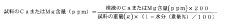How to Maximize Economic Efficiency in Cellulose Acetate Production?
Cellulose Acetate Production Overview and Objectives
Cellulose acetate production has been a cornerstone in the chemical industry for over a century, with applications ranging from textiles to packaging materials. The process involves the acetylation of cellulose, typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, using acetic anhydride in the presence of a catalyst. As global demand for sustainable and biodegradable materials continues to rise, optimizing the economic efficiency of cellulose acetate production has become increasingly crucial.
The primary objective in maximizing economic efficiency in cellulose acetate production is to reduce production costs while maintaining or improving product quality. This involves several key areas of focus, including raw material sourcing, process optimization, energy efficiency, and waste reduction. By addressing these aspects comprehensively, manufacturers can enhance their competitive edge in the market and improve overall profitability.
One of the most significant challenges in cellulose acetate production is the cost of raw materials, particularly cellulose and acetic anhydride. Developing strategies to secure a stable and cost-effective supply of these materials is essential. This may involve exploring alternative sources of cellulose, such as agricultural waste or fast-growing crops, which could potentially reduce costs and improve sustainability.
Process optimization plays a crucial role in enhancing economic efficiency. This includes improving reaction kinetics, optimizing catalyst performance, and refining separation and purification techniques. Advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring can help maintain optimal operating conditions, reducing variability and improving yield. Additionally, implementing continuous flow processes instead of batch operations can lead to significant improvements in productivity and resource utilization.
Energy efficiency is another critical factor in maximizing economic efficiency. Cellulose acetate production is energy-intensive, particularly in the drying and solvent recovery stages. Implementing heat integration strategies, utilizing more efficient equipment, and exploring alternative energy sources can substantially reduce energy costs and environmental impact.
Waste reduction and byproduct valorization present opportunities for improving economic efficiency. Developing methods to recover and reuse solvents, optimizing filtration processes to minimize product loss, and finding valuable applications for byproducts can turn waste streams into additional revenue sources.
As the industry evolves, emerging technologies such as enzymatic acetylation and novel catalysts offer promising avenues for enhancing efficiency. These innovations have the potential to reduce reaction times, improve selectivity, and decrease the environmental footprint of cellulose acetate production.
In conclusion, maximizing economic efficiency in cellulose acetate production requires a multifaceted approach that addresses raw material sourcing, process optimization, energy efficiency, and waste reduction. By focusing on these key areas and embracing innovative technologies, manufacturers can improve their competitive position and ensure the long-term viability of cellulose acetate production in an increasingly sustainability-conscious market.
Market Analysis for Cellulose Acetate Products
The cellulose acetate market has shown steady growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The global cellulose acetate market size was valued at approximately $5.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $7.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising consumption of cellulose acetate in textile fibers, cigarette filters, and packaging applications.
The textile industry remains the largest consumer of cellulose acetate, accounting for over 40% of the market share. Cellulose acetate fibers are widely used in apparel, home furnishings, and industrial fabrics due to their softness, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties. The growing textile industry, particularly in emerging economies like China and India, is expected to drive the demand for cellulose acetate in the coming years.
The cigarette filter segment is another significant market for cellulose acetate, representing approximately 30% of the total market share. Despite increasing regulations on tobacco products, the demand for cellulose acetate tow in cigarette filters remains stable, supported by population growth and smoking habits in developing countries.
In the packaging industry, cellulose acetate films are gaining popularity as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastic packaging. The biodegradable nature of cellulose acetate aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable packaging solutions. This trend is expected to create new opportunities for cellulose acetate manufacturers in the food and beverage, personal care, and pharmaceutical packaging sectors.
Geographically, Asia Pacific dominates the cellulose acetate market, accounting for over 45% of the global market share. The region's strong presence in textile manufacturing, coupled with the growing cigarette production in countries like China and Indonesia, contributes to its market leadership. North America and Europe follow, with established markets in cigarette filters and high-end textile applications.
The market landscape is characterized by the presence of several key players, including Eastman Chemical Company, Solvay, Celanese Corporation, and Daicel Corporation. These companies are focusing on product innovation, capacity expansion, and strategic partnerships to maintain their market positions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
However, the cellulose acetate market faces challenges from increasing environmental concerns and the availability of alternative materials. The growing awareness of plastic pollution has led to scrutiny of cellulose acetate's biodegradability, particularly in cigarette filters. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to improve the environmental profile of cellulose acetate products and explore new applications to diversify their market presence.
Current Challenges in Cellulose Acetate Manufacturing
The cellulose acetate manufacturing industry faces several significant challenges that impact its economic efficiency. One of the primary issues is the high cost of raw materials, particularly cellulose and acetic anhydride. The fluctuating prices of these inputs create uncertainty in production costs and can significantly affect profit margins.
Energy consumption is another major concern in cellulose acetate production. The process is energy-intensive, requiring substantial amounts of heat and electricity for various stages such as acetylation, hydrolysis, and drying. As energy prices continue to rise globally, manufacturers are under increasing pressure to optimize their energy usage without compromising product quality.
Environmental regulations pose a growing challenge for the industry. Stringent emission controls and waste management requirements necessitate substantial investments in pollution control technologies and waste treatment facilities. Compliance with these regulations often leads to increased operational costs and can impact the overall economic efficiency of production processes.
The complexity of the manufacturing process itself presents challenges in terms of efficiency and yield optimization. Achieving consistent product quality while maximizing throughput requires precise control of reaction conditions, which can be difficult to maintain at industrial scales. Variations in process parameters can lead to product defects, increased waste, and reduced overall efficiency.
Water management is another critical issue in cellulose acetate production. The process requires significant amounts of water for washing and purification steps. Efficient water use and treatment are essential not only for environmental compliance but also for reducing operational costs. However, implementing advanced water recycling and treatment systems often requires substantial capital investment.
Labor costs and skilled workforce availability also impact the economic efficiency of cellulose acetate manufacturing. The process requires specialized knowledge and expertise, and attracting and retaining skilled personnel can be challenging and costly, particularly in regions with competitive labor markets.
Technological obsolescence is an ongoing concern for manufacturers. As new, more efficient production methods and equipment become available, companies face the dilemma of whether to invest in upgrades or continue with existing infrastructure. This decision-making process is critical for maintaining competitiveness but can strain financial resources.
Finally, market volatility and changing consumer preferences present challenges in demand forecasting and inventory management. Fluctuations in demand for cellulose acetate products can lead to overproduction or shortages, both of which negatively impact economic efficiency. Manufacturers must balance production capacity with market demand to optimize their operations and maintain profitability.
Existing Economic Optimization Strategies
01 Improved production processes
Advancements in cellulose acetate production processes have led to increased economic efficiency. These improvements include optimized reaction conditions, enhanced catalysts, and more efficient solvent recovery systems. Such innovations result in higher yields, reduced energy consumption, and lower production costs, making cellulose acetate manufacturing more economically viable.- Improved production processes: Advancements in cellulose acetate production processes have led to increased economic efficiency. These improvements include optimized reaction conditions, enhanced catalysts, and more efficient solvent recovery systems. Such innovations result in higher yields, reduced energy consumption, and lower production costs.
- Novel applications and markets: Expanding the range of applications for cellulose acetate has improved its economic viability. New markets include biodegradable plastics, advanced filtration materials, and high-performance textiles. These diverse applications increase demand and create economies of scale in production.
- Raw material sourcing and pretreatment: Efficient sourcing and pretreatment of cellulose raw materials contribute to the economic efficiency of cellulose acetate production. This includes utilizing agricultural waste, optimizing wood pulp processing, and developing new cellulose sources. Improved pretreatment methods enhance the quality of the raw material and reduce processing costs.
- Recycling and waste reduction: Implementing recycling processes and waste reduction strategies in cellulose acetate production improves economic efficiency. This includes recovering and reusing solvents, utilizing byproducts, and developing closed-loop manufacturing systems. These approaches minimize waste, reduce raw material costs, and improve overall process economics.
- Process integration and automation: Integrating various production steps and implementing automation technologies enhance the economic efficiency of cellulose acetate manufacturing. This includes continuous production systems, advanced process control, and real-time monitoring. Such improvements lead to reduced labor costs, increased productivity, and more consistent product quality.
02 Novel applications and markets
Expanding the range of applications for cellulose acetate has improved its economic efficiency. New markets have been developed in areas such as biodegradable plastics, advanced filtration systems, and high-performance textiles. These diverse applications increase demand and production volume, leading to economies of scale and improved overall economic efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Raw material sourcing and alternatives
Economic efficiency of cellulose acetate production has been enhanced through improved raw material sourcing strategies and the development of alternative feedstocks. This includes utilizing agricultural waste, exploring non-wood cellulose sources, and optimizing supply chain logistics to reduce costs and ensure a stable supply of raw materials.Expand Specific Solutions04 Recycling and circular economy approaches
Implementing recycling processes and adopting circular economy principles have contributed to the economic efficiency of cellulose acetate. These approaches include developing methods for recovering and reprocessing cellulose acetate waste, as well as designing products for easier recycling. Such practices reduce raw material costs and minimize waste disposal expenses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-efficient manufacturing techniques
The development of energy-efficient manufacturing techniques has significantly improved the economic efficiency of cellulose acetate production. These advancements include the use of more efficient reactors, improved heat recovery systems, and the integration of renewable energy sources in the production process. Such innovations reduce energy costs and minimize the environmental impact of cellulose acetate manufacturing.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cellulose Acetate Industry
The cellulose acetate production market is in a mature stage, with a global market size estimated at several billion dollars. The industry is characterized by established players like Daicel Corp., BASF Corp., and Asahi Kasei Corp., who have advanced production technologies and extensive market presence. However, emerging companies from China, such as Nantong Cellulose Fibers Co. Ltd. and Zhuhai Cellulose Fibers Co. Ltd., are gaining traction. The technology maturity is high, with ongoing research by institutions like the Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Beijing University of Chemical Technology focusing on improving production efficiency and sustainability. Companies are increasingly investing in R&D to develop eco-friendly processes and enhance product quality, driving the industry towards more sustainable and economically efficient production methods.
Daicel Corp.
BASF Corp.
Innovative Approaches in Production Efficiency
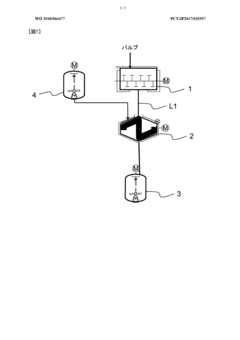
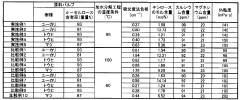
- The method involves cooling a mixture of acetic acid and acetic anhydride to a solid state below the freezing point, mixing it with cellulose, and controlling the reaction temperature to achieve cellulose acetate flakes with a high degree of polymerization, low acetylation, and uniform acetyl substitution, thereby improving filtration efficiency and productivity.
- A method involving crushing wood pulp, pretreating it with acetic acid, reacting with acetic anhydride, and adjusting the degree of acetyl substitution through hydrolysis at specific temperature conditions to produce cellulose acetate with improved hue and moldability, while utilizing low-grade pulp with low α-cellulose content.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The production of cellulose acetate, while economically significant, carries substantial environmental implications that must be carefully considered. The manufacturing process involves the use of various chemicals, including acetic anhydride and sulfuric acid, which can pose risks to the environment if not properly managed. Emissions from the production process, particularly volatile organic compounds (VOCs), contribute to air pollution and may have adverse effects on local air quality.
Water usage is another critical environmental factor in cellulose acetate production. The process requires significant amounts of water for washing and purification steps, potentially straining local water resources. Moreover, the wastewater generated contains dissolved chemicals and organic compounds that necessitate thorough treatment before discharge to prevent water pollution.
Energy consumption in cellulose acetate production is considerable, primarily due to the high temperatures required for acetylation and the subsequent drying processes. This energy demand often translates to increased greenhouse gas emissions, particularly when fossil fuels are the primary energy source. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and exploring renewable energy options can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of production facilities.
Waste management is a crucial aspect of sustainability in cellulose acetate manufacturing. The process generates various by-products and waste materials that require proper disposal or recycling. Developing effective waste reduction strategies and exploring circular economy principles can minimize environmental impact and potentially create additional value streams.
Raw material sourcing is another important consideration. Cellulose, the primary feedstock, is typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters. Ensuring sustainable forestry practices and responsible cotton cultivation is essential to prevent deforestation and maintain biodiversity. Exploring alternative sources of cellulose, such as agricultural residues or recycled materials, could further enhance the sustainability profile of cellulose acetate production.
To maximize economic efficiency while addressing environmental concerns, manufacturers must invest in cleaner production technologies, implement robust environmental management systems, and continuously monitor and improve their environmental performance. This may include adopting advanced pollution control equipment, optimizing process efficiency to reduce resource consumption, and exploring bio-based alternatives for chemical inputs.
Furthermore, life cycle assessment (LCA) studies can provide valuable insights into the overall environmental impact of cellulose acetate products, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. These assessments can guide decision-making processes and help identify areas for improvement in the production chain, ultimately leading to more sustainable and economically viable manufacturing practices.
Raw Material Supply Chain Analysis
The raw material supply chain for cellulose acetate production plays a crucial role in maximizing economic efficiency. The primary raw materials include cellulose, typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, and acetic anhydride. A comprehensive analysis of the supply chain reveals several key factors that impact production costs and overall efficiency.
Cellulose sourcing is a critical aspect of the supply chain. Wood pulp, the most common source, is obtained from various tree species, with softwoods like pine and spruce being preferred due to their higher cellulose content. The global wood pulp market is influenced by factors such as forest management practices, environmental regulations, and competing demands from other industries. Fluctuations in wood pulp prices can significantly affect production costs, necessitating strategic sourcing and long-term supplier relationships.
Cotton linters, an alternative cellulose source, are a byproduct of cotton processing. While generally more expensive than wood pulp, they offer higher purity and can be advantageous for certain high-quality cellulose acetate applications. The availability and pricing of cotton linters are closely tied to the cotton industry, which is subject to agricultural variables and global textile market dynamics.
Acetic anhydride, the other key raw material, is primarily produced from acetic acid. The supply of acetic anhydride is closely linked to the petrochemical industry, as acetic acid is typically derived from methanol or ethylene. Volatility in oil and natural gas prices can therefore impact the cost and availability of acetic anhydride, highlighting the importance of diversified sourcing strategies and potentially exploring bio-based alternatives.
Transportation and logistics play a significant role in the raw material supply chain. The geographical distribution of cellulose sources, acetic anhydride production facilities, and cellulose acetate manufacturing plants influences transportation costs and lead times. Optimizing logistics networks, including the use of multi-modal transportation and strategic inventory management, can contribute to improved economic efficiency.
Sustainability considerations are increasingly important in the raw material supply chain. Responsible sourcing of wood pulp, certified by organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), can mitigate environmental risks and enhance brand value. Similarly, exploring recycled or alternative cellulose sources and bio-based acetic anhydride options can improve the overall sustainability profile of cellulose acetate production.
To maximize economic efficiency, manufacturers must adopt a holistic approach to supply chain management. This includes implementing robust forecasting models to anticipate market trends and raw material price fluctuations, developing strategic partnerships with key suppliers to ensure consistent quality and competitive pricing, and investing in technologies that optimize raw material utilization and reduce waste throughout the production process.