Innovations in Hypochlorous Acid-Based Sanitizing Systems
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCL Tech Background
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has a long history in sanitization, dating back to its discovery in the early 19th century. Initially used for water treatment and disinfection, HOCl's potential as a powerful yet safe sanitizing agent has gained renewed interest in recent years. This resurgence is driven by the growing demand for effective, eco-friendly, and non-toxic disinfection solutions across various industries.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been marked by significant advancements in production methods, stability, and application techniques. Early production relied on electrolysis of salt water, which was inefficient and produced unstable solutions. Modern innovations have led to more sophisticated electrochemical cells and membrane technology, enabling the production of highly pure and stable HOCl solutions.
In the past decade, research has focused on enhancing HOCl's stability and shelf life, which were historically major limitations. Breakthroughs in pH control, packaging materials, and storage conditions have extended the viability of HOCl solutions from mere hours to several months, greatly expanding their commercial potential.
The technological trajectory of HOCl-based sanitizing systems is closely aligned with global trends in health, safety, and environmental sustainability. As concerns over harmful chemical residues and antimicrobial resistance grow, HOCl presents a compelling alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants. Its natural occurrence in human immune systems further underscores its biocompatibility and safety profile.
Recent innovations have expanded HOCl's applications beyond traditional sectors like healthcare and water treatment. Emerging fields include food safety, agriculture, and personal care products. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated research and development in HOCl technology, particularly in air and surface disinfection systems for public spaces.
Looking forward, the technological goals for HOCl-based sanitizing systems are multifaceted. Key objectives include further improving stability and shelf life, developing more efficient and cost-effective production methods, and expanding the range of delivery systems for various applications. There is also a push towards integrating HOCl technology with smart systems and IoT devices for automated and optimized sanitization processes.
As environmental regulations become stricter and consumer preferences shift towards safer, more natural products, HOCl technology is poised for significant growth and innovation. The ongoing research aims to unlock its full potential as a versatile, effective, and environmentally friendly sanitizing solution for the 21st century.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been marked by significant advancements in production methods, stability, and application techniques. Early production relied on electrolysis of salt water, which was inefficient and produced unstable solutions. Modern innovations have led to more sophisticated electrochemical cells and membrane technology, enabling the production of highly pure and stable HOCl solutions.
In the past decade, research has focused on enhancing HOCl's stability and shelf life, which were historically major limitations. Breakthroughs in pH control, packaging materials, and storage conditions have extended the viability of HOCl solutions from mere hours to several months, greatly expanding their commercial potential.
The technological trajectory of HOCl-based sanitizing systems is closely aligned with global trends in health, safety, and environmental sustainability. As concerns over harmful chemical residues and antimicrobial resistance grow, HOCl presents a compelling alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants. Its natural occurrence in human immune systems further underscores its biocompatibility and safety profile.
Recent innovations have expanded HOCl's applications beyond traditional sectors like healthcare and water treatment. Emerging fields include food safety, agriculture, and personal care products. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated research and development in HOCl technology, particularly in air and surface disinfection systems for public spaces.
Looking forward, the technological goals for HOCl-based sanitizing systems are multifaceted. Key objectives include further improving stability and shelf life, developing more efficient and cost-effective production methods, and expanding the range of delivery systems for various applications. There is also a push towards integrating HOCl technology with smart systems and IoT devices for automated and optimized sanitization processes.
As environmental regulations become stricter and consumer preferences shift towards safer, more natural products, HOCl technology is poised for significant growth and innovation. The ongoing research aims to unlock its full potential as a versatile, effective, and environmentally friendly sanitizing solution for the 21st century.
Sanitizer Market Trends
The global sanitizer market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of hygiene and the impact of global health crises. The COVID-19 pandemic, in particular, has accelerated this trend, leading to a surge in demand for sanitizing products across various sectors. This heightened focus on cleanliness and disinfection is expected to continue, albeit at a more moderate pace, as consumers and businesses maintain higher hygiene standards.
In the context of hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems, market trends indicate a growing interest in these solutions due to their effectiveness and safety profile. Hypochlorous acid is recognized for its powerful antimicrobial properties while being gentle on surfaces and skin, making it an attractive option for both industrial and consumer applications. This has led to increased adoption in healthcare facilities, food processing plants, and households.
The market is witnessing a shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly sanitizing solutions. Hypochlorous acid aligns well with this trend, as it can be produced on-site using water, salt, and electricity, reducing the need for transportation and packaging of traditional chemical sanitizers. This aspect is particularly appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Another notable trend is the integration of technology in sanitizing systems. Smart dispensers, IoT-enabled monitoring, and automated sanitizing stations are becoming more prevalent, especially in high-traffic areas and commercial spaces. These innovations enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of sanitizing processes, ensuring consistent application and reducing waste.
The market is also seeing a diversification of product formats. While liquid sanitizers remain popular, there is growing demand for other forms such as gels, foams, and electrostatic sprays. This diversification caters to different user preferences and application requirements, expanding the potential use cases for hypochlorous acid-based sanitizers.
Regulatory changes and standards are influencing market dynamics as well. Increased scrutiny of sanitizer ingredients and efficacy claims by agencies like the FDA and EPA is shaping product development and marketing strategies. Manufacturers of hypochlorous acid-based systems are focusing on obtaining necessary certifications and conducting rigorous testing to demonstrate their products' safety and effectiveness.
Lastly, there is a trend towards localized production and distribution of sanitizing solutions. This is partly driven by supply chain disruptions experienced during the pandemic, leading businesses to seek more reliable and flexible sourcing options. On-site generation of hypochlorous acid aligns well with this trend, offering a degree of self-sufficiency and reducing dependence on external suppliers.
In the context of hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems, market trends indicate a growing interest in these solutions due to their effectiveness and safety profile. Hypochlorous acid is recognized for its powerful antimicrobial properties while being gentle on surfaces and skin, making it an attractive option for both industrial and consumer applications. This has led to increased adoption in healthcare facilities, food processing plants, and households.
The market is witnessing a shift towards more sustainable and eco-friendly sanitizing solutions. Hypochlorous acid aligns well with this trend, as it can be produced on-site using water, salt, and electricity, reducing the need for transportation and packaging of traditional chemical sanitizers. This aspect is particularly appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Another notable trend is the integration of technology in sanitizing systems. Smart dispensers, IoT-enabled monitoring, and automated sanitizing stations are becoming more prevalent, especially in high-traffic areas and commercial spaces. These innovations enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of sanitizing processes, ensuring consistent application and reducing waste.
The market is also seeing a diversification of product formats. While liquid sanitizers remain popular, there is growing demand for other forms such as gels, foams, and electrostatic sprays. This diversification caters to different user preferences and application requirements, expanding the potential use cases for hypochlorous acid-based sanitizers.
Regulatory changes and standards are influencing market dynamics as well. Increased scrutiny of sanitizer ingredients and efficacy claims by agencies like the FDA and EPA is shaping product development and marketing strategies. Manufacturers of hypochlorous acid-based systems are focusing on obtaining necessary certifications and conducting rigorous testing to demonstrate their products' safety and effectiveness.
Lastly, there is a trend towards localized production and distribution of sanitizing solutions. This is partly driven by supply chain disruptions experienced during the pandemic, leading businesses to seek more reliable and flexible sourcing options. On-site generation of hypochlorous acid aligns well with this trend, offering a degree of self-sufficiency and reducing dependence on external suppliers.
HOCL Challenges
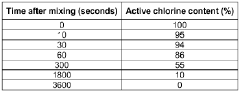
Despite the numerous advantages of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) as a sanitizing agent, several challenges persist in its widespread adoption and implementation. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of HOCl solutions. The compound is inherently unstable and tends to degrade rapidly, especially when exposed to light, heat, or organic matter. This instability significantly limits its shelf life and effectiveness over time, posing difficulties in storage, transportation, and long-term use.
Another major challenge lies in the production and maintenance of consistent HOCl concentrations. The efficacy of HOCl is highly dependent on its concentration, with optimal antimicrobial activity occurring within a specific range. Achieving and maintaining this ideal concentration can be technically demanding, requiring precise control over factors such as pH, temperature, and electrolysis parameters in on-site generation systems. Fluctuations in these parameters can lead to variations in HOCl concentration, potentially compromising its sanitizing effectiveness.
The pH sensitivity of HOCl presents an additional hurdle. The compound is most effective at a slightly acidic pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. Outside this range, HOCl can dissociate into less effective forms or potentially harmful byproducts. Maintaining the optimal pH in various application environments, especially those with diverse chemical compositions or high organic loads, can be challenging and may require sophisticated pH control systems.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness pose significant challenges, particularly for large-scale applications. While on-site generation systems offer advantages in terms of freshness and reduced transportation costs, they often require substantial initial investments in equipment and ongoing maintenance. Balancing the cost of implementation with the benefits of HOCl sanitization remains a key consideration for many potential adopters.
Regulatory hurdles and public perception also present obstacles to the widespread adoption of HOCl-based sanitizing systems. Despite its safety profile, HOCl is often confused with more hazardous chlorine-based disinfectants, leading to misconceptions about its use and potential risks. Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory approvals and educating consumers and industry professionals about the benefits and proper use of HOCl remains an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, the integration of HOCl systems into existing sanitization protocols and infrastructure presents technical and operational challenges. Many industries have established disinfection practices and equipment tailored to traditional sanitizing agents. Adapting these systems to accommodate HOCl-based solutions may require significant modifications to processes, training protocols, and equipment, potentially creating resistance to adoption due to the associated costs and disruptions to established workflows.
Another major challenge lies in the production and maintenance of consistent HOCl concentrations. The efficacy of HOCl is highly dependent on its concentration, with optimal antimicrobial activity occurring within a specific range. Achieving and maintaining this ideal concentration can be technically demanding, requiring precise control over factors such as pH, temperature, and electrolysis parameters in on-site generation systems. Fluctuations in these parameters can lead to variations in HOCl concentration, potentially compromising its sanitizing effectiveness.
The pH sensitivity of HOCl presents an additional hurdle. The compound is most effective at a slightly acidic pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. Outside this range, HOCl can dissociate into less effective forms or potentially harmful byproducts. Maintaining the optimal pH in various application environments, especially those with diverse chemical compositions or high organic loads, can be challenging and may require sophisticated pH control systems.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness pose significant challenges, particularly for large-scale applications. While on-site generation systems offer advantages in terms of freshness and reduced transportation costs, they often require substantial initial investments in equipment and ongoing maintenance. Balancing the cost of implementation with the benefits of HOCl sanitization remains a key consideration for many potential adopters.
Regulatory hurdles and public perception also present obstacles to the widespread adoption of HOCl-based sanitizing systems. Despite its safety profile, HOCl is often confused with more hazardous chlorine-based disinfectants, leading to misconceptions about its use and potential risks. Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory approvals and educating consumers and industry professionals about the benefits and proper use of HOCl remains an ongoing challenge.
Lastly, the integration of HOCl systems into existing sanitization protocols and infrastructure presents technical and operational challenges. Many industries have established disinfection practices and equipment tailored to traditional sanitizing agents. Adapting these systems to accommodate HOCl-based solutions may require significant modifications to processes, training protocols, and equipment, potentially creating resistance to adoption due to the associated costs and disruptions to established workflows.
Current HOCL Solutions
01 Composition and preparation of hypochlorous acid solutions
Hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems often involve specific compositions and preparation methods to ensure optimal effectiveness. These may include precise control of pH levels, concentration of active ingredients, and stabilization techniques to maintain the potency of the solution over time.- Composition and preparation of hypochlorous acid solutions: Hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems often involve specific compositions and preparation methods to ensure optimal effectiveness. These may include precise control of pH levels, concentration of active ingredients, and stabilization techniques to maintain the potency of the solution over time.
- Application methods for enhanced sanitizing effectiveness: Various application methods are employed to maximize the sanitizing effectiveness of hypochlorous acid-based systems. These can include spray systems, fogging devices, or immersion techniques, each designed to ensure thorough coverage and contact time with surfaces or objects to be sanitized.
- Synergistic combinations with other sanitizing agents: Hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems may be combined with other sanitizing agents or additives to enhance their overall effectiveness. These combinations can lead to broader spectrum antimicrobial activity or improved stability of the sanitizing solution.
- Efficacy against specific pathogens and biofilms: Research and development efforts focus on demonstrating the efficacy of hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems against various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Additionally, these systems are evaluated for their ability to penetrate and disrupt biofilms, which are often resistant to conventional sanitizing methods.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems are often developed with a focus on environmental friendliness and safety for users. This includes formulations that break down into non-toxic byproducts, have low corrosivity, and are safe for use on food contact surfaces or in sensitive environments.
02 Application methods for enhanced sanitizing effectiveness
Various application methods are employed to maximize the sanitizing effectiveness of hypochlorous acid-based systems. These can include spraying, fogging, immersion, or electrostatic application techniques, each designed to ensure thorough coverage and contact time with target surfaces or environments.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synergistic combinations with other sanitizing agents
Hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems may be combined with other sanitizing agents or additives to enhance their overall effectiveness. These combinations can lead to broader spectrum antimicrobial activity or improved performance against specific pathogens.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stability and shelf-life enhancement
Improving the stability and shelf-life of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining their sanitizing effectiveness over time. Various stabilization techniques and formulation strategies are employed to prevent degradation and ensure consistent performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Efficacy testing and validation methods
Rigorous testing and validation methods are essential to demonstrate the sanitizing effectiveness of hypochlorous acid-based systems. These may include standardized laboratory tests, real-world application studies, and comparative analyses against other sanitizing agents to establish efficacy claims.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HOCL Players
The market for hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for effective and eco-friendly disinfection solutions. The global market size is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Aquaox, Parasol Medical, and GOJO Industries leading innovation. These firms are developing more efficient production methods, improved stability formulations, and novel application systems. Established players such as Unilever and Clorox are also entering this space, leveraging their extensive distribution networks. The technology's maturity is progressing, with ongoing research focused on enhancing efficacy, shelf-life, and scalability of hypochlorous acid solutions.
Aquaox, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aquaox has developed an innovative on-site generation system for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) sanitizing solutions. Their technology utilizes a proprietary electrolysis process to produce stable, highly effective HOCl from salt, water, and electricity[1]. The system can generate HOCl solutions with concentrations ranging from 50-500 ppm, allowing for customization based on specific application needs[2]. Aquaox's HOCl generators are designed for continuous production, ensuring a constant supply of fresh sanitizing solution. The company has also implemented advanced monitoring and control systems to maintain consistent HOCl quality and concentration[3].
Strengths: On-demand production eliminates storage and transportation issues; Customizable concentrations for various applications; Environmentally friendly process using only salt and water. Weaknesses: Requires initial investment in equipment; Dependent on stable electricity supply; May need regular maintenance for optimal performance.
WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB
Technical Solution: WIAB has pioneered a novel approach to HOCl production using their patented ECA (Electro-Chemical Activation) technology. Their system employs a unique cell design that allows for the efficient generation of HOCl with minimal by-products[4]. WIAB's innovation lies in their ability to produce highly stable HOCl solutions with a longer shelf life compared to traditional methods. The company has developed a range of ECA devices, from small portable units to large-scale industrial systems, catering to various market needs[5]. WIAB's technology also incorporates real-time monitoring and automated adjustment of pH and free available chlorine (FAC) levels, ensuring consistent and reliable HOCl production[6].
Strengths: Produces highly stable HOCl solutions; Scalable technology for various applications; Advanced monitoring and control systems. Weaknesses: May have higher initial costs compared to traditional disinfection methods; Requires specific minerals for optimal operation; Limited market presence outside of Europe.
HOCL Core Patents
Sanitising system
PatentWO2018103973A1
Innovation
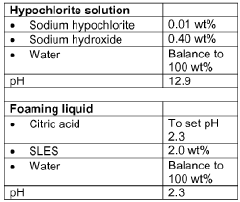
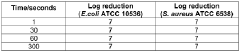
- A sanitizing system comprising an alkaline aqueous hypochlorite solution and an acid aqueous foaming liquid, mixed in a specific ratio to produce a sanitizing foam with a pH of 5 to 7, which is discharged as a hypochlorous acid solution, providing effective antimicrobial properties while minimizing skin exposure to hypochlorous acid.
Apparatus and method for generating a stabilized sanitizing solution
PatentInactiveUS20130146472A1
Innovation
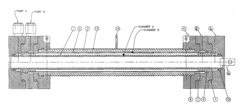
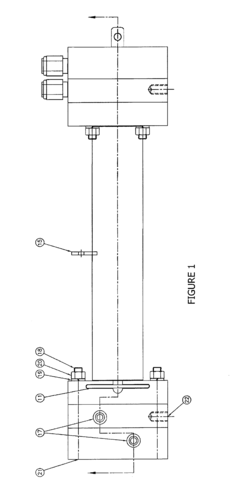
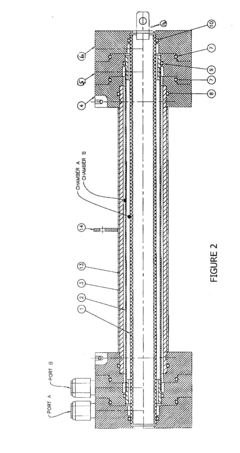
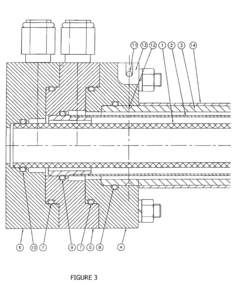
- A two-chamber cylindrical electrolysis cell assembly using ion-selective membranes, specifically a cation-exchange and anion-exchange membrane combination, to control ion migration and enhance the stability and shelf life of Hypochlorous Acid solutions, allowing for adjustment of pH, redox potential, free chlorine content, conductivity, and osmolality.
HOCL Safety Standards
The safety standards for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) based sanitizing systems are crucial for ensuring the effective and secure use of this technology in various applications. These standards encompass several key aspects, including concentration levels, storage conditions, handling procedures, and application methods.
One of the primary safety considerations is the concentration of HOCl in sanitizing solutions. Typically, effective concentrations range from 50 to 200 parts per million (ppm), depending on the specific application. Higher concentrations may be used in industrial settings, while lower concentrations are suitable for food-contact surfaces and general sanitization. It is essential to maintain accurate concentration levels to ensure efficacy while minimizing potential risks.
Storage and handling of HOCl solutions require specific safety measures. The solutions should be stored in opaque, airtight containers to prevent degradation from light exposure and maintain stability. Temperature control is also critical, with recommended storage temperatures between 4°C and 25°C (39°F to 77°F). Proper labeling of containers, including concentration information and expiration dates, is mandatory to prevent misuse and ensure product integrity.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements for handling HOCl solutions are generally less stringent compared to other chemical sanitizers. However, basic precautions such as wearing gloves and eye protection are recommended, especially when handling concentrated solutions or during prolonged exposure.
Application methods for HOCl sanitizing systems must adhere to specific safety protocols. These include proper dilution procedures, ensuring adequate contact time with surfaces, and thorough rinsing when required. In food processing environments, additional measures may be necessary to prevent contamination of food products.
Environmental safety considerations are also integral to HOCl safety standards. The breakdown of HOCl into harmless byproducts (primarily salt and water) makes it environmentally friendly. However, proper disposal practices should still be followed, especially for solutions containing other additives or stabilizers.
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of HOCl safety standards. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HOCl as a pesticide under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). Manufacturers must register their products and adhere to specific labeling requirements. Similarly, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of HOCl in food-related applications.
Ongoing monitoring and quality control measures are essential components of HOCl safety standards. Regular testing of solution concentrations, pH levels, and efficacy against target microorganisms ensures consistent performance and safety. Documentation of these tests and any corrective actions taken is typically required for compliance with regulatory standards.
One of the primary safety considerations is the concentration of HOCl in sanitizing solutions. Typically, effective concentrations range from 50 to 200 parts per million (ppm), depending on the specific application. Higher concentrations may be used in industrial settings, while lower concentrations are suitable for food-contact surfaces and general sanitization. It is essential to maintain accurate concentration levels to ensure efficacy while minimizing potential risks.
Storage and handling of HOCl solutions require specific safety measures. The solutions should be stored in opaque, airtight containers to prevent degradation from light exposure and maintain stability. Temperature control is also critical, with recommended storage temperatures between 4°C and 25°C (39°F to 77°F). Proper labeling of containers, including concentration information and expiration dates, is mandatory to prevent misuse and ensure product integrity.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements for handling HOCl solutions are generally less stringent compared to other chemical sanitizers. However, basic precautions such as wearing gloves and eye protection are recommended, especially when handling concentrated solutions or during prolonged exposure.
Application methods for HOCl sanitizing systems must adhere to specific safety protocols. These include proper dilution procedures, ensuring adequate contact time with surfaces, and thorough rinsing when required. In food processing environments, additional measures may be necessary to prevent contamination of food products.
Environmental safety considerations are also integral to HOCl safety standards. The breakdown of HOCl into harmless byproducts (primarily salt and water) makes it environmentally friendly. However, proper disposal practices should still be followed, especially for solutions containing other additives or stabilizers.
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of HOCl safety standards. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates HOCl as a pesticide under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). Manufacturers must register their products and adhere to specific labeling requirements. Similarly, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of HOCl in food-related applications.
Ongoing monitoring and quality control measures are essential components of HOCl safety standards. Regular testing of solution concentrations, pH levels, and efficacy against target microorganisms ensures consistent performance and safety. Documentation of these tests and any corrective actions taken is typically required for compliance with regulatory standards.
Eco-friendly Impact
Hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems have gained significant attention due to their eco-friendly impact on various industries and applications. These systems offer a sustainable alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants, aligning with the growing global emphasis on environmental conservation and responsible resource management.
One of the primary eco-friendly benefits of hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems is their minimal environmental footprint. Unlike many conventional sanitizers that contain harsh chemicals, hypochlorous acid is a naturally occurring substance that breaks down into simple salt and water. This decomposition process ensures that no harmful residues are left behind, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and ecosystem disruption.
The production of hypochlorous acid solutions typically requires only salt, water, and electricity, making it a resource-efficient option. This simplicity in manufacturing translates to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions compared to the production of complex chemical disinfectants. Furthermore, the on-site generation capabilities of many hypochlorous acid systems eliminate the need for transportation and storage of large quantities of chemicals, further reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional sanitizing methods.
In terms of water conservation, hypochlorous acid-based systems often require less water for rinsing compared to conventional chemical sanitizers. This attribute is particularly valuable in industries such as food processing and agriculture, where large volumes of water are typically used for cleaning and sanitizing processes. By reducing water consumption, these systems contribute to the preservation of this vital resource and support sustainable water management practices.
The non-toxic nature of hypochlorous acid also presents significant ecological advantages. It poses minimal risk to aquatic life when released into water systems, unlike many chemical sanitizers that can harm marine ecosystems. This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for applications in sensitive environments or areas near water bodies.
Moreover, the use of hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems can lead to a reduction in plastic waste. Many traditional sanitizers are packaged in single-use plastic containers, contributing to the global plastic pollution crisis. In contrast, on-site generation of hypochlorous acid solutions eliminates the need for disposable packaging, aligning with circular economy principles and waste reduction initiatives.
The eco-friendly impact of these systems extends to indoor air quality as well. Unlike chlorine-based disinfectants that can release harmful fumes, hypochlorous acid solutions are generally odorless and do not contribute to indoor air pollution. This aspect is particularly beneficial in enclosed spaces such as hospitals, schools, and office buildings, where air quality is a critical concern for occupant health and well-being.
One of the primary eco-friendly benefits of hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems is their minimal environmental footprint. Unlike many conventional sanitizers that contain harsh chemicals, hypochlorous acid is a naturally occurring substance that breaks down into simple salt and water. This decomposition process ensures that no harmful residues are left behind, reducing the risk of environmental contamination and ecosystem disruption.
The production of hypochlorous acid solutions typically requires only salt, water, and electricity, making it a resource-efficient option. This simplicity in manufacturing translates to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions compared to the production of complex chemical disinfectants. Furthermore, the on-site generation capabilities of many hypochlorous acid systems eliminate the need for transportation and storage of large quantities of chemicals, further reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional sanitizing methods.
In terms of water conservation, hypochlorous acid-based systems often require less water for rinsing compared to conventional chemical sanitizers. This attribute is particularly valuable in industries such as food processing and agriculture, where large volumes of water are typically used for cleaning and sanitizing processes. By reducing water consumption, these systems contribute to the preservation of this vital resource and support sustainable water management practices.
The non-toxic nature of hypochlorous acid also presents significant ecological advantages. It poses minimal risk to aquatic life when released into water systems, unlike many chemical sanitizers that can harm marine ecosystems. This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for applications in sensitive environments or areas near water bodies.
Moreover, the use of hypochlorous acid-based sanitizing systems can lead to a reduction in plastic waste. Many traditional sanitizers are packaged in single-use plastic containers, contributing to the global plastic pollution crisis. In contrast, on-site generation of hypochlorous acid solutions eliminates the need for disposable packaging, aligning with circular economy principles and waste reduction initiatives.
The eco-friendly impact of these systems extends to indoor air quality as well. Unlike chlorine-based disinfectants that can release harmful fumes, hypochlorous acid solutions are generally odorless and do not contribute to indoor air pollution. This aspect is particularly beneficial in enclosed spaces such as hospitals, schools, and office buildings, where air quality is a critical concern for occupant health and well-being.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!