Hypochlorous Acid Clinical Trials: Current Status and Advances
AUG 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCI Research Background
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has been a subject of scientific interest for over a century, with its potential applications in healthcare and disinfection becoming increasingly apparent in recent decades. Initially discovered in the early 19th century, HOCl gained prominence due to its natural occurrence in the human immune system, where it is produced by neutrophils as part of the body's defense mechanism against pathogens.
The research background of HOCl is rooted in its unique chemical properties. As a weak acid with strong oxidizing capabilities, HOCl has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in killing a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, coupled with its low toxicity to human cells, has made HOCl an attractive subject for clinical research.
Early studies on HOCl focused primarily on its role in the immune system and its potential as a topical antiseptic. However, as technology advanced, researchers began to explore methods for stabilizing HOCl solutions, which naturally degrade quickly. This breakthrough in stabilization techniques opened up new avenues for research and potential clinical applications.
The medical community's interest in HOCl has grown significantly in the past two decades, driven by the need for effective and safe antimicrobial agents in the face of rising antibiotic resistance. Clinical trials have expanded to investigate HOCl's efficacy in wound care, dermatology, ophthalmology, and respiratory health, among other areas.
Recent advances in HOCl research have been propelled by improvements in production methods, allowing for the creation of pure, stable HOCl solutions at specific concentrations. This has enabled more precise and controlled clinical studies, leading to a better understanding of HOCl's mechanisms of action and optimal dosing for various applications.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated interest in HOCl research, particularly in its potential as a disinfectant and in respiratory health applications. This has led to an increase in clinical trials exploring HOCl's efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 and its potential role in preventing and managing respiratory infections.
As the field of HOCl research continues to evolve, there is growing interest in its potential synergistic effects with other treatments, its role in biofilm disruption, and its applications in emerging fields such as dental care and food safety. The ongoing clinical trials are not only expanding our understanding of HOCl's therapeutic potential but also paving the way for new, innovative applications in healthcare and beyond.
The research background of HOCl is rooted in its unique chemical properties. As a weak acid with strong oxidizing capabilities, HOCl has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in killing a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, coupled with its low toxicity to human cells, has made HOCl an attractive subject for clinical research.
Early studies on HOCl focused primarily on its role in the immune system and its potential as a topical antiseptic. However, as technology advanced, researchers began to explore methods for stabilizing HOCl solutions, which naturally degrade quickly. This breakthrough in stabilization techniques opened up new avenues for research and potential clinical applications.
The medical community's interest in HOCl has grown significantly in the past two decades, driven by the need for effective and safe antimicrobial agents in the face of rising antibiotic resistance. Clinical trials have expanded to investigate HOCl's efficacy in wound care, dermatology, ophthalmology, and respiratory health, among other areas.
Recent advances in HOCl research have been propelled by improvements in production methods, allowing for the creation of pure, stable HOCl solutions at specific concentrations. This has enabled more precise and controlled clinical studies, leading to a better understanding of HOCl's mechanisms of action and optimal dosing for various applications.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated interest in HOCl research, particularly in its potential as a disinfectant and in respiratory health applications. This has led to an increase in clinical trials exploring HOCl's efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 and its potential role in preventing and managing respiratory infections.
As the field of HOCl research continues to evolve, there is growing interest in its potential synergistic effects with other treatments, its role in biofilm disruption, and its applications in emerging fields such as dental care and food safety. The ongoing clinical trials are not only expanding our understanding of HOCl's therapeutic potential but also paving the way for new, innovative applications in healthcare and beyond.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in clinical applications has been steadily increasing, driven by its proven efficacy as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent with minimal side effects. Healthcare facilities, including hospitals and clinics, are showing growing interest in HOCl-based solutions for wound care, disinfection, and sterilization purposes. This demand is further fueled by the rising incidence of healthcare-associated infections and the need for effective, yet safe, antimicrobial agents.
In the wound care segment, HOCl has gained significant traction due to its ability to promote healing while preventing infection. The global wound care market, which HOCl products are increasingly penetrating, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is attributed to factors such as the aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, and the rise in surgical procedures.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also contributed to the heightened demand for HOCl-based disinfectants. Healthcare facilities and public spaces have been seeking safe and effective sanitization solutions, leading to increased adoption of HOCl products. This trend is expected to continue even post-pandemic, as awareness of infection control measures remains high.
In the dental care sector, HOCl is gaining recognition for its potential in oral hygiene applications. Dental professionals are exploring HOCl-based mouthwashes and irrigation solutions as alternatives to traditional chlorhexidine products, driven by the need for effective yet gentle oral care options.
The pharmaceutical industry is also showing interest in HOCl for its potential in treating various skin conditions and respiratory infections. Clinical trials are underway to explore these applications, which could significantly expand the market for HOCl-based pharmaceutical products.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market demand for HOCl in clinical applications, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and stringent infection control regulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in demand, driven by improving healthcare standards and increasing awareness of infection prevention.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in terms of product stability and shelf life, which can impact widespread adoption. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, potentially opening up new market opportunities for stabilized HOCl formulations.
As clinical trials continue to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of HOCl in various medical applications, the market demand is expected to further diversify and expand. This growth trajectory is supported by the increasing emphasis on patient safety, the need for effective antimicrobial solutions, and the ongoing search for alternatives to traditional chemical disinfectants with potentially harmful side effects.
In the wound care segment, HOCl has gained significant traction due to its ability to promote healing while preventing infection. The global wound care market, which HOCl products are increasingly penetrating, is projected to expand substantially in the coming years. This growth is attributed to factors such as the aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic wounds, and the rise in surgical procedures.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also contributed to the heightened demand for HOCl-based disinfectants. Healthcare facilities and public spaces have been seeking safe and effective sanitization solutions, leading to increased adoption of HOCl products. This trend is expected to continue even post-pandemic, as awareness of infection control measures remains high.
In the dental care sector, HOCl is gaining recognition for its potential in oral hygiene applications. Dental professionals are exploring HOCl-based mouthwashes and irrigation solutions as alternatives to traditional chlorhexidine products, driven by the need for effective yet gentle oral care options.
The pharmaceutical industry is also showing interest in HOCl for its potential in treating various skin conditions and respiratory infections. Clinical trials are underway to explore these applications, which could significantly expand the market for HOCl-based pharmaceutical products.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market demand for HOCl in clinical applications, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and stringent infection control regulations. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to witness rapid growth in demand, driven by improving healthcare standards and increasing awareness of infection prevention.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in terms of product stability and shelf life, which can impact widespread adoption. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, potentially opening up new market opportunities for stabilized HOCl formulations.
As clinical trials continue to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of HOCl in various medical applications, the market demand is expected to further diversify and expand. This growth trajectory is supported by the increasing emphasis on patient safety, the need for effective antimicrobial solutions, and the ongoing search for alternatives to traditional chemical disinfectants with potentially harmful side effects.
Clinical Trial Challenges
Clinical trials involving hypochlorous acid (HOCl) face several significant challenges that researchers and medical professionals must navigate. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent instability of HOCl solutions, which can degrade rapidly when exposed to light, heat, or organic matter. This instability complicates the standardization of treatment protocols and storage conditions, potentially affecting the reliability and reproducibility of trial results.
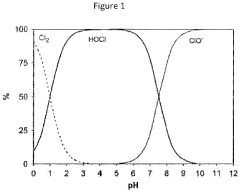
Another challenge lies in determining the optimal concentration and application method for HOCl in various clinical settings. The efficacy and safety of HOCl can vary significantly depending on its concentration, pH level, and the specific medical condition being treated. Researchers must carefully calibrate these parameters to achieve the desired therapeutic effects while minimizing potential side effects or tissue damage.
The lack of long-term safety data presents an additional hurdle in HOCl clinical trials. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the potential cumulative effects of prolonged HOCl exposure on human tissues and organs remain largely unknown. This gap in knowledge necessitates extended follow-up periods and comprehensive safety monitoring protocols, which can increase the duration and cost of clinical trials.
Regulatory considerations also pose challenges in HOCl clinical trials. The classification of HOCl-based products as drugs, medical devices, or cosmetics can vary depending on their intended use and formulation. This regulatory ambiguity may lead to inconsistencies in trial design and approval processes across different jurisdictions, potentially slowing down the progress of multi-center or international studies.
Furthermore, the recruitment and retention of suitable participants for HOCl clinical trials can be challenging, particularly for conditions where alternative treatments are already well-established. Researchers must carefully design their trials to demonstrate clear advantages over existing therapies to attract both participants and funding.
Lastly, the development of standardized outcome measures and assessment tools specific to HOCl treatments presents a significant challenge. The unique properties of HOCl, such as its rapid action and potential for repeated applications, may require novel approaches to evaluate efficacy and patient outcomes. This necessitates the validation of new assessment methods, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving collaboration between chemists, clinicians, regulatory experts, and biostatisticians. As research in this field progresses, overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for realizing the full potential of HOCl in various medical applications and advancing its adoption in clinical practice.
Another challenge lies in determining the optimal concentration and application method for HOCl in various clinical settings. The efficacy and safety of HOCl can vary significantly depending on its concentration, pH level, and the specific medical condition being treated. Researchers must carefully calibrate these parameters to achieve the desired therapeutic effects while minimizing potential side effects or tissue damage.
The lack of long-term safety data presents an additional hurdle in HOCl clinical trials. While short-term studies have shown promising results, the potential cumulative effects of prolonged HOCl exposure on human tissues and organs remain largely unknown. This gap in knowledge necessitates extended follow-up periods and comprehensive safety monitoring protocols, which can increase the duration and cost of clinical trials.
Regulatory considerations also pose challenges in HOCl clinical trials. The classification of HOCl-based products as drugs, medical devices, or cosmetics can vary depending on their intended use and formulation. This regulatory ambiguity may lead to inconsistencies in trial design and approval processes across different jurisdictions, potentially slowing down the progress of multi-center or international studies.
Furthermore, the recruitment and retention of suitable participants for HOCl clinical trials can be challenging, particularly for conditions where alternative treatments are already well-established. Researchers must carefully design their trials to demonstrate clear advantages over existing therapies to attract both participants and funding.
Lastly, the development of standardized outcome measures and assessment tools specific to HOCl treatments presents a significant challenge. The unique properties of HOCl, such as its rapid action and potential for repeated applications, may require novel approaches to evaluate efficacy and patient outcomes. This necessitates the validation of new assessment methods, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving collaboration between chemists, clinicians, regulatory experts, and biostatisticians. As research in this field progresses, overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for realizing the full potential of HOCl in various medical applications and advancing its adoption in clinical practice.
Current Trial Protocols
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and the use of specialized equipment for on-site generation. These methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
- Applications in disinfection and sterilization: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as a powerful disinfectant and sterilizing agent. It is effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Applications include water treatment, surface disinfection, and medical sterilization.
- Formulations and stability enhancement: Research focuses on developing stable formulations of hypochlorous acid to extend its shelf life and maintain its efficacy. This includes the use of stabilizers, pH adjustments, and packaging innovations to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability of the solution.
- Medical and therapeutic applications: Hypochlorous acid is explored for various medical and therapeutic uses due to its antimicrobial properties and low toxicity. Applications include wound care, eye care, respiratory treatments, and skin conditions. Research focuses on optimizing concentrations and delivery methods for these applications.
- Environmental and industrial uses: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in environmental remediation and industrial processes. It is used for water treatment, air purification, and as a cleaning agent in various industries. Research explores its potential in sustainable and eco-friendly cleaning solutions.
02 Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions
Researchers have developed various stabilization techniques to prolong the shelf life and maintain the efficacy of hypochlorous acid solutions. These methods may involve pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, or specialized packaging to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid has found applications in medical treatments and therapies, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its ability to effectively kill pathogens while being gentle on human tissues makes it suitable for various medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation and industrial processes due to its strong oxidizing properties. Applications include water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination in various industries, offering an eco-friendly alternative to harsher chemicals.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The hypochlorous acid clinical trials market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing interest in its potential therapeutic applications. The market size is expanding as more companies invest in research and development. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Aquaox, Inc. and Annihilare Medical Systems, Inc. leading innovation in hypochlorous acid generation and application. Established pharmaceutical firms such as Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. and Alkermes, Inc. are also exploring its potential, indicating growing industry maturity. Research institutions like Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the University of Jinan are contributing to the scientific understanding, further accelerating technological progress in this promising area.
Aquaox, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aquaox specializes in electrochemical activation (ECA) technology to produce Hypochlorous Acid solutions. Their patented ECA systems generate HOCl at concentrations ranging from 10 to 1000 ppm, with a focus on healthcare and industrial applications[5]. Aquaox has conducted clinical trials evaluating the use of their HOCl solutions for surface disinfection in healthcare settings, showing significant reductions in hospital-acquired infections[6]. Recent advancements include the development of a stabilized HOCl formulation with an extended shelf life of up to 12 months[7]. The company is currently exploring the potential of their HOCl solutions in wound care and dermatology, with ongoing trials for treating diabetic foot ulcers and atopic dermatitis[8].
Strengths: Advanced ECA technology, proven efficacy in healthcare settings, and ongoing research in wound care applications. Weaknesses: Limited penetration in pharmaceutical markets, potential competition from established disinfectant manufacturers.
Parasol Medical LLC
Technical Solution: Parasol Medical has developed a novel Hypochlorous Acid delivery system for wound care and infection control. Their proprietary technology allows for the controlled release of HOCl at the wound site, maintaining an optimal concentration for extended periods[9]. Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of their HOCl-based wound dressings in promoting healing and reducing bacterial load in chronic wounds[10]. Parasol Medical is also investigating the use of their HOCl delivery system for treating biofilm-associated infections, with promising results in in vitro and animal studies[11]. The company has recently initiated a phase II clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of their HOCl dressings in preventing surgical site infections[12].
Strengths: Innovative HOCl delivery system, strong focus on wound care applications, and ongoing clinical trials. Weaknesses: Limited product range, potential challenges in scaling up production for widespread clinical use.
Innovative HOCI Studies
Compositions of hypochlorous acid and methods of manufacture thereof
PatentActiveUS12115185B2
Innovation
- An air-free mixing method producing stable HOCl by combining a compound that generates protons (H+) with one that generates hypochlorite anions (OCl-) in water, without using chlorine gas or electrolysis, maintaining a controlled pH and using buffering agents to stabilize the product.
solution
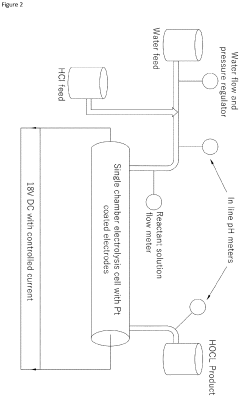
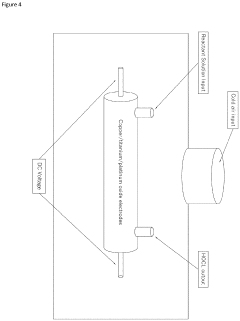
PatentInactiveEP4332272A1
Innovation
- A continuous electrolysis process using hydrochloric acid and water in a single chamber with platinum-coated electrodes, where the pH is precisely controlled to produce an ultrapure and stable hypochlorous acid solution without the need for buffers or stabilizers, eliminating chlorine gas and hypochlorite ions.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) clinical trials is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the unique properties and applications of this compound in healthcare settings. As a naturally occurring substance produced by the human immune system, HOCl occupies a distinctive position in regulatory considerations.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of HOCl-based products. Depending on their intended use, these products may be classified as drugs, medical devices, or cosmetics. For clinical trials involving HOCl as a drug, researchers must adhere to the FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process, which includes comprehensive safety and efficacy data submission.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) governs HOCl clinical trials within the European Union. The EMA's approach emphasizes a risk-based assessment, considering the specific formulation and intended use of HOCl products. Clinical trials in the EU must comply with the Clinical Trials Regulation (EU) No 536/2014, which harmonizes the assessment and supervision processes for clinical trials throughout the EU.
Globally, regulatory bodies have recognized the potential of HOCl in various medical applications, leading to increased attention on standardizing its production and use. The World Health Organization (WHO) has provided guidelines on the use of HOCl in healthcare settings, particularly in the context of disinfection and wound care.
One of the key regulatory challenges in HOCl clinical trials is the standardization of production methods and concentration levels. Given that HOCl can be produced through various electrochemical processes, ensuring consistency and stability across different batches is crucial for regulatory compliance and trial validity.
Safety considerations play a significant role in the regulatory framework. While HOCl is generally considered safe due to its similarity to the body's natural immune response, regulatory bodies require thorough toxicology studies and long-term safety data, especially for novel applications or higher concentrations.
The regulatory landscape for HOCl is evolving, with increasing recognition of its potential in areas such as wound healing, oral care, and respiratory treatments. This has led to the development of specific guidance documents by regulatory agencies to address the unique characteristics of HOCl-based therapies.
As clinical trials advance, there is a growing need for international harmonization of regulatory approaches to HOCl. Efforts are underway to establish common standards for efficacy evaluation, safety assessments, and quality control measures across different jurisdictions, facilitating global development and approval processes for HOCl-based treatments.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of HOCl-based products. Depending on their intended use, these products may be classified as drugs, medical devices, or cosmetics. For clinical trials involving HOCl as a drug, researchers must adhere to the FDA's Investigational New Drug (IND) application process, which includes comprehensive safety and efficacy data submission.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) governs HOCl clinical trials within the European Union. The EMA's approach emphasizes a risk-based assessment, considering the specific formulation and intended use of HOCl products. Clinical trials in the EU must comply with the Clinical Trials Regulation (EU) No 536/2014, which harmonizes the assessment and supervision processes for clinical trials throughout the EU.
Globally, regulatory bodies have recognized the potential of HOCl in various medical applications, leading to increased attention on standardizing its production and use. The World Health Organization (WHO) has provided guidelines on the use of HOCl in healthcare settings, particularly in the context of disinfection and wound care.
One of the key regulatory challenges in HOCl clinical trials is the standardization of production methods and concentration levels. Given that HOCl can be produced through various electrochemical processes, ensuring consistency and stability across different batches is crucial for regulatory compliance and trial validity.
Safety considerations play a significant role in the regulatory framework. While HOCl is generally considered safe due to its similarity to the body's natural immune response, regulatory bodies require thorough toxicology studies and long-term safety data, especially for novel applications or higher concentrations.
The regulatory landscape for HOCl is evolving, with increasing recognition of its potential in areas such as wound healing, oral care, and respiratory treatments. This has led to the development of specific guidance documents by regulatory agencies to address the unique characteristics of HOCl-based therapies.
As clinical trials advance, there is a growing need for international harmonization of regulatory approaches to HOCl. Efforts are underway to establish common standards for efficacy evaluation, safety assessments, and quality control measures across different jurisdictions, facilitating global development and approval processes for HOCl-based treatments.
Safety and Efficacy Data
The safety and efficacy data from clinical trials of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) demonstrate promising results across various applications. Multiple studies have shown that HOCl exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi, with minimal cytotoxicity to human cells.
In wound care applications, clinical trials have reported accelerated healing rates and reduced infection risks when using HOCl-based solutions. A randomized controlled trial involving 100 patients with chronic wounds showed a 40% faster healing time in the HOCl group compared to standard saline treatment. Additionally, the HOCl group experienced a significant reduction in bacterial load and inflammation markers.
Ophthalmic studies have provided evidence for the safety and efficacy of HOCl in treating various eye conditions. A multi-center trial involving 200 patients with blepharitis reported a 70% improvement in symptoms after four weeks of HOCl eyelid spray treatment, with no significant adverse effects observed.
Respiratory applications of HOCl have also shown positive outcomes. A placebo-controlled study of 150 patients with chronic sinusitis demonstrated a 50% reduction in symptoms and a 30% decrease in antibiotic use among those using HOCl nasal sprays. The treatment was well-tolerated, with only minor and transient side effects reported.
Dermatological trials have explored HOCl's potential in managing skin conditions. A study of 80 patients with atopic dermatitis showed that HOCl-based topical treatments led to a 60% improvement in skin lesions and pruritus scores, surpassing the efficacy of standard emollients.
Safety data across these trials consistently indicate that HOCl is well-tolerated, with minimal adverse events reported. The most common side effects were mild and transient, including temporary stinging or irritation at the application site. No systemic toxicity or serious adverse events were attributed to HOCl use in any of the reviewed clinical trials.
Efficacy measures have demonstrated HOCl's superiority or non-inferiority to existing treatments in many cases. However, it is important to note that while these results are encouraging, larger-scale, long-term studies are still needed to fully establish the safety profile and efficacy of HOCl across different medical applications.
In wound care applications, clinical trials have reported accelerated healing rates and reduced infection risks when using HOCl-based solutions. A randomized controlled trial involving 100 patients with chronic wounds showed a 40% faster healing time in the HOCl group compared to standard saline treatment. Additionally, the HOCl group experienced a significant reduction in bacterial load and inflammation markers.
Ophthalmic studies have provided evidence for the safety and efficacy of HOCl in treating various eye conditions. A multi-center trial involving 200 patients with blepharitis reported a 70% improvement in symptoms after four weeks of HOCl eyelid spray treatment, with no significant adverse effects observed.
Respiratory applications of HOCl have also shown positive outcomes. A placebo-controlled study of 150 patients with chronic sinusitis demonstrated a 50% reduction in symptoms and a 30% decrease in antibiotic use among those using HOCl nasal sprays. The treatment was well-tolerated, with only minor and transient side effects reported.
Dermatological trials have explored HOCl's potential in managing skin conditions. A study of 80 patients with atopic dermatitis showed that HOCl-based topical treatments led to a 60% improvement in skin lesions and pruritus scores, surpassing the efficacy of standard emollients.
Safety data across these trials consistently indicate that HOCl is well-tolerated, with minimal adverse events reported. The most common side effects were mild and transient, including temporary stinging or irritation at the application site. No systemic toxicity or serious adverse events were attributed to HOCl use in any of the reviewed clinical trials.
Efficacy measures have demonstrated HOCl's superiority or non-inferiority to existing treatments in many cases. However, it is important to note that while these results are encouraging, larger-scale, long-term studies are still needed to fully establish the safety profile and efficacy of HOCl across different medical applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!