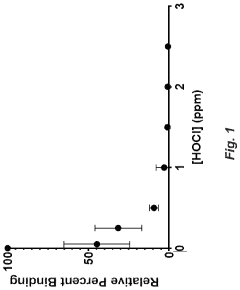
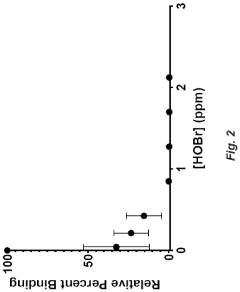
Hypochlorous Acid Research: Impacts on Public Health Policies
AUG 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCL Background & Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a significant focus in public health research due to its potent antimicrobial properties and potential applications in various sectors. The evolution of HOCl technology can be traced back to its discovery in the early 19th century, with subsequent developments in production methods and understanding of its mechanisms of action.
The primary objective of current HOCl research is to explore its efficacy in addressing pressing public health challenges, particularly in the context of infection control and environmental sanitation. This research aims to evaluate HOCl's potential as a safe, eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants, which often pose risks to human health and the environment.
Recent technological advancements have significantly improved HOCl production processes, making it more stable and cost-effective. These developments have opened up new possibilities for its widespread application in healthcare settings, food safety, water treatment, and general hygiene practices. The growing interest in HOCl is further fueled by the global emphasis on sustainable and non-toxic solutions for maintaining public health.
A key focus of ongoing research is to establish standardized protocols for HOCl use across different sectors. This includes determining optimal concentrations, application methods, and storage conditions to maximize its effectiveness while ensuring safety. Additionally, researchers are investigating the long-term impacts of HOCl use on microbial resistance patterns and environmental ecosystems.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated interest in HOCl research, highlighting its potential role in combating infectious diseases. Studies are underway to assess its efficacy against various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi, in both clinical and community settings. This research is crucial for informing public health policies and guidelines on disinfection practices.
Another important aspect of HOCl research is its potential integration into existing public health infrastructure. This includes exploring its use in water treatment systems, air purification technologies, and surface disinfection protocols in public spaces. The goal is to develop comprehensive strategies that leverage HOCl's properties to enhance overall community health and reduce the burden of infectious diseases.
As research progresses, there is a growing need to address regulatory and safety considerations surrounding HOCl use. This involves conducting thorough toxicological studies, assessing potential environmental impacts, and establishing clear guidelines for its production and application. These efforts are essential for gaining regulatory approvals and ensuring public trust in HOCl-based solutions.
The primary objective of current HOCl research is to explore its efficacy in addressing pressing public health challenges, particularly in the context of infection control and environmental sanitation. This research aims to evaluate HOCl's potential as a safe, eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants, which often pose risks to human health and the environment.
Recent technological advancements have significantly improved HOCl production processes, making it more stable and cost-effective. These developments have opened up new possibilities for its widespread application in healthcare settings, food safety, water treatment, and general hygiene practices. The growing interest in HOCl is further fueled by the global emphasis on sustainable and non-toxic solutions for maintaining public health.
A key focus of ongoing research is to establish standardized protocols for HOCl use across different sectors. This includes determining optimal concentrations, application methods, and storage conditions to maximize its effectiveness while ensuring safety. Additionally, researchers are investigating the long-term impacts of HOCl use on microbial resistance patterns and environmental ecosystems.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated interest in HOCl research, highlighting its potential role in combating infectious diseases. Studies are underway to assess its efficacy against various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi, in both clinical and community settings. This research is crucial for informing public health policies and guidelines on disinfection practices.
Another important aspect of HOCl research is its potential integration into existing public health infrastructure. This includes exploring its use in water treatment systems, air purification technologies, and surface disinfection protocols in public spaces. The goal is to develop comprehensive strategies that leverage HOCl's properties to enhance overall community health and reduce the burden of infectious diseases.
As research progresses, there is a growing need to address regulatory and safety considerations surrounding HOCl use. This involves conducting thorough toxicological studies, assessing potential environmental impacts, and establishing clear guidelines for its production and application. These efforts are essential for gaining regulatory approvals and ensuring public trust in HOCl-based solutions.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has been steadily increasing, driven by its versatile applications in public health, healthcare, and sanitation sectors. As a powerful yet safe disinfectant, HOCl has gained significant attention, especially in light of recent global health challenges.
In the healthcare industry, there is a growing demand for HOCl-based products in hospital disinfection, wound care, and dental hygiene. The non-toxic nature of HOCl makes it an attractive alternative to harsh chemical disinfectants, aligning with the industry's shift towards safer and more environmentally friendly solutions.
The food and beverage sector has also shown increased interest in HOCl for sanitization purposes. With stringent food safety regulations and consumer demand for clean-label products, HOCl offers an effective solution for food processing facilities, restaurants, and packaging industries.
Water treatment represents another significant market for HOCl. Municipal water suppliers and wastewater treatment plants are exploring HOCl as a chlorine alternative, due to its efficacy in pathogen elimination without harmful by-products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for HOCl in various applications. Its effectiveness against viruses, including coronaviruses, has led to increased adoption in public spaces, transportation systems, and personal hygiene products.
Consumer awareness of HOCl's benefits is growing, leading to a rise in demand for household cleaning products and personal care items containing this compound. This trend is expected to continue as consumers prioritize health and safety in their daily lives.
The agriculture sector is another emerging market for HOCl, with applications in crop protection, livestock health, and produce disinfection. Farmers are increasingly turning to HOCl as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional pesticides and disinfectants.
Market analysis indicates that the global HOCl market is poised for substantial growth in the coming years. Factors such as increasing health consciousness, stringent regulations on chemical disinfectants, and the need for sustainable solutions are driving this growth.
However, challenges remain in terms of product stability and shelf life, which could impact widespread adoption. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues to meet the growing market demand.
As public health policies continue to evolve, emphasizing prevention and environmental safety, the demand for HOCl is expected to further increase. This presents significant opportunities for manufacturers, researchers, and policymakers to collaborate in developing innovative HOCl-based solutions that address current and future public health challenges.
In the healthcare industry, there is a growing demand for HOCl-based products in hospital disinfection, wound care, and dental hygiene. The non-toxic nature of HOCl makes it an attractive alternative to harsh chemical disinfectants, aligning with the industry's shift towards safer and more environmentally friendly solutions.
The food and beverage sector has also shown increased interest in HOCl for sanitization purposes. With stringent food safety regulations and consumer demand for clean-label products, HOCl offers an effective solution for food processing facilities, restaurants, and packaging industries.
Water treatment represents another significant market for HOCl. Municipal water suppliers and wastewater treatment plants are exploring HOCl as a chlorine alternative, due to its efficacy in pathogen elimination without harmful by-products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for HOCl in various applications. Its effectiveness against viruses, including coronaviruses, has led to increased adoption in public spaces, transportation systems, and personal hygiene products.
Consumer awareness of HOCl's benefits is growing, leading to a rise in demand for household cleaning products and personal care items containing this compound. This trend is expected to continue as consumers prioritize health and safety in their daily lives.
The agriculture sector is another emerging market for HOCl, with applications in crop protection, livestock health, and produce disinfection. Farmers are increasingly turning to HOCl as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional pesticides and disinfectants.
Market analysis indicates that the global HOCl market is poised for substantial growth in the coming years. Factors such as increasing health consciousness, stringent regulations on chemical disinfectants, and the need for sustainable solutions are driving this growth.
However, challenges remain in terms of product stability and shelf life, which could impact widespread adoption. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues to meet the growing market demand.
As public health policies continue to evolve, emphasizing prevention and environmental safety, the demand for HOCl is expected to further increase. This presents significant opportunities for manufacturers, researchers, and policymakers to collaborate in developing innovative HOCl-based solutions that address current and future public health challenges.
Technical Challenges
The development and application of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in public health policies face several technical challenges that require careful consideration and innovative solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the stability of HOCl solutions. Due to its reactive nature, HOCl tends to degrade rapidly, limiting its shelf life and effectiveness in various applications. This instability poses significant challenges for storage, transportation, and long-term use in public health initiatives.
Another technical hurdle is the precise control of HOCl concentration. Maintaining the optimal concentration is crucial for ensuring its efficacy as a disinfectant while avoiding potential harmful effects. The concentration can be affected by various factors, including pH levels, temperature, and exposure to organic matter. Developing reliable methods for real-time monitoring and adjustment of HOCl concentration in different environments remains a significant challenge.
The production of HOCl at scale also presents technical difficulties. While small-scale generation is relatively straightforward, scaling up production for widespread public health use requires sophisticated engineering solutions. Ensuring consistent quality and purity of HOCl across large-scale production batches is essential for its reliable application in public health policies.
Furthermore, the integration of HOCl-based disinfection systems into existing infrastructure poses technical challenges. Retrofitting current water treatment facilities, healthcare environments, and public spaces to incorporate HOCl technology requires careful planning and engineering. Compatibility issues with existing materials and equipment must be addressed to prevent corrosion or degradation of infrastructure.
The development of efficient delivery systems for HOCl is another area of technical challenge. Creating effective methods for applying HOCl in various settings, such as air disinfection, surface sanitization, and water treatment, requires innovative approaches. This includes designing specialized equipment for aerosolization, misting, and controlled release of HOCl in different environments.
Lastly, the environmental impact of widespread HOCl use needs to be carefully evaluated. While HOCl is generally considered environmentally friendly due to its decomposition into harmless byproducts, the long-term effects of large-scale application on ecosystems and water bodies require further study. Developing methods to monitor and mitigate any potential environmental consequences is a crucial technical challenge in implementing HOCl-based public health policies.
Another technical hurdle is the precise control of HOCl concentration. Maintaining the optimal concentration is crucial for ensuring its efficacy as a disinfectant while avoiding potential harmful effects. The concentration can be affected by various factors, including pH levels, temperature, and exposure to organic matter. Developing reliable methods for real-time monitoring and adjustment of HOCl concentration in different environments remains a significant challenge.
The production of HOCl at scale also presents technical difficulties. While small-scale generation is relatively straightforward, scaling up production for widespread public health use requires sophisticated engineering solutions. Ensuring consistent quality and purity of HOCl across large-scale production batches is essential for its reliable application in public health policies.
Furthermore, the integration of HOCl-based disinfection systems into existing infrastructure poses technical challenges. Retrofitting current water treatment facilities, healthcare environments, and public spaces to incorporate HOCl technology requires careful planning and engineering. Compatibility issues with existing materials and equipment must be addressed to prevent corrosion or degradation of infrastructure.
The development of efficient delivery systems for HOCl is another area of technical challenge. Creating effective methods for applying HOCl in various settings, such as air disinfection, surface sanitization, and water treatment, requires innovative approaches. This includes designing specialized equipment for aerosolization, misting, and controlled release of HOCl in different environments.
Lastly, the environmental impact of widespread HOCl use needs to be carefully evaluated. While HOCl is generally considered environmentally friendly due to its decomposition into harmless byproducts, the long-term effects of large-scale application on ecosystems and water bodies require further study. Developing methods to monitor and mitigate any potential environmental consequences is a crucial technical challenge in implementing HOCl-based public health policies.
Current HOCL Solutions
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: Stabilizing hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining their efficacy over time. Various techniques are employed, such as pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging methods, to prevent degradation and extend the shelf life of hypochlorous acid products.
- Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its natural occurrence in the human immune system and its ability to promote healing while combating infections make it a valuable compound in healthcare settings.
- Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in various environmental and industrial applications, such as water treatment, agriculture, and surface disinfection. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness in removing contaminants make it a preferred choice for sustainable cleaning and sanitization processes.
02 Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions
Researchers have developed various stabilization techniques to prolong the shelf life and maintain the efficacy of hypochlorous acid solutions. These methods may involve pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, or specialized packaging to prevent degradation and ensure consistent performance over time.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid has found applications in various medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its ability to effectively kill pathogens while being gentle on human tissues makes it a promising option for treating infections and promoting healing.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation and industrial processes due to its strong oxidizing properties and eco-friendly nature. Applications include water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination in various industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The research on Hypochlorous Acid and its impacts on public health policies is in a developing stage, with growing market potential and increasing technological maturity. The industry is transitioning from early-stage research to practical applications, driven by the rising demand for effective disinfection solutions. Key players like ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC., Aquaox, Inc., and Wonder Spray LLC are advancing the technology, while academic institutions such as Xiamen University and China Pharmaceutical University contribute to the scientific understanding. The market is expanding as more companies recognize the potential of hypochlorous acid in healthcare and sanitation, with established firms like Robert Bosch GmbH also showing interest in this emerging field.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: Annihilare Medical Systems has developed a proprietary electrochemical activation (ECA) technology for producing hypochlorous acid (HOCl) solutions. Their system generates HOCl on-site, ensuring a consistent and stable concentration for various applications. The company's research focuses on optimizing HOCl production methods to enhance stability and efficacy. They have conducted studies demonstrating the broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of their HOCl solutions against bacteria, viruses, and fungi [1][3]. Annihilare's technology allows for the production of HOCl with a neutral pH, which enhances its safety profile for use in healthcare settings and public spaces.
Strengths: On-site generation ensures fresh and consistent HOCl solutions. Neutral pH formulation enhances safety and versatility. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment for production, potentially limiting widespread adoption.
Aquaox, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aquaox has developed an advanced electrochemical activation (ECA) technology for producing hypochlorous acid. Their patented system generates HOCl at a near-neutral pH, which enhances its stability and effectiveness. The company's research has focused on optimizing the production process to create HOCl solutions with precise concentrations and minimal by-products. Aquaox has conducted extensive studies on the efficacy of their HOCl solutions against a wide range of pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant bacteria and viruses [2][5]. Their technology allows for the scalable production of HOCl, from small portable devices to large industrial systems, addressing various public health needs.
Strengths: Scalable production technology suitable for various applications. Near-neutral pH formulation enhances stability and safety. Weaknesses: May face challenges in educating the public and policymakers about the benefits of HOCl compared to traditional disinfectants.
Core HOCL Innovations
Compositions of hypochlorous acid and methods of manufacture thereof
PatentActiveUS20230065525A1
Innovation
- An air-free mixing method involving a compound that generates a proton and a compound that generates a hypochlorite anion in water, without using electrolysis or chlorine gas, to produce a stable HOCl formulation that can be stored for several months.
Hypohalous acids for treating inflammatory diseases and inhibiting growth of malignancies
PatentInactiveUS20220202853A1
Innovation
- Development of a novel electrochemical method to produce stable, pure hypohalous acids (HOCl and HOBr) that are free from hypochlorites and hypobromites, allowing for topical and inhalation-based delivery to inactivate IL-6 and other cytokines, thereby addressing the limitations of existing therapies and stability issues with hypohalous acids.
Public Health Implications
The research on hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has significant implications for public health policies. As a potent antimicrobial agent, HOCl has demonstrated effectiveness against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This broad-spectrum efficacy has led to increased interest in its potential applications in healthcare settings, water treatment, and environmental disinfection.
One of the key advantages of HOCl is its safety profile. Unlike many traditional disinfectants, HOCl is non-toxic to humans and animals when used at appropriate concentrations. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for use in public spaces, healthcare facilities, and food processing environments. Public health policies may need to be updated to reflect the potential benefits of HOCl-based disinfection strategies, particularly in light of emerging infectious diseases and antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
The use of HOCl in water treatment systems could have far-reaching effects on public health. Its ability to effectively disinfect water without producing harmful byproducts, as is often the case with chlorine-based treatments, may lead to changes in water treatment regulations and guidelines. This could result in improved water quality and reduced exposure to potentially harmful disinfection byproducts for large populations.
In healthcare settings, the adoption of HOCl-based disinfection protocols could contribute to reducing healthcare-associated infections. This would have significant implications for patient safety policies and infection control guidelines. The potential for HOCl to be used in wound care and as a hand sanitizer may also influence healthcare practices and recommendations for both medical professionals and the general public.
Environmental health policies may also be impacted by HOCl research. The eco-friendly nature of HOCl, which breaks down into harmless components, aligns well with sustainable practices and green chemistry initiatives. This could lead to changes in regulations regarding the use of chemical disinfectants in various industries and public spaces.
As research continues to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of HOCl, public health policies may need to be revised to incorporate this technology into standard practices for disease prevention and control. This could include guidelines for its use in schools, public transportation, and other high-traffic areas to reduce the spread of infectious diseases. Additionally, policies regarding emergency preparedness and response to outbreaks may be updated to include HOCl-based interventions as part of a comprehensive public health strategy.
One of the key advantages of HOCl is its safety profile. Unlike many traditional disinfectants, HOCl is non-toxic to humans and animals when used at appropriate concentrations. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for use in public spaces, healthcare facilities, and food processing environments. Public health policies may need to be updated to reflect the potential benefits of HOCl-based disinfection strategies, particularly in light of emerging infectious diseases and antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
The use of HOCl in water treatment systems could have far-reaching effects on public health. Its ability to effectively disinfect water without producing harmful byproducts, as is often the case with chlorine-based treatments, may lead to changes in water treatment regulations and guidelines. This could result in improved water quality and reduced exposure to potentially harmful disinfection byproducts for large populations.
In healthcare settings, the adoption of HOCl-based disinfection protocols could contribute to reducing healthcare-associated infections. This would have significant implications for patient safety policies and infection control guidelines. The potential for HOCl to be used in wound care and as a hand sanitizer may also influence healthcare practices and recommendations for both medical professionals and the general public.
Environmental health policies may also be impacted by HOCl research. The eco-friendly nature of HOCl, which breaks down into harmless components, aligns well with sustainable practices and green chemistry initiatives. This could lead to changes in regulations regarding the use of chemical disinfectants in various industries and public spaces.
As research continues to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of HOCl, public health policies may need to be revised to incorporate this technology into standard practices for disease prevention and control. This could include guidelines for its use in schools, public transportation, and other high-traffic areas to reduce the spread of infectious diseases. Additionally, policies regarding emergency preparedness and response to outbreaks may be updated to include HOCl-based interventions as part of a comprehensive public health strategy.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is complex and multifaceted, reflecting its diverse applications and potential impacts on public health. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating HOCl as a pesticide and disinfectant under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA). The EPA requires manufacturers to register HOCl-based products and provide extensive data on their safety and efficacy before market approval.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also oversees HOCl use in food processing, medical devices, and certain healthcare applications. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, the FDA has established guidelines for HOCl concentrations and applications in these sectors. For instance, the agency has approved HOCl solutions for use as sanitizers in food processing facilities, subject to specific concentration and application requirements.
Internationally, regulatory approaches to HOCl vary. The European Union, through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), regulates HOCl under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This framework requires manufacturers and importers to register HOCl and provide safety data, ensuring its safe use across member states.
In the context of public health policies, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized HOCl as an effective disinfectant, particularly in healthcare settings. This recognition has influenced global health policies, with many countries incorporating HOCl into their infection control guidelines. However, the WHO also emphasizes the need for proper handling and application of HOCl to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential risks.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of HOCl in public health strategies. Many regulatory bodies, including the EPA and FDA, have expedited approval processes for HOCl-based disinfectants as part of emergency response measures. This has led to increased scrutiny of regulatory frameworks, with calls for more harmonized global standards for HOCl production, testing, and application.
As research continues to uncover new applications and potential benefits of HOCl, regulatory bodies are faced with the challenge of adapting their frameworks to keep pace with scientific advancements. This includes ongoing assessments of environmental impacts, occupational safety considerations, and potential long-term health effects associated with HOCl use. The evolving regulatory landscape reflects a balance between promoting innovation in public health solutions and ensuring the safety and efficacy of HOCl-based products.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also oversees HOCl use in food processing, medical devices, and certain healthcare applications. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, the FDA has established guidelines for HOCl concentrations and applications in these sectors. For instance, the agency has approved HOCl solutions for use as sanitizers in food processing facilities, subject to specific concentration and application requirements.
Internationally, regulatory approaches to HOCl vary. The European Union, through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), regulates HOCl under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This framework requires manufacturers and importers to register HOCl and provide safety data, ensuring its safe use across member states.
In the context of public health policies, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized HOCl as an effective disinfectant, particularly in healthcare settings. This recognition has influenced global health policies, with many countries incorporating HOCl into their infection control guidelines. However, the WHO also emphasizes the need for proper handling and application of HOCl to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential risks.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of HOCl in public health strategies. Many regulatory bodies, including the EPA and FDA, have expedited approval processes for HOCl-based disinfectants as part of emergency response measures. This has led to increased scrutiny of regulatory frameworks, with calls for more harmonized global standards for HOCl production, testing, and application.
As research continues to uncover new applications and potential benefits of HOCl, regulatory bodies are faced with the challenge of adapting their frameworks to keep pace with scientific advancements. This includes ongoing assessments of environmental impacts, occupational safety considerations, and potential long-term health effects associated with HOCl use. The evolving regulatory landscape reflects a balance between promoting innovation in public health solutions and ensuring the safety and efficacy of HOCl-based products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!