How to Improve The Running Stability Of Thrust Bearing?
Technology Background and Goals
This section delves into the current state of thrust bearing technology, identifying the key challenges and limitations that hinder their stable operation. It examines the underlying causes of instability, such as fluid-structure interactions, thermal effects, and material degradation. By analyzing these factors, potential areas for improvement can be identified, paving the way for the development of more robust and reliable thrust bearing designs.
Market Demand Analysis
- Market Size and Growth
Analyze the current and projected market size for thrust bearing applications, considering factors like industrial machinery, aerospace, automotive, and other relevant sectors. Provide insights into the market's growth potential and drivers. - Industry Trends
Identify key trends shaping the demand for stable thrust bearings, such as the need for higher efficiency, longer service life, and reduced maintenance requirements in various industries. - Regional Demand Analysis
Assess the regional demand patterns for thrust bearings with improved stability, considering factors like industrial development, infrastructure projects, and regulatory environments in different geographical markets. - Application-Specific Requirements
Evaluate the specific requirements for thrust bearing stability in critical applications, such as high-speed machinery, heavy-duty equipment, or extreme operating conditions, and their impact on market demand. - Competitive Landscape
Analyze the competitive landscape, including major players, their market share, and strategies for addressing the demand for stable thrust bearings. Identify potential opportunities or threats in the market.
Technology Status and Challenges
- Thrust Bearing Stability Fundamentals
Thrust bearings support axial loads in rotating machinery. Their stability is crucial for smooth operation and preventing excessive vibrations or failures. - Factors Affecting Stability
Key factors include bearing geometry, lubricant properties, operating conditions (load, speed, temperature), and rotor-bearing dynamics. - Instability Mechanisms
Common instability modes are fluid-induced instabilities (e.g., whirl, whip), thermal instabilities due to frictional heating, and material degradation. - Modeling and Analysis Techniques
Analytical models, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), finite element analysis (FEA), and experimental testing are used to study bearing stability.
Current Technical Solutions
01 Optimized Thrust Bearing Design
Various design features and configurations can enhance thrust bearing stability, including optimized geometry, material selection, and surface treatments to reduce friction and wear, improving overall operational stability.- Optimized Thrust Bearing Design: Various design features and configurations can enhance thrust bearing stability, including optimized geometry, material selection, and surface treatments to reduce friction and wear, improving overall operational stability.
- Advanced Lubrication Systems: Specialized lubricants, lubricant delivery mechanisms, and monitoring systems ensure optimal lubrication conditions, minimizing friction and wear, playing a crucial role in maintaining thrust bearing stability.
- Advanced Bearing Materials: Advanced materials, such as ceramics, composites, or coatings, offer enhanced wear resistance, thermal stability, and reduced friction, contributing to improved overall thrust bearing stability.
- Monitoring and Control Systems: Sensors, data acquisition, and control algorithms can detect and mitigate potential instabilities, such as vibrations, temperature fluctuations, or lubricant degradation, ensuring stable thrust bearing operation.
- Damping Mechanisms: Damping mechanisms, involving specialized damping materials, fluid-based dampers, or structural damping features, can dissipate vibrations and reduce resonance effects, enhancing thrust bearing running stability.
02 Effective Lubrication Systems
Specialized lubricants, lubrication channels, and control mechanisms ensure proper lubrication distribution, minimizing friction and wear, playing a crucial role in maintaining thrust bearing stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced Bearing Materials
Selecting appropriate materials with high strength, wear resistance, and lubricant compatibility can significantly impact thrust bearing stability and performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Monitoring and Control Systems
Implementing sensors, data acquisition, and control algorithms can detect and mitigate potential instabilities or abnormal operating conditions, helping maintain thrust bearing stability.Expand Specific Solutions05 Damping Mechanisms
Incorporating damping elements, materials, or configurations can dissipate energy and reduce vibrations, improving the running stability of thrust bearings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players Analysis
NTN Corp.
NSK Ltd.
Key Technology Interpretation
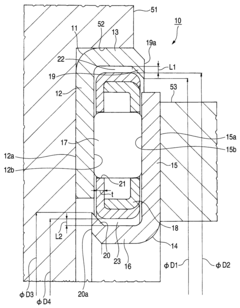
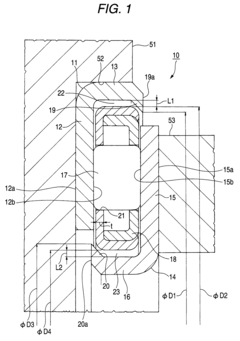
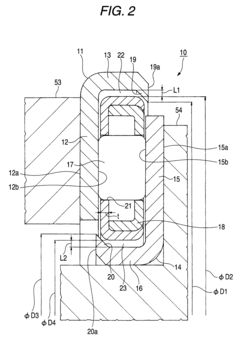
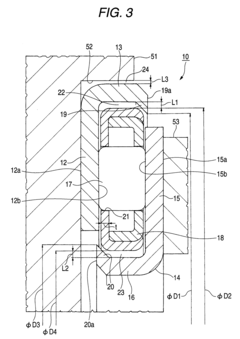
- 1. The bearing includes a cylindrical guide portion and a one-sided in-bearing gap to absorb the eccentricity between the outer and inner rings.
- 2. The bearing has outer and inner locking portions to prevent separation between the race portions and the cage.
- 3. The bearing cage is designed to increase durability when there is a large amount of eccentricity between the supporting members.
Thrust Bearings Stability Improvement Economic Analysis
Additionally, the initial investment required for implementing stability improvements should be evaluated against the projected long-term benefits. This may involve upgrading existing equipment, adopting new materials or designs, or implementing advanced monitoring and control systems. The return on investment (ROI) and payback period will be crucial considerations for decision-makers.
Furthermore, the economic analysis should account for potential productivity gains resulting from improved bearing stability. Increased operational uptime and reduced unplanned shutdowns can translate into higher output and revenue for the organization. The impact on overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and its financial implications should be carefully assessed.
Thrust Bearings Stability Regulatory and Environmental Considerations
The stability of thrust bearings is influenced by various regulatory and environmental factors that must be carefully considered.
Regulatory factors encompass industry standards, safety guidelines, and environmental regulations that govern the design, manufacturing, and operation of thrust bearings. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure the safe and reliable performance of the bearings while minimizing their environmental impact.
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of contaminants, can significantly affect the stability and longevity of thrust bearings. Extreme temperatures can cause thermal expansion or contraction, altering the clearances and leading to increased friction and wear. Humidity can promote corrosion and degradation of bearing materials, while contaminants like dust or debris can accelerate wear and reduce bearing life. Understanding and mitigating these environmental factors is crucial for maintaining optimal bearing performance and extending their service life.