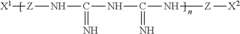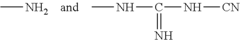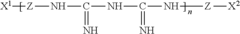Insights into Hypochlorous Acid-Based Contact Lens Solutions
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Lens Solution Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising component in contact lens solutions, marking a significant advancement in eye care technology. This innovative approach builds upon decades of research in ocular surface health and contact lens maintenance. The evolution of contact lens solutions has been driven by the need to address common issues such as microbial contamination, protein buildup, and ocular discomfort associated with lens wear.
The primary objective of HOCl-based contact lens solutions is to provide a more effective and biocompatible alternative to traditional disinfecting systems. These solutions aim to enhance lens hygiene while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions often associated with conventional multipurpose solutions. By harnessing the natural antimicrobial properties of HOCl, researchers seek to develop a cleaning and disinfecting system that closely mimics the eye's innate defense mechanisms.
The development of HOCl lens solutions is rooted in the understanding of the ocular surface microbiome and the body's natural defense systems. HOCl is a key component of the immune response, produced by neutrophils to combat pathogens. This biological relevance has sparked interest in its potential applications in eye care, particularly for contact lens wearers who are at increased risk of ocular infections.
Recent technological advancements have enabled the stable formulation of HOCl at concentrations suitable for contact lens care. This breakthrough has opened new avenues for research and development in the field. The goal is to create a solution that not only effectively cleans and disinfects lenses but also supports ocular surface health by maintaining a balanced microbiome and reducing inflammation.
As the contact lens market continues to grow, driven by increasing myopia rates and aging populations, the demand for safer and more effective lens care solutions has intensified. HOCl-based solutions represent a response to this demand, aiming to address the limitations of existing products and improve the overall contact lens wearing experience. The technology seeks to reduce the incidence of lens-related complications and enhance user compliance with proper lens care routines.
The development of HOCl lens solutions aligns with broader trends in healthcare towards more natural and biocompatible treatments. This approach reflects a shift in focus from merely treating symptoms to supporting the body's natural defense mechanisms. In the context of contact lens care, this translates to solutions that work in harmony with the eye's physiology, potentially offering benefits beyond basic lens disinfection.
The primary objective of HOCl-based contact lens solutions is to provide a more effective and biocompatible alternative to traditional disinfecting systems. These solutions aim to enhance lens hygiene while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions often associated with conventional multipurpose solutions. By harnessing the natural antimicrobial properties of HOCl, researchers seek to develop a cleaning and disinfecting system that closely mimics the eye's innate defense mechanisms.
The development of HOCl lens solutions is rooted in the understanding of the ocular surface microbiome and the body's natural defense systems. HOCl is a key component of the immune response, produced by neutrophils to combat pathogens. This biological relevance has sparked interest in its potential applications in eye care, particularly for contact lens wearers who are at increased risk of ocular infections.
Recent technological advancements have enabled the stable formulation of HOCl at concentrations suitable for contact lens care. This breakthrough has opened new avenues for research and development in the field. The goal is to create a solution that not only effectively cleans and disinfects lenses but also supports ocular surface health by maintaining a balanced microbiome and reducing inflammation.
As the contact lens market continues to grow, driven by increasing myopia rates and aging populations, the demand for safer and more effective lens care solutions has intensified. HOCl-based solutions represent a response to this demand, aiming to address the limitations of existing products and improve the overall contact lens wearing experience. The technology seeks to reduce the incidence of lens-related complications and enhance user compliance with proper lens care routines.
The development of HOCl lens solutions aligns with broader trends in healthcare towards more natural and biocompatible treatments. This approach reflects a shift in focus from merely treating symptoms to supporting the body's natural defense mechanisms. In the context of contact lens care, this translates to solutions that work in harmony with the eye's physiology, potentially offering benefits beyond basic lens disinfection.
Market Analysis for HOCl Contact Lens Care
The global contact lens care market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing prevalence of vision problems, growing awareness about eye health, and the rising popularity of cosmetic lenses. Within this market, hypochlorous acid (HOCl) based solutions are emerging as a promising segment, offering unique benefits for contact lens wearers.
The HOCl contact lens care market is currently in its nascent stage but shows significant potential for expansion. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing demand for more effective and safer cleaning solutions. Traditional hydrogen peroxide and multipurpose solutions have dominated the market, but concerns about eye irritation and the development of antimicrobial resistance have led to a search for alternatives.
HOCl solutions address many of these concerns, offering broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity without causing significant eye irritation. This has led to a growing interest from both consumers and eye care professionals. Market research indicates that the HOCl segment is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall contact lens care market in the coming years.
Consumer trends also play a crucial role in shaping the HOCl contact lens care market. There is an increasing preference for natural and gentle products, which aligns well with HOCl's properties as it mimics the body's natural defense mechanisms. Additionally, the convenience factor of HOCl solutions, which often require fewer steps in the cleaning process compared to traditional methods, appeals to busy consumers.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in the adoption of HOCl-based contact lens solutions, primarily due to higher awareness and availability of these products. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to be a key growth market in the coming years, driven by the increasing prevalence of myopia and the growing middle-class population in countries like China and India.
Despite the promising outlook, the HOCl contact lens care market faces certain challenges. These include the need for more extensive clinical studies to validate long-term efficacy and safety, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the need to overcome consumer habits and brand loyalty to established cleaning solution products.
In terms of market structure, the HOCl segment is currently dominated by a few key players who have invested in research and development of these solutions. However, as the market expands, it is likely to attract more entrants, potentially leading to increased competition and innovation in formulations and delivery methods.
The HOCl contact lens care market is currently in its nascent stage but shows significant potential for expansion. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing demand for more effective and safer cleaning solutions. Traditional hydrogen peroxide and multipurpose solutions have dominated the market, but concerns about eye irritation and the development of antimicrobial resistance have led to a search for alternatives.
HOCl solutions address many of these concerns, offering broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity without causing significant eye irritation. This has led to a growing interest from both consumers and eye care professionals. Market research indicates that the HOCl segment is expected to grow at a faster rate than the overall contact lens care market in the coming years.
Consumer trends also play a crucial role in shaping the HOCl contact lens care market. There is an increasing preference for natural and gentle products, which aligns well with HOCl's properties as it mimics the body's natural defense mechanisms. Additionally, the convenience factor of HOCl solutions, which often require fewer steps in the cleaning process compared to traditional methods, appeals to busy consumers.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead in the adoption of HOCl-based contact lens solutions, primarily due to higher awareness and availability of these products. However, Asia-Pacific is expected to be a key growth market in the coming years, driven by the increasing prevalence of myopia and the growing middle-class population in countries like China and India.
Despite the promising outlook, the HOCl contact lens care market faces certain challenges. These include the need for more extensive clinical studies to validate long-term efficacy and safety, regulatory hurdles in some regions, and the need to overcome consumer habits and brand loyalty to established cleaning solution products.
In terms of market structure, the HOCl segment is currently dominated by a few key players who have invested in research and development of these solutions. However, as the market expands, it is likely to attract more entrants, potentially leading to increased competition and innovation in formulations and delivery methods.
Current Challenges in HOCl Lens Solution Development
The development of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) based contact lens solutions faces several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is maintaining the stability of HOCl in solution over extended periods. HOCl is inherently unstable and tends to decompose into less effective chlorine species, reducing its antimicrobial potency over time. This instability necessitates careful formulation and packaging considerations to ensure the solution remains effective throughout its shelf life.
Another critical challenge lies in achieving the optimal concentration of HOCl that balances antimicrobial efficacy with ocular safety. While higher concentrations may provide superior disinfection, they also increase the risk of ocular irritation and potential damage to the corneal epithelium. Conversely, lower concentrations may be safer but might not offer sufficient antimicrobial protection, especially against resistant microorganisms commonly associated with contact lens-related infections.
The pH sensitivity of HOCl solutions presents an additional hurdle. The antimicrobial activity of HOCl is highly dependent on pH, with maximum efficacy typically observed in slightly acidic conditions. However, maintaining this optimal pH range can be challenging, as it may conflict with the comfort requirements for contact lens wearers and the physiological pH of the ocular surface.
Compatibility with various contact lens materials is another significant concern. HOCl solutions must be formulated to effectively clean and disinfect lenses without causing material degradation or altering the lens properties. This is particularly challenging given the diverse range of contact lens materials available in the market, each with its unique chemical composition and surface characteristics.
Furthermore, the potential for HOCl to interact with other components commonly found in contact lens care regimens, such as proteins, lipids, and preservatives, poses additional formulation challenges. These interactions could potentially reduce the effectiveness of the HOCl or lead to the formation of undesirable by-products.
Regulatory hurdles also present significant challenges in the development of HOCl-based contact lens solutions. Stringent safety and efficacy requirements set by regulatory bodies necessitate extensive testing and validation processes, which can be time-consuming and costly. Meeting these regulatory standards while maintaining the desired antimicrobial efficacy and user comfort is a delicate balancing act for developers.
Lastly, consumer perception and acceptance of HOCl-based solutions remain a challenge. Despite their potential benefits, the unfamiliarity of HOCl as a disinfecting agent in contact lens care may lead to skepticism or reluctance among users accustomed to traditional hydrogen peroxide or multi-purpose solutions. Overcoming this barrier requires effective education and marketing strategies to communicate the advantages of HOCl-based solutions to both eye care professionals and consumers.
Another critical challenge lies in achieving the optimal concentration of HOCl that balances antimicrobial efficacy with ocular safety. While higher concentrations may provide superior disinfection, they also increase the risk of ocular irritation and potential damage to the corneal epithelium. Conversely, lower concentrations may be safer but might not offer sufficient antimicrobial protection, especially against resistant microorganisms commonly associated with contact lens-related infections.
The pH sensitivity of HOCl solutions presents an additional hurdle. The antimicrobial activity of HOCl is highly dependent on pH, with maximum efficacy typically observed in slightly acidic conditions. However, maintaining this optimal pH range can be challenging, as it may conflict with the comfort requirements for contact lens wearers and the physiological pH of the ocular surface.
Compatibility with various contact lens materials is another significant concern. HOCl solutions must be formulated to effectively clean and disinfect lenses without causing material degradation or altering the lens properties. This is particularly challenging given the diverse range of contact lens materials available in the market, each with its unique chemical composition and surface characteristics.
Furthermore, the potential for HOCl to interact with other components commonly found in contact lens care regimens, such as proteins, lipids, and preservatives, poses additional formulation challenges. These interactions could potentially reduce the effectiveness of the HOCl or lead to the formation of undesirable by-products.
Regulatory hurdles also present significant challenges in the development of HOCl-based contact lens solutions. Stringent safety and efficacy requirements set by regulatory bodies necessitate extensive testing and validation processes, which can be time-consuming and costly. Meeting these regulatory standards while maintaining the desired antimicrobial efficacy and user comfort is a delicate balancing act for developers.
Lastly, consumer perception and acceptance of HOCl-based solutions remain a challenge. Despite their potential benefits, the unfamiliarity of HOCl as a disinfecting agent in contact lens care may lead to skepticism or reluctance among users accustomed to traditional hydrogen peroxide or multi-purpose solutions. Overcoming this barrier requires effective education and marketing strategies to communicate the advantages of HOCl-based solutions to both eye care professionals and consumers.
Existing HOCl Lens Solution Formulations
01 Composition of hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions
Hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions are formulated with specific concentrations of hypochlorous acid to provide effective disinfection and cleaning properties. These solutions may also include additional components such as buffers, stabilizers, and preservatives to enhance their efficacy and shelf life.- Composition of hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions: Hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions are formulated with specific concentrations of hypochlorous acid to provide effective disinfection and cleaning properties. These solutions may also include additional components such as buffers, stabilizers, and preservatives to enhance their efficacy and shelf life.
- Methods of producing hypochlorous acid for contact lens solutions: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid for use in contact lens solutions. These may include electrolysis of saline solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine-containing compounds, or other novel approaches to generate stable and pure hypochlorous acid suitable for ophthalmic applications.
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: To maintain the efficacy of hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions over time, various stabilization techniques are employed. These may include pH adjustment, addition of specific stabilizing agents, or packaging innovations to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability of the active ingredient.
- Compatibility with different types of contact lenses: Hypochlorous acid-based solutions are designed to be compatible with various types of contact lenses, including soft, rigid gas permeable, and silicone hydrogel lenses. Formulations are optimized to ensure effective cleaning and disinfection without compromising the material properties or comfort of different lens types.
- Safety and efficacy studies of hypochlorous acid for ocular use: Extensive research and clinical studies are conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions for ocular use. These studies assess factors such as antimicrobial effectiveness, ocular surface compatibility, and potential for adverse reactions to ensure the solutions meet regulatory standards and provide optimal eye health benefits.
02 Methods of producing hypochlorous acid for contact lens solutions
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid for use in contact lens solutions. These may include electrolysis of saline solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine-containing compounds, or on-demand generation systems. The production methods aim to ensure the stability and purity of the hypochlorous acid.Expand Specific Solutions03 Antimicrobial properties of hypochlorous acid in contact lens care
Hypochlorous acid exhibits strong antimicrobial properties, making it effective against a wide range of microorganisms that can contaminate contact lenses. Its ability to kill bacteria, fungi, and viruses contributes to improved lens hygiene and reduced risk of eye infections for contact lens wearers.Expand Specific Solutions04 Compatibility of hypochlorous acid with contact lens materials
Research focuses on ensuring the compatibility of hypochlorous acid-based solutions with various contact lens materials. This includes studying the interactions between the solution and different types of lenses, such as soft, rigid gas permeable, and silicone hydrogel lenses, to prevent any adverse effects on lens properties or wearer comfort.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safety and efficacy studies of hypochlorous acid contact lens solutions
Extensive research is conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions. This includes clinical trials, toxicology studies, and long-term use assessments to ensure that these solutions are safe for ocular use and effective in maintaining lens cleanliness and eye health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCl Lens Solution Industry
The hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing awareness of eye health and the rising prevalence of vision problems. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, these solutions are advancing, with major players like Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, CooperVision, and Alcon leading innovation. These companies, along with others such as Bausch & Lomb and Novartis, are investing heavily in R&D to improve product efficacy and safety. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants and specialized eye care companies, each striving to differentiate their offerings through enhanced formulations and user-friendly designs.
Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc.
Technical Solution: Johnson & Johnson Vision Care has developed advanced hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solutions, leveraging their proprietary ACUVUE® technology. Their solution incorporates a stabilized form of hypochlorous acid, which provides powerful antimicrobial properties while remaining gentle on the eye. The company has conducted extensive clinical trials demonstrating the efficacy of their solution in eliminating harmful microorganisms and preventing biofilm formation on contact lenses [1][3]. Their formulation also includes additional moisturizing agents to enhance comfort and reduce dryness during lens wear. Johnson & Johnson's solution is compatible with a wide range of contact lens materials, including silicone hydrogels [2].
Strengths: Strong brand recognition, extensive R&D capabilities, and a wide distribution network. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to some competitors, potential for product recalls affecting market perception.
Bausch & Lomb, Inc.
Technical Solution: Bausch & Lomb has introduced a hypochlorous acid-based contact lens solution that utilizes their patented OcuPure® technology. This solution is designed to provide enhanced disinfection while maintaining a pH level close to that of natural tears. The company's formulation includes a precise concentration of hypochlorous acid that effectively eliminates bacteria, fungi, and amoebae commonly associated with contact lens-related infections [4]. Bausch & Lomb's solution also incorporates a unique buffering system that helps maintain the stability of the hypochlorous acid over an extended period, ensuring consistent efficacy throughout the product's shelf life [5]. Additionally, their solution features lubricating agents that help reduce friction between the lens and the eye surface, improving overall comfort for users.
Strengths: Long-standing reputation in eye care, diverse product portfolio, and strong global presence. Weaknesses: Intense competition in the contact lens care market, potential for regulatory challenges.
Core Innovations in HOCl Stability and Efficacy
Hypochlorous acid based eye drop and ophthalmic composition
PatentInactiveUS20200069728A1
Innovation
- Development of an ophthalmic composition using stabilized hypochlorous acid as a non-toxic preservative and antimicrobial agent, with a predetermined concentration and stabilization protocol to maintain potency and shelf life, allowing it to act against pathogens including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and prions without causing ocular irritation.
Ophthalmic and contact lens solutions containing peptides as preservative
PatentInactiveUS20110212885A1
Innovation
- Incorporating amphipathic peptides, such as defensin-class, melittin-class, and cecropin-class peptides, in combination with cationic preservatives like polyhexamethylene biguanide, to enhance preservative efficacy and reduce deposition on contact lenses, while maintaining comfort and safety.
Regulatory Framework for Contact Lens Solutions
The regulatory framework for contact lens solutions, particularly those containing hypochlorous acid, is a complex and evolving landscape. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies contact lens solutions as medical devices, subjecting them to rigorous safety and efficacy standards. The FDA's Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) oversees the regulation of these products, requiring manufacturers to submit premarket notifications (510(k)) or premarket approval applications (PMA) depending on the product's classification.
For hypochlorous acid-based solutions, the regulatory pathway typically involves demonstrating substantial equivalence to predicate devices through the 510(k) process. This includes providing comprehensive data on the solution's chemistry, microbiology, toxicology, and clinical performance. The FDA also mandates adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality and safety.
In the European Union, contact lens solutions fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR imposes stricter requirements for clinical evaluation, post-market surveillance, and traceability compared to its predecessor, the Medical Device Directive (MDD). Manufacturers must obtain CE marking by demonstrating compliance with the MDR's essential requirements, which include safety, performance, and risk management.
Japan's regulatory framework for contact lens solutions is governed by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA). The approval process involves submitting detailed technical documentation and clinical data to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The Japanese regulations place particular emphasis on biocompatibility and the solution's interaction with various lens materials.
International standards play a crucial role in harmonizing regulatory requirements across different regions. ISO 14729 and ISO 14730 specifically address the microbiological requirements and preservative efficacy testing for contact lens care products. These standards are widely recognized and often incorporated into national regulations, facilitating global market access for manufacturers.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the long-term effects of contact lens solutions on ocular health. This has led to more stringent requirements for post-market surveillance and reporting of adverse events. Manufacturers of hypochlorous acid-based solutions must demonstrate not only immediate safety and efficacy but also long-term compatibility with various lens materials and ocular tissues.
As the understanding of ocular microbiology and the potential impacts of disinfecting solutions evolves, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt. This may include updated guidelines on testing for emerging pathogens or new requirements for demonstrating the balance between antimicrobial efficacy and ocular surface health. Manufacturers and researchers in this field must stay abreast of these regulatory developments to ensure continued compliance and market access for their products.
For hypochlorous acid-based solutions, the regulatory pathway typically involves demonstrating substantial equivalence to predicate devices through the 510(k) process. This includes providing comprehensive data on the solution's chemistry, microbiology, toxicology, and clinical performance. The FDA also mandates adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure consistent product quality and safety.
In the European Union, contact lens solutions fall under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which came into full effect in May 2021. The MDR imposes stricter requirements for clinical evaluation, post-market surveillance, and traceability compared to its predecessor, the Medical Device Directive (MDD). Manufacturers must obtain CE marking by demonstrating compliance with the MDR's essential requirements, which include safety, performance, and risk management.
Japan's regulatory framework for contact lens solutions is governed by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA). The approval process involves submitting detailed technical documentation and clinical data to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The Japanese regulations place particular emphasis on biocompatibility and the solution's interaction with various lens materials.
International standards play a crucial role in harmonizing regulatory requirements across different regions. ISO 14729 and ISO 14730 specifically address the microbiological requirements and preservative efficacy testing for contact lens care products. These standards are widely recognized and often incorporated into national regulations, facilitating global market access for manufacturers.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the long-term effects of contact lens solutions on ocular health. This has led to more stringent requirements for post-market surveillance and reporting of adverse events. Manufacturers of hypochlorous acid-based solutions must demonstrate not only immediate safety and efficacy but also long-term compatibility with various lens materials and ocular tissues.
As the understanding of ocular microbiology and the potential impacts of disinfecting solutions evolves, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt. This may include updated guidelines on testing for emerging pathogens or new requirements for demonstrating the balance between antimicrobial efficacy and ocular surface health. Manufacturers and researchers in this field must stay abreast of these regulatory developments to ensure continued compliance and market access for their products.
Environmental Impact of HOCl-Based Solutions
The environmental impact of hypochlorous acid (HOCl)-based contact lens solutions is an important consideration in the development and use of these products. HOCl-based solutions offer several advantages in terms of their environmental footprint compared to traditional contact lens care systems.
One of the primary benefits of HOCl-based solutions is their biodegradability. HOCl naturally breaks down into harmless components, primarily water and salt, which do not persist in the environment or accumulate in ecosystems. This characteristic significantly reduces the potential for long-term environmental contamination associated with the disposal of contact lens solutions.
The production process of HOCl-based solutions generally requires fewer chemical inputs compared to conventional multipurpose solutions. This can lead to a reduction in the overall chemical footprint of the manufacturing process, potentially lowering the environmental impact associated with production.
HOCl-based solutions also demonstrate efficacy at lower concentrations than some traditional disinfectants. This means that smaller quantities of active ingredients are needed to achieve the desired antimicrobial effect, potentially reducing the volume of chemicals released into the environment through normal use and disposal.
The stability of HOCl in solution has improved with recent technological advancements, allowing for longer shelf life and reduced need for preservatives. This can contribute to a decrease in packaging waste and transportation-related emissions associated with more frequent product replacements.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of HOCl-based solutions is not solely determined by the active ingredient. Packaging materials, manufacturing processes, and distribution methods all play significant roles in the overall environmental footprint of these products.
The potential for HOCl-based solutions to be produced on-site using electrolysis of saltwater solutions could further reduce the environmental impact by eliminating the need for transportation and packaging of pre-made solutions. This approach, while not yet widely implemented in the contact lens care market, holds promise for future sustainability improvements.
As with any chemical product, proper disposal of HOCl-based solutions is crucial to minimize environmental impact. While these solutions are generally considered safe for disposal through normal wastewater systems, educating consumers about responsible use and disposal practices remains an important aspect of environmental stewardship in this product category.
One of the primary benefits of HOCl-based solutions is their biodegradability. HOCl naturally breaks down into harmless components, primarily water and salt, which do not persist in the environment or accumulate in ecosystems. This characteristic significantly reduces the potential for long-term environmental contamination associated with the disposal of contact lens solutions.
The production process of HOCl-based solutions generally requires fewer chemical inputs compared to conventional multipurpose solutions. This can lead to a reduction in the overall chemical footprint of the manufacturing process, potentially lowering the environmental impact associated with production.
HOCl-based solutions also demonstrate efficacy at lower concentrations than some traditional disinfectants. This means that smaller quantities of active ingredients are needed to achieve the desired antimicrobial effect, potentially reducing the volume of chemicals released into the environment through normal use and disposal.
The stability of HOCl in solution has improved with recent technological advancements, allowing for longer shelf life and reduced need for preservatives. This can contribute to a decrease in packaging waste and transportation-related emissions associated with more frequent product replacements.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of HOCl-based solutions is not solely determined by the active ingredient. Packaging materials, manufacturing processes, and distribution methods all play significant roles in the overall environmental footprint of these products.
The potential for HOCl-based solutions to be produced on-site using electrolysis of saltwater solutions could further reduce the environmental impact by eliminating the need for transportation and packaging of pre-made solutions. This approach, while not yet widely implemented in the contact lens care market, holds promise for future sustainability improvements.
As with any chemical product, proper disposal of HOCl-based solutions is crucial to minimize environmental impact. While these solutions are generally considered safe for disposal through normal wastewater systems, educating consumers about responsible use and disposal practices remains an important aspect of environmental stewardship in this product category.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!