Hypochlorous Acid: Advanced Studies in Preserving Microbial Ecosystems
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCI Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a pivotal subject in the field of microbial ecosystem preservation, marking a significant advancement in our understanding of biological interactions and environmental stewardship. This naturally occurring molecule, produced by the human immune system and found in various ecosystems, has garnered increasing attention due to its unique properties and potential applications.
The evolution of HOCl research spans several decades, with initial discoveries dating back to the early 20th century. However, it is only in recent years that its full potential in preserving microbial ecosystems has been recognized. This renewed interest stems from a growing awareness of the delicate balance within microbial communities and their crucial role in environmental and human health.
The primary objective of advanced studies in HOCl and microbial ecosystem preservation is to elucidate the mechanisms by which this compound interacts with diverse microorganisms. Researchers aim to understand how HOCl can selectively target harmful pathogens while maintaining the integrity of beneficial microbial populations. This selective action is particularly intriguing, as it offers the possibility of developing more nuanced approaches to ecosystem management.
Another key goal is to explore the potential of HOCl as a sustainable alternative to traditional chemical preservatives and antimicrobial agents. As concerns about antibiotic resistance and environmental toxicity continue to grow, HOCl presents a promising solution due to its natural origin and biodegradability. Studies are focused on optimizing its production, stability, and application methods to ensure its efficacy across various environmental conditions.
Furthermore, researchers are investigating the broader ecological implications of HOCl use. This includes assessing its impact on soil health, water quality, and the overall biodiversity of microbial ecosystems. The aim is to develop comprehensive strategies that leverage HOCl's properties to maintain ecological balance without disrupting essential microbial functions.
As technology advances, there is also a push to integrate HOCl research with cutting-edge fields such as genomics and bioinformatics. This interdisciplinary approach seeks to map the intricate relationships between HOCl, microorganisms, and their environments at a molecular level. By doing so, scientists hope to unlock new insights into microbial ecology and develop more targeted preservation techniques.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of advanced studies in HOCl for preserving microbial ecosystems reflect a paradigm shift in our approach to environmental management and health. By delving deeper into the properties and applications of this remarkable compound, researchers are paving the way for innovative solutions that promise to revolutionize our understanding and preservation of complex microbial worlds.
The evolution of HOCl research spans several decades, with initial discoveries dating back to the early 20th century. However, it is only in recent years that its full potential in preserving microbial ecosystems has been recognized. This renewed interest stems from a growing awareness of the delicate balance within microbial communities and their crucial role in environmental and human health.
The primary objective of advanced studies in HOCl and microbial ecosystem preservation is to elucidate the mechanisms by which this compound interacts with diverse microorganisms. Researchers aim to understand how HOCl can selectively target harmful pathogens while maintaining the integrity of beneficial microbial populations. This selective action is particularly intriguing, as it offers the possibility of developing more nuanced approaches to ecosystem management.
Another key goal is to explore the potential of HOCl as a sustainable alternative to traditional chemical preservatives and antimicrobial agents. As concerns about antibiotic resistance and environmental toxicity continue to grow, HOCl presents a promising solution due to its natural origin and biodegradability. Studies are focused on optimizing its production, stability, and application methods to ensure its efficacy across various environmental conditions.
Furthermore, researchers are investigating the broader ecological implications of HOCl use. This includes assessing its impact on soil health, water quality, and the overall biodiversity of microbial ecosystems. The aim is to develop comprehensive strategies that leverage HOCl's properties to maintain ecological balance without disrupting essential microbial functions.
As technology advances, there is also a push to integrate HOCl research with cutting-edge fields such as genomics and bioinformatics. This interdisciplinary approach seeks to map the intricate relationships between HOCl, microorganisms, and their environments at a molecular level. By doing so, scientists hope to unlock new insights into microbial ecology and develop more targeted preservation techniques.
In conclusion, the background and objectives of advanced studies in HOCl for preserving microbial ecosystems reflect a paradigm shift in our approach to environmental management and health. By delving deeper into the properties and applications of this remarkable compound, researchers are paving the way for innovative solutions that promise to revolutionize our understanding and preservation of complex microbial worlds.
Market Analysis for HOCI Applications
The market for Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) applications has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of its effectiveness as a disinfectant and its potential in preserving microbial ecosystems. The global HOCl market is projected to expand substantially, with key growth sectors including healthcare, agriculture, water treatment, and food processing.
In the healthcare sector, HOCl has gained traction as a powerful yet safe disinfectant for wound care, dental hygiene, and surface sanitization. Hospitals and clinics are increasingly adopting HOCl-based solutions due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties and low toxicity profile. The ongoing global focus on infection control and prevention is expected to further boost demand in this sector.
The agriculture industry represents another significant market for HOCl applications. Farmers are turning to HOCl as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional pesticides and disinfectants. Its use in crop protection, seed treatment, and post-harvest preservation aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable farming practices. The ability of HOCl to maintain beneficial microbial ecosystems while controlling harmful pathogens makes it particularly attractive in this sector.
Water treatment is emerging as a promising market for HOCl applications. Municipal water suppliers and industrial facilities are exploring HOCl as an alternative to chlorine-based disinfectants, due to its effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms and reduced formation of harmful by-products. The increasing global concern over water quality and safety is expected to drive further adoption in this sector.
In the food processing industry, HOCl is gaining popularity as a sanitizer for equipment, surfaces, and food products. Its ability to effectively eliminate pathogens without leaving harmful residues aligns with stringent food safety regulations and consumer demand for chemical-free food processing methods. The market in this sector is anticipated to grow as food manufacturers seek safer and more sustainable sanitation solutions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the HOCl market, owing to stringent regulations on disinfectants and growing adoption in healthcare settings. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by increasing industrialization, rising healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of food safety.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the HOCl market. These include the need for improved stability of HOCl solutions, development of more efficient production methods, and education of end-users about its benefits compared to traditional disinfectants. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of HOCl applications in preserving microbial ecosystems and beyond.
In the healthcare sector, HOCl has gained traction as a powerful yet safe disinfectant for wound care, dental hygiene, and surface sanitization. Hospitals and clinics are increasingly adopting HOCl-based solutions due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties and low toxicity profile. The ongoing global focus on infection control and prevention is expected to further boost demand in this sector.
The agriculture industry represents another significant market for HOCl applications. Farmers are turning to HOCl as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional pesticides and disinfectants. Its use in crop protection, seed treatment, and post-harvest preservation aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable farming practices. The ability of HOCl to maintain beneficial microbial ecosystems while controlling harmful pathogens makes it particularly attractive in this sector.
Water treatment is emerging as a promising market for HOCl applications. Municipal water suppliers and industrial facilities are exploring HOCl as an alternative to chlorine-based disinfectants, due to its effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms and reduced formation of harmful by-products. The increasing global concern over water quality and safety is expected to drive further adoption in this sector.
In the food processing industry, HOCl is gaining popularity as a sanitizer for equipment, surfaces, and food products. Its ability to effectively eliminate pathogens without leaving harmful residues aligns with stringent food safety regulations and consumer demand for chemical-free food processing methods. The market in this sector is anticipated to grow as food manufacturers seek safer and more sustainable sanitation solutions.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the HOCl market, owing to stringent regulations on disinfectants and growing adoption in healthcare settings. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by increasing industrialization, rising healthcare expenditure, and growing awareness of food safety.
Despite the positive outlook, challenges remain in the HOCl market. These include the need for improved stability of HOCl solutions, development of more efficient production methods, and education of end-users about its benefits compared to traditional disinfectants. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for realizing the full market potential of HOCl applications in preserving microbial ecosystems and beyond.
HOCI Technology Status and Challenges
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) technology has made significant strides in recent years, particularly in the field of preserving microbial ecosystems. However, the current status of this technology presents both promising advancements and notable challenges.
One of the primary developments in HOCl technology is its increased stability and shelf life. Traditionally, HOCl solutions were known for their rapid degradation, limiting their practical applications. Recent innovations in production methods and stabilization techniques have extended the usable lifespan of HOCl solutions, making them more viable for commercial and industrial use.
The efficacy of HOCl in microbial control has been well-established, with numerous studies demonstrating its broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties. Its ability to effectively eliminate harmful pathogens while maintaining a balance in beneficial microbial populations has positioned HOCl as a potential game-changer in various fields, including agriculture, food safety, and healthcare.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in HOCl technology. One significant hurdle is the standardization of production methods. The varying quality and concentration of HOCl solutions produced by different manufacturers can lead to inconsistent results in applications, hindering widespread adoption.
Another challenge lies in the scalability of HOCl production. While small-scale generation of HOCl is relatively straightforward, scaling up to meet industrial demands while maintaining quality and stability remains a complex issue. This challenge is particularly evident in sectors requiring large volumes of HOCl, such as water treatment and large-scale agricultural applications.
The interaction of HOCl with different materials and environments presents another area of concern. Its corrosive nature can potentially damage certain surfaces or equipment, necessitating careful consideration in its application and storage. Additionally, the impact of HOCl on diverse microbial ecosystems in various environmental conditions requires further study to ensure its safe and effective use.
Regulatory challenges also play a significant role in the current status of HOCl technology. The classification and approval processes for HOCl-based products vary across different regions and applications, creating a complex landscape for manufacturers and users alike. This regulatory uncertainty can impede innovation and market penetration.
Lastly, the perception and understanding of HOCl technology among potential users and the general public remain limited. Despite its effectiveness and relative safety, misconceptions about its nature and applications persist, potentially slowing its adoption in various sectors.
In conclusion, while HOCl technology shows great promise in preserving microbial ecosystems, it faces a range of challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. Overcoming these hurdles will require continued research, technological innovation, and collaborative efforts across various disciplines and industries.
One of the primary developments in HOCl technology is its increased stability and shelf life. Traditionally, HOCl solutions were known for their rapid degradation, limiting their practical applications. Recent innovations in production methods and stabilization techniques have extended the usable lifespan of HOCl solutions, making them more viable for commercial and industrial use.
The efficacy of HOCl in microbial control has been well-established, with numerous studies demonstrating its broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties. Its ability to effectively eliminate harmful pathogens while maintaining a balance in beneficial microbial populations has positioned HOCl as a potential game-changer in various fields, including agriculture, food safety, and healthcare.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in HOCl technology. One significant hurdle is the standardization of production methods. The varying quality and concentration of HOCl solutions produced by different manufacturers can lead to inconsistent results in applications, hindering widespread adoption.
Another challenge lies in the scalability of HOCl production. While small-scale generation of HOCl is relatively straightforward, scaling up to meet industrial demands while maintaining quality and stability remains a complex issue. This challenge is particularly evident in sectors requiring large volumes of HOCl, such as water treatment and large-scale agricultural applications.
The interaction of HOCl with different materials and environments presents another area of concern. Its corrosive nature can potentially damage certain surfaces or equipment, necessitating careful consideration in its application and storage. Additionally, the impact of HOCl on diverse microbial ecosystems in various environmental conditions requires further study to ensure its safe and effective use.
Regulatory challenges also play a significant role in the current status of HOCl technology. The classification and approval processes for HOCl-based products vary across different regions and applications, creating a complex landscape for manufacturers and users alike. This regulatory uncertainty can impede innovation and market penetration.
Lastly, the perception and understanding of HOCl technology among potential users and the general public remain limited. Despite its effectiveness and relative safety, misconceptions about its nature and applications persist, potentially slowing its adoption in various sectors.
In conclusion, while HOCl technology shows great promise in preserving microbial ecosystems, it faces a range of challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. Overcoming these hurdles will require continued research, technological innovation, and collaborative efforts across various disciplines and industries.
Current HOCI Solutions
01 Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in various antimicrobial applications due to its effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms. It can be used in disinfectants, sanitizers, and sterilization processes to control microbial growth in different environments, including healthcare settings, food processing facilities, and water treatment systems.- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in various antimicrobial applications due to its effectiveness against a wide range of microorganisms. It can be used in disinfectants, sanitizers, and sterilization processes to control microbial growth in different environments, including healthcare settings, food processing facilities, and water treatment systems.
- Hypochlorous acid in wound care and skin treatments: Hypochlorous acid is employed in wound care and skin treatments due to its antimicrobial properties and low toxicity to human cells. It can be formulated into solutions, gels, or sprays for treating various skin conditions, promoting wound healing, and preventing infections without causing significant irritation.
- Hypochlorous acid generation and stabilization methods: Various methods are developed for generating and stabilizing hypochlorous acid solutions to maintain their efficacy over time. These may include electrochemical processes, chemical reactions, or specialized formulations that enhance the stability and shelf-life of hypochlorous acid products for use in different applications.
- Environmental applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is used in environmental applications such as water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination. Its ability to effectively neutralize various pollutants and pathogens makes it suitable for maintaining clean and safe environments in both industrial and residential settings.
- Hypochlorous acid in agriculture and food safety: Hypochlorous acid finds applications in agriculture and food safety, including crop protection, post-harvest treatments, and food processing. It can be used to control plant pathogens, reduce spoilage microorganisms, and ensure food safety without leaving harmful residues on produce or in the environment.
02 Hypochlorous acid in wound care and skin treatments
Hypochlorous acid is employed in wound care and skin treatments due to its antimicrobial properties and ability to promote healing. It can be formulated into topical solutions, gels, or sprays for treating various skin conditions, including infections, burns, and chronic wounds, while maintaining the natural microbial balance of the skin.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hypochlorous acid generation and stabilization methods
Various methods are developed for generating and stabilizing hypochlorous acid to maintain its effectiveness in microbial control. These techniques may involve electrochemical processes, chemical reactions, or specialized equipment to produce stable hypochlorous acid solutions with consistent concentrations for use in different applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Hypochlorous acid in water treatment and environmental applications
Hypochlorous acid is used in water treatment and environmental applications to control microbial ecosystems in various settings. It can be employed in swimming pools, cooling towers, and industrial water systems to prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms while maintaining overall ecosystem balance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Synergistic effects of hypochlorous acid with other compounds
Research explores the synergistic effects of combining hypochlorous acid with other compounds to enhance its antimicrobial efficacy and broaden its applications in controlling microbial ecosystems. These combinations may include natural extracts, other disinfectants, or specific chemical agents to create more effective and versatile solutions for microbial management.Expand Specific Solutions
Key HOCI Industry Players
The field of hypochlorous acid and microbial ecosystem preservation is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for hypochlorous acid is expanding, driven by its applications in water treatment, healthcare, and agriculture. Companies like Industrie De Nora SpA and Ecolab USA, Inc. are leading players, leveraging their expertise in electrochemical and cleaning technologies. Research institutions such as the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics and Colorado State University are contributing to the technological maturity through advanced studies. Emerging players like Annihilare Medical Systems and Wonder Spray LLC are focusing on innovative applications, particularly in disinfection and medical systems, indicating a diversifying market with potential for further growth and technological refinement.
Aquaox, Inc.
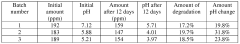
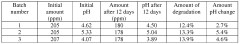
Technical Solution: Aquaox has developed a proprietary Electrochemical Activation (ECA) technology for producing Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) solutions. Their process involves electrolysis of salt water to generate HOCl with precise control over pH and Free Available Chlorine (FAC) levels. The company's ECA systems can produce HOCl solutions with concentrations ranging from 50 to 500 ppm, maintaining a stable pH between 6.5 and 7.5 [1]. This technology allows for on-site generation of HOCl, ensuring freshness and potency. Aquaox's HOCl solutions have demonstrated efficacy in preserving microbial ecosystems by selectively targeting harmful pathogens while maintaining beneficial microorganisms [2]. The company has also developed specialized application methods for various industries, including agriculture, healthcare, and food processing.
Strengths: On-site generation ensures fresh, potent HOCl; precise control over pH and FAC levels; versatile applications across industries. Weaknesses: Requires specialized equipment for production; may have higher initial costs compared to traditional disinfectants.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: Annihilare Medical Systems has pioneered an advanced HOCl production system that focuses on maintaining the stability and efficacy of the solution for extended periods. Their proprietary process involves a multi-stage filtration and purification system, coupled with a controlled electrolysis technique that produces HOCl with a consistent pH range of 6.8 to 7.2 [3]. The company has developed a unique packaging and storage solution that significantly extends the shelf life of HOCl, maintaining its antimicrobial properties for up to 18 months [4]. Annihilare's research has shown that their HOCl formulation can effectively preserve microbial ecosystems by selectively eliminating pathogenic microorganisms while leaving beneficial bacteria largely unaffected. This selective action is attributed to the solution's carefully controlled oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) [5].
Strengths: Extended shelf life of HOCl solutions; selective antimicrobial action preserving beneficial microbes; consistent pH range suitable for various applications. Weaknesses: May require specialized storage conditions; potentially higher production costs due to advanced purification processes.
HOCI Core Innovations
Mixing device
PatentWO2013121295A2
Innovation
- A mixing device that produces fluidic vortices within a chamber with strategically placed apertures to stabilize hypochlorous acid by controlling proton concentration and pH through the use of buffering agents like acetic acid, allowing for its production and storage for extended periods without the need for onsite generation.
Compositions of hypochlorous acid and methods of manufacture thereof
PatentActiveUS12115185B2
Innovation
- An air-free mixing method producing stable HOCl by combining a compound that generates protons (H+) with one that generates hypochlorite anions (OCl-) in water, without using chlorine gas or electrolysis, maintaining a controlled pH and using buffering agents to stabilize the product.
HOCI Safety and Regulations
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential in preserving microbial ecosystems. As with any chemical compound used in various applications, safety considerations and regulatory compliance are paramount. The safety profile of HOCl is generally favorable, owing to its natural occurrence in the human body as part of the immune system's defense mechanism against pathogens.
In terms of safety, HOCl is considered non-toxic when used at appropriate concentrations. It does not produce harmful byproducts and breaks down into simple salt and water. This characteristic makes it an environmentally friendly option for disinfection and preservation purposes. However, it is essential to note that while HOCl is safe for human use, it can be irritating to eyes and skin in high concentrations. Therefore, proper handling and protective equipment are recommended when working with concentrated solutions.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have recognized the safety and efficacy of HOCl in various applications. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has approved HOCl as a disinfectant for use against SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared HOCl-based products for wound care and eye care applications.
In the European Union, HOCl is regulated under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR) and is approved for use as a disinfectant. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified HOCl as a low-risk substance, further supporting its safety profile. In Japan, HOCl is recognized as a food additive and is permitted for use in food processing and preservation.
Despite its generally favorable regulatory status, it is crucial to adhere to specific guidelines and regulations when using HOCl in different applications. Concentration levels, exposure times, and application methods may vary depending on the intended use and regulatory jurisdiction. Manufacturers and users of HOCl-based products must ensure compliance with local and international standards, including proper labeling, storage, and disposal practices.
As research in HOCl applications for preserving microbial ecosystems advances, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve to address new findings and potential uses. Ongoing studies focusing on the long-term effects of HOCl on beneficial microorganisms and ecosystem balance will inform future regulatory decisions and safety guidelines. This dynamic regulatory landscape underscores the importance of staying informed about the latest developments in HOCl research and regulatory updates to ensure continued safe and effective use of this promising compound.
In terms of safety, HOCl is considered non-toxic when used at appropriate concentrations. It does not produce harmful byproducts and breaks down into simple salt and water. This characteristic makes it an environmentally friendly option for disinfection and preservation purposes. However, it is essential to note that while HOCl is safe for human use, it can be irritating to eyes and skin in high concentrations. Therefore, proper handling and protective equipment are recommended when working with concentrated solutions.
Regulatory bodies worldwide have recognized the safety and efficacy of HOCl in various applications. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has approved HOCl as a disinfectant for use against SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared HOCl-based products for wound care and eye care applications.
In the European Union, HOCl is regulated under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR) and is approved for use as a disinfectant. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has classified HOCl as a low-risk substance, further supporting its safety profile. In Japan, HOCl is recognized as a food additive and is permitted for use in food processing and preservation.
Despite its generally favorable regulatory status, it is crucial to adhere to specific guidelines and regulations when using HOCl in different applications. Concentration levels, exposure times, and application methods may vary depending on the intended use and regulatory jurisdiction. Manufacturers and users of HOCl-based products must ensure compliance with local and international standards, including proper labeling, storage, and disposal practices.
As research in HOCl applications for preserving microbial ecosystems advances, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve to address new findings and potential uses. Ongoing studies focusing on the long-term effects of HOCl on beneficial microorganisms and ecosystem balance will inform future regulatory decisions and safety guidelines. This dynamic regulatory landscape underscores the importance of staying informed about the latest developments in HOCl research and regulatory updates to ensure continued safe and effective use of this promising compound.
HOCI Environmental Impact
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential as an environmentally friendly disinfectant and preservative. As research into its applications in preserving microbial ecosystems advances, it is crucial to assess the environmental impact of HOCl use.
HOCl is a naturally occurring compound produced by the human immune system and other organisms as a defense mechanism against pathogens. Its environmental impact is generally considered to be minimal due to its rapid breakdown into harmless components. When HOCl decomposes, it primarily forms water and chloride ions, which are already abundant in nature and do not pose significant environmental risks.
One of the key advantages of HOCl from an environmental perspective is its ability to effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms without leaving behind toxic residues. Unlike many traditional chemical disinfectants, HOCl does not contribute to the formation of harmful byproducts or persistent organic pollutants. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for use in sensitive environments, such as water treatment facilities, food processing plants, and healthcare settings.
The use of HOCl in preserving microbial ecosystems may have positive implications for biodiversity conservation. By selectively targeting harmful microorganisms while preserving beneficial ones, HOCl could help maintain the delicate balance of microbial communities in various ecosystems. This selective action could potentially reduce the need for broad-spectrum antimicrobials, which often have more significant environmental impacts.
However, it is important to note that the widespread use of HOCl may have some indirect environmental consequences. The production and distribution of HOCl solutions require energy and resources, which could contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion if not managed sustainably. Additionally, the increased demand for chlorine-based compounds used in HOCl production may lead to environmental pressures in chlorine extraction and processing industries.
Research into the long-term effects of HOCl on aquatic ecosystems is ongoing. While initial studies suggest minimal impact on fish and other aquatic organisms at typical use concentrations, further investigation is needed to fully understand the potential effects on sensitive species and complex ecosystem dynamics.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of HOCl in preserving microbial ecosystems appears to be relatively low compared to many traditional disinfectants. Its rapid decomposition, lack of toxic residues, and potential for selective antimicrobial action make it an environmentally promising option. However, ongoing research and careful monitoring of its large-scale application are necessary to ensure that any potential negative impacts are identified and mitigated.
HOCl is a naturally occurring compound produced by the human immune system and other organisms as a defense mechanism against pathogens. Its environmental impact is generally considered to be minimal due to its rapid breakdown into harmless components. When HOCl decomposes, it primarily forms water and chloride ions, which are already abundant in nature and do not pose significant environmental risks.
One of the key advantages of HOCl from an environmental perspective is its ability to effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms without leaving behind toxic residues. Unlike many traditional chemical disinfectants, HOCl does not contribute to the formation of harmful byproducts or persistent organic pollutants. This characteristic makes it particularly attractive for use in sensitive environments, such as water treatment facilities, food processing plants, and healthcare settings.
The use of HOCl in preserving microbial ecosystems may have positive implications for biodiversity conservation. By selectively targeting harmful microorganisms while preserving beneficial ones, HOCl could help maintain the delicate balance of microbial communities in various ecosystems. This selective action could potentially reduce the need for broad-spectrum antimicrobials, which often have more significant environmental impacts.
However, it is important to note that the widespread use of HOCl may have some indirect environmental consequences. The production and distribution of HOCl solutions require energy and resources, which could contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion if not managed sustainably. Additionally, the increased demand for chlorine-based compounds used in HOCl production may lead to environmental pressures in chlorine extraction and processing industries.
Research into the long-term effects of HOCl on aquatic ecosystems is ongoing. While initial studies suggest minimal impact on fish and other aquatic organisms at typical use concentrations, further investigation is needed to fully understand the potential effects on sensitive species and complex ecosystem dynamics.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of HOCl in preserving microbial ecosystems appears to be relatively low compared to many traditional disinfectants. Its rapid decomposition, lack of toxic residues, and potential for selective antimicrobial action make it an environmentally promising option. However, ongoing research and careful monitoring of its large-scale application are necessary to ensure that any potential negative impacts are identified and mitigated.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!