt their compliance strategies accordingly. This may involve regular audits of existing processes, investing in new technologies, and collaborating with industry partners and regulatory bodies to develop best practices.
Ultimately, the goal of isocyanate regulatory compliance is to strike a balance between protecting human health and the environment while allowing for the continued use of these versatile chemicals in industrial applications. By prioritizing safety, implementing robust control measures, and fostering a culture of compliance, organizations can navigate the complex regulatory landscape surrounding isocyanates and achieve excellence in their operations.
Market Demand for Isocyanate-Compliant Products
The market demand for isocyanate-compliant products has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by stringent regulatory requirements and growing awareness of health and environmental concerns. Industries such as automotive, construction, furniture, and electronics are actively seeking alternatives to traditional isocyanate-based products, creating a significant market opportunity for compliant solutions.
In the automotive sector, there is a strong demand for isocyanate-compliant coatings and adhesives. Manufacturers are looking for products that can meet performance requirements while adhering to strict regulatory standards. This has led to the development of new formulations that offer similar durability and adhesion properties without the use of harmful isocyanates.
The construction industry has also seen a surge in demand for isocyanate-compliant products, particularly in insulation materials and sealants. As building codes become more stringent and sustainability concerns take center stage, contractors and developers are seeking safer alternatives that can still provide excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance.
Furniture manufacturers are responding to consumer preferences for eco-friendly and health-conscious products by adopting isocyanate-compliant foams and adhesives. This shift is particularly evident in the mattress and upholstery segments, where prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals is a significant concern.
In the electronics industry, the demand for isocyanate-compliant encapsulants and coatings is growing rapidly. With the increasing miniaturization of electronic components and the need for reliable protection against environmental factors, manufacturers are investing in compliant solutions that can meet both regulatory and performance requirements.
The medical device sector represents another area of significant market demand for isocyanate-compliant products. As patient safety becomes paramount, there is a growing need for biocompatible materials that can be used in various medical applications without the risks associated with isocyanates.
Market analysts project that the global market for isocyanate-compliant products will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate of over 5% in the coming years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with strict regulatory environments, such as Europe and North America.
However, challenges remain in meeting this market demand. Many industries are facing difficulties in finding cost-effective alternatives that can match the performance of isocyanate-based products. This has created opportunities for innovative companies to develop new technologies and formulations that can bridge this gap, potentially capturing significant market share.
In the automotive sector, there is a strong demand for isocyanate-compliant coatings and adhesives. Manufacturers are looking for products that can meet performance requirements while adhering to strict regulatory standards. This has led to the development of new formulations that offer similar durability and adhesion properties without the use of harmful isocyanates.
The construction industry has also seen a surge in demand for isocyanate-compliant products, particularly in insulation materials and sealants. As building codes become more stringent and sustainability concerns take center stage, contractors and developers are seeking safer alternatives that can still provide excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance.
Furniture manufacturers are responding to consumer preferences for eco-friendly and health-conscious products by adopting isocyanate-compliant foams and adhesives. This shift is particularly evident in the mattress and upholstery segments, where prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals is a significant concern.
In the electronics industry, the demand for isocyanate-compliant encapsulants and coatings is growing rapidly. With the increasing miniaturization of electronic components and the need for reliable protection against environmental factors, manufacturers are investing in compliant solutions that can meet both regulatory and performance requirements.
The medical device sector represents another area of significant market demand for isocyanate-compliant products. As patient safety becomes paramount, there is a growing need for biocompatible materials that can be used in various medical applications without the risks associated with isocyanates.
Market analysts project that the global market for isocyanate-compliant products will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate of over 5% in the coming years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with strict regulatory environments, such as Europe and North America.
However, challenges remain in meeting this market demand. Many industries are facing difficulties in finding cost-effective alternatives that can match the performance of isocyanate-based products. This has created opportunities for innovative companies to develop new technologies and formulations that can bridge this gap, potentially capturing significant market share.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Regulatory Compliance
The current landscape of isocyanate regulatory compliance presents several significant challenges for industries utilizing these chemicals. One of the primary hurdles is the evolving nature of regulations across different regions and countries. As awareness of the potential health and environmental impacts of isocyanates grows, regulatory bodies are continually updating and tightening their requirements, making it difficult for companies to maintain consistent compliance across their global operations.
Another major challenge lies in the complexity of monitoring and controlling isocyanate exposure in various industrial settings. The volatile nature of these compounds, combined with their potential to cause severe respiratory sensitization, necessitates sophisticated air monitoring systems and robust personal protective equipment protocols. Implementing and maintaining these systems across diverse manufacturing environments can be both technically challenging and financially burdensome for many organizations.
The lack of standardized testing methods for isocyanate detection and quantification further complicates compliance efforts. Different regulatory agencies may require varying analytical techniques, leading to inconsistencies in reporting and potential compliance gaps. This disparity in methodologies also makes it challenging for companies to compare their performance against industry benchmarks or to establish uniform internal standards across their facilities.
Employee training and awareness represent another critical challenge in isocyanate regulatory compliance. Given the severe health risks associated with isocyanate exposure, comprehensive and ongoing education programs are essential. However, ensuring that all personnel, including temporary workers and contractors, are adequately trained and follow proper safety protocols can be logistically complex and resource-intensive.
Supply chain management adds another layer of complexity to isocyanate compliance. Companies must not only ensure their own operations meet regulatory standards but also verify that their suppliers and downstream users are compliant. This extended responsibility requires robust tracking systems and clear communication channels throughout the supply chain, which can be particularly challenging for smaller enterprises with limited resources.
Lastly, the rapid pace of technological innovation in isocyanate applications presents a moving target for regulatory compliance. As new formulations and applications emerge, regulatory frameworks may lag behind, creating uncertainty for companies investing in novel technologies. Balancing innovation with compliance requires a proactive approach to risk assessment and engagement with regulatory bodies, which can strain the resources of many organizations.
Another major challenge lies in the complexity of monitoring and controlling isocyanate exposure in various industrial settings. The volatile nature of these compounds, combined with their potential to cause severe respiratory sensitization, necessitates sophisticated air monitoring systems and robust personal protective equipment protocols. Implementing and maintaining these systems across diverse manufacturing environments can be both technically challenging and financially burdensome for many organizations.
The lack of standardized testing methods for isocyanate detection and quantification further complicates compliance efforts. Different regulatory agencies may require varying analytical techniques, leading to inconsistencies in reporting and potential compliance gaps. This disparity in methodologies also makes it challenging for companies to compare their performance against industry benchmarks or to establish uniform internal standards across their facilities.
Employee training and awareness represent another critical challenge in isocyanate regulatory compliance. Given the severe health risks associated with isocyanate exposure, comprehensive and ongoing education programs are essential. However, ensuring that all personnel, including temporary workers and contractors, are adequately trained and follow proper safety protocols can be logistically complex and resource-intensive.
Supply chain management adds another layer of complexity to isocyanate compliance. Companies must not only ensure their own operations meet regulatory standards but also verify that their suppliers and downstream users are compliant. This extended responsibility requires robust tracking systems and clear communication channels throughout the supply chain, which can be particularly challenging for smaller enterprises with limited resources.
Lastly, the rapid pace of technological innovation in isocyanate applications presents a moving target for regulatory compliance. As new formulations and applications emerge, regulatory frameworks may lag behind, creating uncertainty for companies investing in novel technologies. Balancing innovation with compliance requires a proactive approach to risk assessment and engagement with regulatory bodies, which can strain the resources of many organizations.
Existing Strategies for Isocyanate Regulatory Compliance
01 Regulatory compliance management systems
Automated systems for managing and tracking regulatory compliance related to isocyanates. These systems can help organizations stay up-to-date with changing regulations, monitor compliance status, and generate reports for auditing purposes.- Regulatory compliance management systems: Automated systems for managing and tracking regulatory compliance related to isocyanates. These systems can help organizations stay up-to-date with changing regulations, monitor compliance status, and generate reports for auditing purposes.
- Risk assessment and mitigation for isocyanate handling: Methods and tools for assessing risks associated with isocyanate use and implementing mitigation strategies. This includes identifying potential hazards, evaluating exposure risks, and developing safety protocols to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Environmental impact monitoring and reporting: Systems and methods for monitoring the environmental impact of isocyanate use and generating reports to demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations. This may include tracking emissions, waste management, and implementing pollution prevention measures.
- Supply chain management for isocyanate compliance: Tools and processes for managing the supply chain to ensure regulatory compliance throughout the lifecycle of isocyanate products. This includes tracking raw materials, monitoring transportation and storage conditions, and verifying supplier compliance with relevant regulations.
- Training and certification programs for isocyanate handling: Development and implementation of training programs and certification systems to ensure that personnel handling isocyanates are properly educated on regulatory requirements and safety procedures. This helps organizations maintain compliance and reduce the risk of accidents or violations.
02 Risk assessment and mitigation for isocyanate handling
Methods and tools for assessing risks associated with isocyanate use and implementing mitigation strategies. This includes identifying potential hazards, evaluating exposure risks, and developing safety protocols to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Supply chain management for isocyanate compliance
Systems and methods for managing the supply chain to ensure regulatory compliance of isocyanate-containing products. This includes tracking raw materials, monitoring supplier certifications, and maintaining documentation throughout the product lifecycle.Expand Specific Solutions04 Training and certification programs for isocyanate handling
Development and implementation of training programs to ensure proper handling of isocyanates in compliance with regulations. This includes certification processes, ongoing education, and documentation of employee competencies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental monitoring and reporting for isocyanate emissions
Systems and methods for monitoring, measuring, and reporting isocyanate emissions to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. This includes real-time monitoring technologies, data analysis tools, and automated reporting mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Compliance Solutions
The market for isocyanate regulatory compliance strategies is in a mature stage, with established players and well-defined regulations. The global market size for isocyanates is substantial, driven by demand in polyurethane production across various industries. Technologically, compliance solutions are advanced, with major companies like Wanhua Chemical, Covestro, and BASF leading innovation. These firms have developed sophisticated systems for monitoring, controlling, and reporting isocyanate usage to meet stringent regulatory requirements. Emerging players such as Asahi Kasei and Mitsui Chemicals are also making significant strides in compliance technology, focusing on eco-friendly alternatives and improved safety measures to address evolving regulatory challenges.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed a comprehensive strategy for isocyanate regulatory compliance excellence. Their approach includes the implementation of advanced process safety management systems, continuous monitoring technologies, and the development of low-emission isocyanate products. The company has invested in state-of-the-art production facilities that incorporate closed-loop systems and advanced scrubbing technologies to minimize isocyanate emissions[1]. They have also developed water-based polyurethane dispersions that significantly reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, aligning with stringent environmental regulations[2]. Wanhua's commitment to sustainability is evident in their research into bio-based isocyanates, which aim to reduce reliance on fossil-based raw materials while maintaining high performance standards[3].
Strengths: Advanced emission control technologies, innovative product development, strong focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs, challenges in scaling up new technologies across all product lines.
Covestro Deutschland AG
Technical Solution: Covestro has implemented a multi-faceted approach to isocyanate regulatory compliance. The company has developed a proprietary Safe Use of Diisocyanates training program, which has been adopted industry-wide and meets the requirements of the REACH regulation[4]. They have also invested in process innovations that reduce worker exposure, such as their gas-phase technology for TDI production, which significantly lowers emission levels[5]. Covestro's commitment to sustainability is demonstrated through their development of partially bio-based isocyanates, reducing the carbon footprint of their products while maintaining high performance[6]. Additionally, they have implemented advanced risk assessment tools and exposure monitoring systems to ensure compliance with evolving regulatory standards across different regions.
Strengths: Industry-leading training programs, innovative production technologies, strong focus on bio-based alternatives. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in adapting to rapidly changing regulations across different markets.
Innovative Approaches to Isocyanate Risk Management
Polyisocyanate composition, preparation method therefor and application thereof
PatentPendingUS20230374194A1
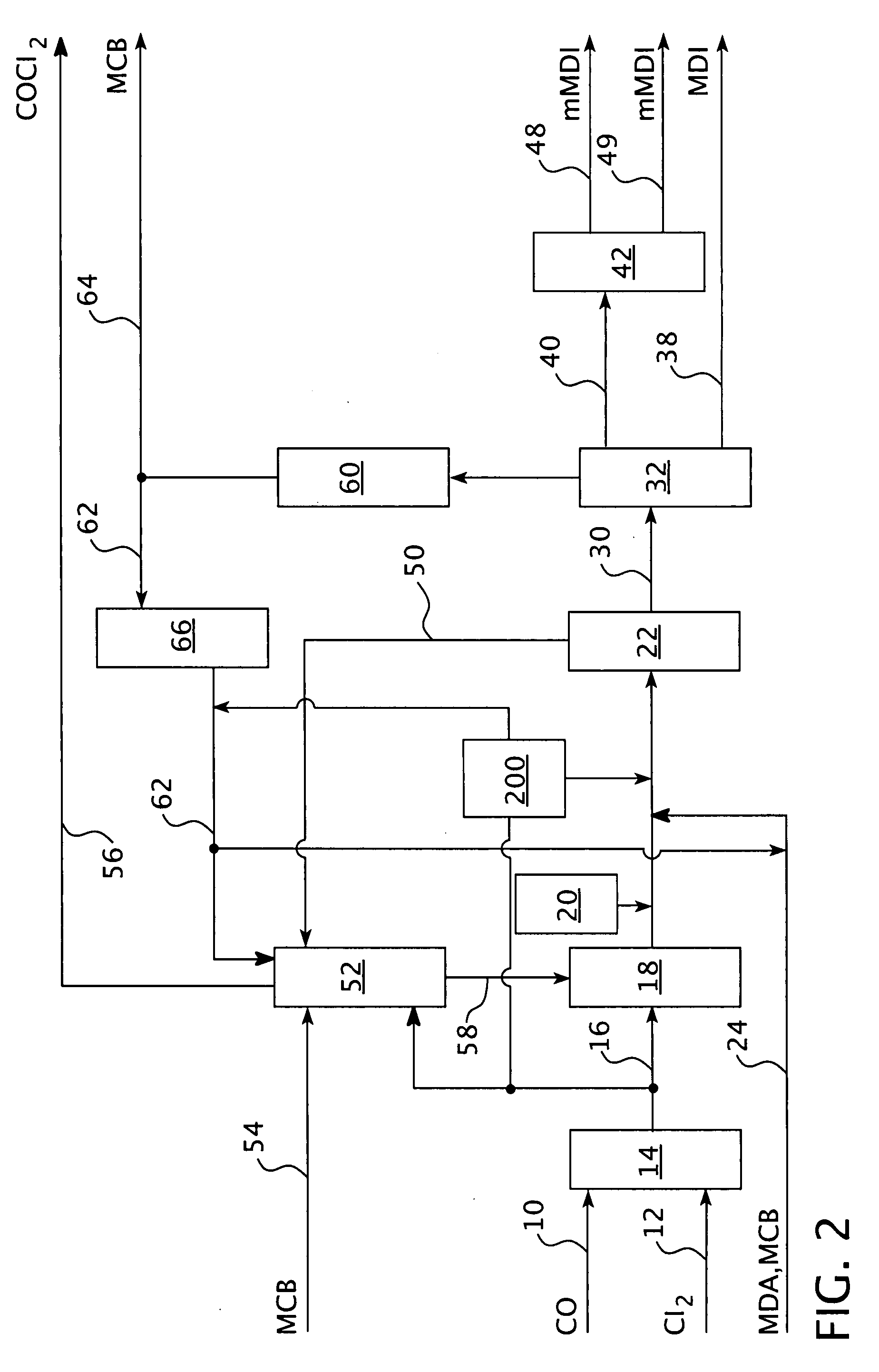
Innovation
- A polyisocyanate composition with a controlled mass content of alkaline-dissociated chlorine, ranging from 0.1 ppm to 100 ppm, is developed to prevent overheating and maintain reaction stability, incorporating anti-aging additives for enhanced storage stability and yellowing resistance.
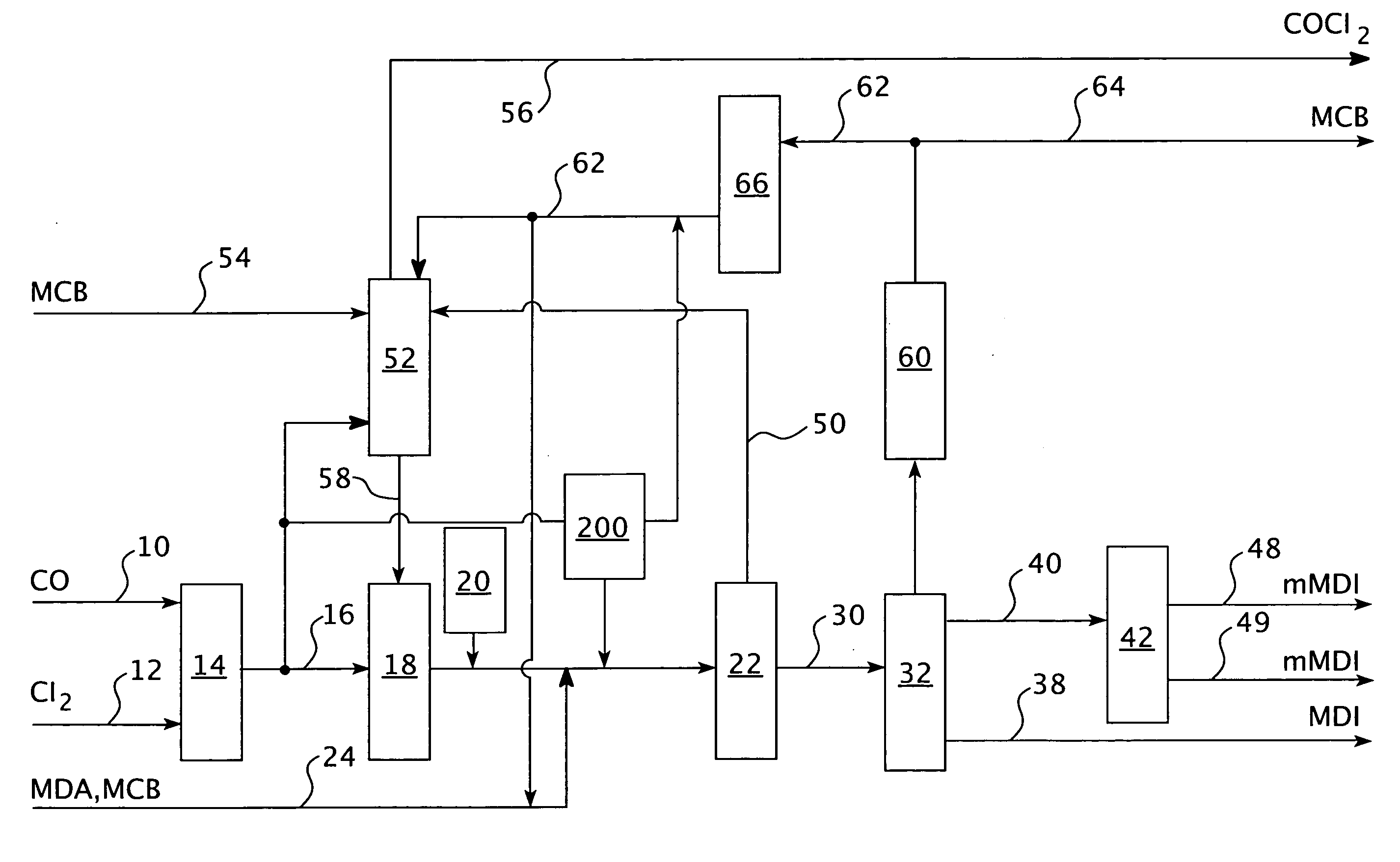
Process for controlling a production process
PatentInactiveUS20080147208A1
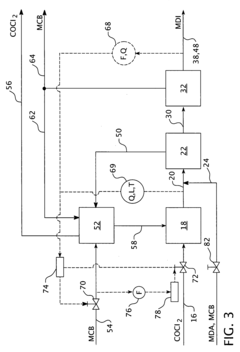
Innovation
- The process controls the phosgene and solvent feed streams as primary variables, allowing for independent control of subsystems and optimization of the isocyanate production process, enabling the recovery of unused reactants and reducing unwanted substances, thereby stabilizing and automating the process.
Environmental Impact of Isocyanate Compliance Measures
The implementation of isocyanate regulatory compliance measures has significant environmental implications that extend beyond the immediate workplace. These measures, designed to protect human health and safety, also contribute to broader environmental protection efforts.
One of the primary environmental benefits of isocyanate compliance is the reduction of atmospheric emissions. Stringent controls on isocyanate handling and application processes minimize the release of these compounds into the air. This reduction in emissions helps mitigate air pollution and its associated environmental impacts, such as smog formation and potential harm to flora and fauna.
Water pollution prevention is another crucial environmental aspect of isocyanate compliance. Proper containment and disposal practices for isocyanate-containing materials prevent these chemicals from entering water systems. This protection of water resources is vital for aquatic ecosystems and helps maintain water quality for both human and environmental needs.
Compliance measures often necessitate the use of more advanced equipment and technologies, which can lead to improved energy efficiency in manufacturing processes. This increased efficiency translates to reduced energy consumption and, consequently, lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production.
The focus on proper storage and handling of isocyanates also contributes to soil protection. By preventing spills and leaks, compliance measures help maintain soil quality and protect underground water sources from contamination. This preservation of soil integrity is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Waste reduction is another significant environmental benefit of isocyanate compliance. Improved process controls and material management practices often result in less waste generation. Additionally, compliance measures typically include guidelines for proper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste, ensuring that these materials are handled in an environmentally responsible manner.
The emphasis on worker safety in isocyanate compliance indirectly benefits the environment by promoting a culture of responsibility and care. This mindset often extends to environmental considerations, fostering a more holistic approach to industrial practices that considers both human and environmental health.
Lastly, the development and implementation of isocyanate compliance measures drive innovation in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices. This push for safer alternatives and more environmentally friendly processes can lead to the development of new technologies and materials that have broader positive environmental impacts across various industries.
One of the primary environmental benefits of isocyanate compliance is the reduction of atmospheric emissions. Stringent controls on isocyanate handling and application processes minimize the release of these compounds into the air. This reduction in emissions helps mitigate air pollution and its associated environmental impacts, such as smog formation and potential harm to flora and fauna.
Water pollution prevention is another crucial environmental aspect of isocyanate compliance. Proper containment and disposal practices for isocyanate-containing materials prevent these chemicals from entering water systems. This protection of water resources is vital for aquatic ecosystems and helps maintain water quality for both human and environmental needs.
Compliance measures often necessitate the use of more advanced equipment and technologies, which can lead to improved energy efficiency in manufacturing processes. This increased efficiency translates to reduced energy consumption and, consequently, lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production.
The focus on proper storage and handling of isocyanates also contributes to soil protection. By preventing spills and leaks, compliance measures help maintain soil quality and protect underground water sources from contamination. This preservation of soil integrity is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Waste reduction is another significant environmental benefit of isocyanate compliance. Improved process controls and material management practices often result in less waste generation. Additionally, compliance measures typically include guidelines for proper disposal of isocyanate-containing waste, ensuring that these materials are handled in an environmentally responsible manner.
The emphasis on worker safety in isocyanate compliance indirectly benefits the environment by promoting a culture of responsibility and care. This mindset often extends to environmental considerations, fostering a more holistic approach to industrial practices that considers both human and environmental health.
Lastly, the development and implementation of isocyanate compliance measures drive innovation in green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices. This push for safer alternatives and more environmentally friendly processes can lead to the development of new technologies and materials that have broader positive environmental impacts across various industries.
Global Harmonization of Isocyanate Regulations
The global harmonization of isocyanate regulations represents a critical step towards ensuring consistent safety standards and compliance practices across international borders. This initiative aims to align regulatory frameworks, streamline reporting requirements, and establish uniform safety protocols for the handling, use, and disposal of isocyanates worldwide.
One of the primary drivers for this harmonization effort is the increasing globalization of supply chains in industries that utilize isocyanates, such as automotive, construction, and furniture manufacturing. As companies operate across multiple jurisdictions, they face challenges in navigating diverse regulatory landscapes, which can lead to increased compliance costs and potential safety risks.
The harmonization process involves collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and international organizations. Key areas of focus include standardizing hazard classification systems, aligning exposure limits, and developing consistent labeling and safety data sheet requirements. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) serves as a foundation for many of these efforts, providing a common language for communicating chemical hazards.
Regulatory agencies from major economies, including the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), and China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment, are actively engaged in dialogue to bridge gaps between their respective isocyanate regulations. This cooperation aims to reduce trade barriers while maintaining high safety standards.
Industry associations, such as the International Isocyanate Institute and the American Chemistry Council, play a crucial role in facilitating discussions between regulators and businesses. These organizations provide valuable insights into the practical implications of proposed regulatory changes and help ensure that harmonization efforts are both effective and feasible for implementation.
The benefits of global harmonization extend beyond regulatory compliance. A unified approach to isocyanate management can lead to improved worker safety, enhanced environmental protection, and more efficient product development and market access. It also promotes the sharing of best practices and technological innovations across borders, fostering a culture of continuous improvement in isocyanate handling and use.
However, challenges remain in achieving full harmonization. Differences in regulatory philosophies, existing legal frameworks, and varying levels of economic development among countries can complicate the process. Overcoming these obstacles requires sustained diplomatic efforts, technical cooperation, and a commitment to finding common ground while respecting national sovereignty.
One of the primary drivers for this harmonization effort is the increasing globalization of supply chains in industries that utilize isocyanates, such as automotive, construction, and furniture manufacturing. As companies operate across multiple jurisdictions, they face challenges in navigating diverse regulatory landscapes, which can lead to increased compliance costs and potential safety risks.
The harmonization process involves collaboration between regulatory bodies, industry stakeholders, and international organizations. Key areas of focus include standardizing hazard classification systems, aligning exposure limits, and developing consistent labeling and safety data sheet requirements. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) serves as a foundation for many of these efforts, providing a common language for communicating chemical hazards.
Regulatory agencies from major economies, including the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), and China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment, are actively engaged in dialogue to bridge gaps between their respective isocyanate regulations. This cooperation aims to reduce trade barriers while maintaining high safety standards.
Industry associations, such as the International Isocyanate Institute and the American Chemistry Council, play a crucial role in facilitating discussions between regulators and businesses. These organizations provide valuable insights into the practical implications of proposed regulatory changes and help ensure that harmonization efforts are both effective and feasible for implementation.
The benefits of global harmonization extend beyond regulatory compliance. A unified approach to isocyanate management can lead to improved worker safety, enhanced environmental protection, and more efficient product development and market access. It also promotes the sharing of best practices and technological innovations across borders, fostering a culture of continuous improvement in isocyanate handling and use.
However, challenges remain in achieving full harmonization. Differences in regulatory philosophies, existing legal frameworks, and varying levels of economic development among countries can complicate the process. Overcoming these obstacles requires sustained diplomatic efforts, technical cooperation, and a commitment to finding common ground while respecting national sovereignty.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!