How to Leverage Hypochlorous Acid in Hospital Surface Treatments?
AUG 4, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising solution for hospital surface treatments, offering a potent yet safe disinfection method. This naturally occurring compound, produced by the human immune system to fight infections, has gained attention in healthcare settings due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties and environmental friendliness.
The development of HOCl as a disinfectant traces back to the early 20th century when it was first used for wound care during World War I. However, its unstable nature initially limited widespread adoption. Recent technological advancements have overcome these stability issues, leading to a resurgence of interest in HOCl for various applications, including hospital surface disinfection.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been driven by the growing need for effective, non-toxic disinfectants in healthcare environments. Traditional chemical disinfectants often pose risks to human health and the environment, creating a demand for safer alternatives. HOCl addresses this need by offering powerful antimicrobial action without the drawbacks associated with harsh chemicals.
Current trends in HOCl technology focus on improving production methods, enhancing stability, and optimizing application techniques. Researchers are exploring ways to generate HOCl on-site, reducing reliance on pre-packaged solutions and extending shelf life. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop more efficient delivery systems, such as electrostatic sprayers, to ensure comprehensive coverage of hospital surfaces.
The primary objective of leveraging HOCl in hospital surface treatments is to enhance infection control measures while minimizing environmental impact and health risks to patients and staff. Specific goals include reducing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), decreasing the use of harmful chemicals, and improving overall hygiene standards in healthcare facilities.
Another key objective is to address the growing concern of antimicrobial resistance. Unlike many traditional disinfectants, HOCl's mechanism of action makes it less likely for microorganisms to develop resistance, potentially offering a long-term solution for hospital disinfection protocols.
As research continues, the aim is to fully understand HOCl's efficacy against a wide range of pathogens, including emerging threats, and to optimize its use in various healthcare settings. This includes investigating its potential for air disinfection and its role in combating biofilms on medical devices and surfaces.
The development of HOCl as a disinfectant traces back to the early 20th century when it was first used for wound care during World War I. However, its unstable nature initially limited widespread adoption. Recent technological advancements have overcome these stability issues, leading to a resurgence of interest in HOCl for various applications, including hospital surface disinfection.
The evolution of HOCl technology has been driven by the growing need for effective, non-toxic disinfectants in healthcare environments. Traditional chemical disinfectants often pose risks to human health and the environment, creating a demand for safer alternatives. HOCl addresses this need by offering powerful antimicrobial action without the drawbacks associated with harsh chemicals.
Current trends in HOCl technology focus on improving production methods, enhancing stability, and optimizing application techniques. Researchers are exploring ways to generate HOCl on-site, reducing reliance on pre-packaged solutions and extending shelf life. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop more efficient delivery systems, such as electrostatic sprayers, to ensure comprehensive coverage of hospital surfaces.
The primary objective of leveraging HOCl in hospital surface treatments is to enhance infection control measures while minimizing environmental impact and health risks to patients and staff. Specific goals include reducing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), decreasing the use of harmful chemicals, and improving overall hygiene standards in healthcare facilities.
Another key objective is to address the growing concern of antimicrobial resistance. Unlike many traditional disinfectants, HOCl's mechanism of action makes it less likely for microorganisms to develop resistance, potentially offering a long-term solution for hospital disinfection protocols.
As research continues, the aim is to fully understand HOCl's efficacy against a wide range of pathogens, including emerging threats, and to optimize its use in various healthcare settings. This includes investigating its potential for air disinfection and its role in combating biofilms on medical devices and surfaces.
Market Analysis for Hospital Disinfectants
The hospital disinfectant market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and the need for stringent hygiene protocols in healthcare settings. The global hospital disinfectant market was valued at approximately $7.1 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $9.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 5.5% during the forecast period.
Several factors contribute to this market expansion. The COVID-19 pandemic has heightened the importance of effective surface disinfection in hospitals, leading to increased demand for advanced disinfectant products. Additionally, the rising prevalence of HAIs and the growing number of surgical procedures performed globally have further fueled market growth.
The market is segmented based on type, form, and end-user. Types of hospital disinfectants include liquid, gel, and wipe formulations, with liquid disinfectants holding the largest market share due to their ease of use and effectiveness. Among end-users, hospitals and clinics dominate the market, followed by diagnostic laboratories and research institutes.
Geographically, North America leads the hospital disinfectant market, accounting for approximately 35% of the global market share. This dominance is attributed to stringent regulations, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and high healthcare expenditure. Europe follows closely, while the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth due to improving healthcare facilities and increasing awareness of infection control.
Key players in the hospital disinfectant market include 3M Company, Ecolab Inc., Procter & Gamble, Reckitt Benckiser Group plc, and Johnson & Johnson. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to maintain their market positions and expand their product portfolios.
The market for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) as a hospital surface disinfectant is gaining traction due to its efficacy, safety profile, and eco-friendly nature. HOCl-based disinfectants are increasingly being adopted in healthcare settings, presenting a significant growth opportunity within the broader hospital disinfectant market.
Several factors contribute to this market expansion. The COVID-19 pandemic has heightened the importance of effective surface disinfection in hospitals, leading to increased demand for advanced disinfectant products. Additionally, the rising prevalence of HAIs and the growing number of surgical procedures performed globally have further fueled market growth.
The market is segmented based on type, form, and end-user. Types of hospital disinfectants include liquid, gel, and wipe formulations, with liquid disinfectants holding the largest market share due to their ease of use and effectiveness. Among end-users, hospitals and clinics dominate the market, followed by diagnostic laboratories and research institutes.
Geographically, North America leads the hospital disinfectant market, accounting for approximately 35% of the global market share. This dominance is attributed to stringent regulations, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and high healthcare expenditure. Europe follows closely, while the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth due to improving healthcare facilities and increasing awareness of infection control.
Key players in the hospital disinfectant market include 3M Company, Ecolab Inc., Procter & Gamble, Reckitt Benckiser Group plc, and Johnson & Johnson. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to maintain their market positions and expand their product portfolios.
The market for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) as a hospital surface disinfectant is gaining traction due to its efficacy, safety profile, and eco-friendly nature. HOCl-based disinfectants are increasingly being adopted in healthcare settings, presenting a significant growth opportunity within the broader hospital disinfectant market.
HOCl Technology Status and Challenges
The current status of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) technology in hospital surface treatments presents both promising advancements and significant challenges. HOCl has gained attention as a potent disinfectant due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties and environmental friendliness. Its efficacy against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, makes it particularly suitable for hospital environments where infection control is paramount.
Recent developments have improved the stability and shelf life of HOCl solutions, addressing one of the primary historical limitations of this technology. Advanced production methods now allow for the creation of more concentrated and longer-lasting HOCl formulations, enhancing its practicality for widespread use in healthcare settings. Additionally, innovative delivery systems, such as electrostatic sprayers and fogging devices, have improved the application efficiency and coverage of HOCl on various surfaces.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in the widespread adoption of HOCl technology for hospital surface treatments. One significant hurdle is the lack of standardization in HOCl production and application protocols across healthcare facilities. This inconsistency can lead to variations in efficacy and potentially compromise infection control measures. Furthermore, the relatively higher cost of HOCl systems compared to traditional disinfectants remains a barrier for many healthcare institutions, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Another challenge lies in the need for more comprehensive, long-term studies on the effectiveness of HOCl in real-world hospital environments. While laboratory studies have demonstrated its antimicrobial efficacy, translating these results to complex healthcare settings with diverse surface materials and varying levels of organic soil presents ongoing research challenges. Additionally, concerns about potential material compatibility issues, especially with sensitive electronic equipment commonly found in hospitals, require further investigation and mitigation strategies.
The regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl technology also presents challenges. While it is generally recognized as safe, the varying classifications and approval processes across different countries can complicate its global adoption. Some regions may require additional safety and efficacy data before fully endorsing HOCl for hospital-wide use, potentially slowing its integration into standard infection control protocols.
Lastly, the education and training of healthcare staff in the proper use and handling of HOCl systems represent an ongoing challenge. Ensuring consistent and effective application while maintaining safety standards requires comprehensive training programs and clear operational guidelines, which may be resource-intensive for healthcare facilities to implement and maintain.
Recent developments have improved the stability and shelf life of HOCl solutions, addressing one of the primary historical limitations of this technology. Advanced production methods now allow for the creation of more concentrated and longer-lasting HOCl formulations, enhancing its practicality for widespread use in healthcare settings. Additionally, innovative delivery systems, such as electrostatic sprayers and fogging devices, have improved the application efficiency and coverage of HOCl on various surfaces.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in the widespread adoption of HOCl technology for hospital surface treatments. One significant hurdle is the lack of standardization in HOCl production and application protocols across healthcare facilities. This inconsistency can lead to variations in efficacy and potentially compromise infection control measures. Furthermore, the relatively higher cost of HOCl systems compared to traditional disinfectants remains a barrier for many healthcare institutions, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Another challenge lies in the need for more comprehensive, long-term studies on the effectiveness of HOCl in real-world hospital environments. While laboratory studies have demonstrated its antimicrobial efficacy, translating these results to complex healthcare settings with diverse surface materials and varying levels of organic soil presents ongoing research challenges. Additionally, concerns about potential material compatibility issues, especially with sensitive electronic equipment commonly found in hospitals, require further investigation and mitigation strategies.
The regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl technology also presents challenges. While it is generally recognized as safe, the varying classifications and approval processes across different countries can complicate its global adoption. Some regions may require additional safety and efficacy data before fully endorsing HOCl for hospital-wide use, potentially slowing its integration into standard infection control protocols.
Lastly, the education and training of healthcare staff in the proper use and handling of HOCl systems represent an ongoing challenge. Ensuring consistent and effective application while maintaining safety standards requires comprehensive training programs and clear operational guidelines, which may be resource-intensive for healthcare facilities to implement and maintain.
Current HOCl Application Methods
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and novel techniques for generating stable hypochlorous acid solutions. These methods aim to create high-purity, effective hypochlorous acid for various applications.
- Applications in disinfection and sterilization: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as a powerful disinfectant and sterilizing agent. It is effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Applications include water treatment, surface disinfection, and medical sterilization.
- Medical and healthcare applications: Hypochlorous acid finds extensive use in medical and healthcare settings. It is utilized in wound care, dental hygiene, eye care, and as a general antiseptic. Its non-toxic nature and effectiveness make it suitable for various medical treatments and procedures.
- Formulation and stability enhancement: Research focuses on improving the stability and shelf life of hypochlorous acid solutions. This includes developing specialized formulations, packaging methods, and additives to maintain the acid's effectiveness over time. Efforts are also made to create concentrated forms for easier storage and transportation.
- Environmental and industrial applications: Hypochlorous acid is employed in various environmental and industrial processes. It is used in water treatment, agriculture, food processing, and as a cleaning agent in industrial settings. Its eco-friendly nature makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring minimal environmental impact.
02 Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization and formulation of hypochlorous acid solutions
Techniques for stabilizing hypochlorous acid solutions to extend their shelf life and maintain efficacy are crucial. This includes pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging to prevent degradation and ensure consistent performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid finds applications in wound care, dermatology, and respiratory treatments. Its ability to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and combat infections without harming healthy tissue makes it valuable in medical settings for treating various conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation, wastewater treatment, and industrial cleaning processes. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness in breaking down contaminants make it suitable for large-scale applications in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCl Disinfection Industry
The hypochlorous acid market in hospital surface treatments is in a growth phase, driven by increasing focus on infection control and hygiene in healthcare settings. The market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of 7-8% over the next five years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB, Annihilare Medical Systems, and Parasol Medical LLC leading innovation in HOCl generation and application methods. Established players such as The Clorox Co. and Realm Therapeutics are also investing in R&D to enhance their product offerings. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing research focused on improving stability, efficacy, and delivery systems for hypochlorous acid solutions in hospital environments.
The Clorox Co.
Technical Solution: The Clorox Company has developed a range of hypochlorous acid-based products for hospital surface treatments. Their technology involves stabilizing hypochlorous acid at a near-neutral pH, which enhances its efficacy and safety profile. The company's formulation process ensures a consistent concentration of hypochlorous acid, typically around 200-500 ppm, which is effective against a broad spectrum of pathogens[1]. Clorox's products are designed for easy application through electrostatic sprayers or as ready-to-use solutions, allowing for efficient coverage of large surface areas in healthcare settings[2]. The company has also invested in research to demonstrate the non-corrosive nature of their hypochlorous acid solutions on various hospital surfaces, addressing a common concern in healthcare environments[3].
Strengths: Wide distribution network, established brand reputation in cleaning products, and extensive research backing. Weaknesses: Potential competition from specialized medical technology companies and the need for continuous innovation to maintain market position.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS has pioneered an advanced hypochlorous acid generation system specifically tailored for hospital environments. Their technology utilizes an electrochemical process to produce hypochlorous acid on-site, ensuring a fresh and potent solution for surface disinfection. The system generates hypochlorous acid at a concentration of 500 ppm, which has been shown to be effective against a wide range of hospital-acquired pathogens, including antibiotic-resistant strains[4]. ANNIHILARE's approach includes a proprietary stabilization method that extends the shelf life of the generated hypochlorous acid, allowing for more flexible use in various hospital departments. The company has also developed smart dispensing systems that can be integrated into existing hospital cleaning protocols, ensuring precise application and reducing waste[5].
Strengths: On-site generation capability, customizable solutions for different hospital needs, and integration with existing hospital systems. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial investment costs and the need for staff training on new equipment.
HOCl Efficacy and Safety Studies
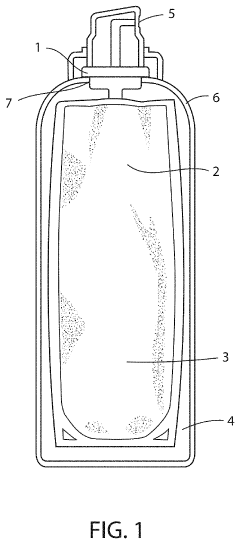
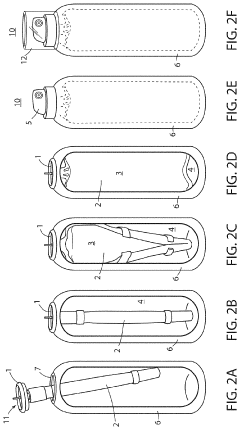
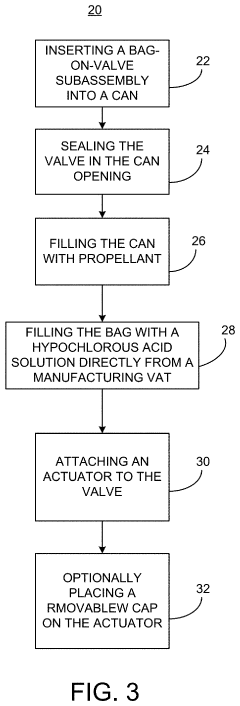
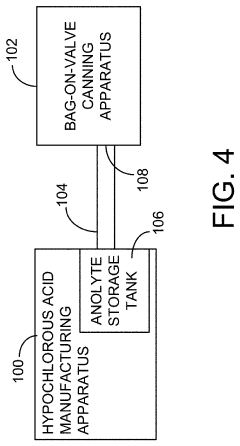
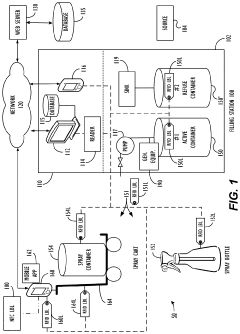
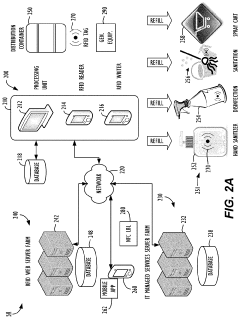
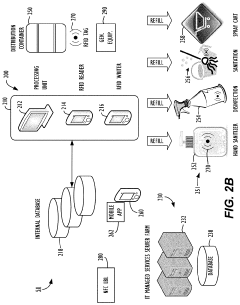
Method and device for storing a hypochlorous acid solution
PatentActiveUS20220041315A1
Innovation
- A method and apparatus that directly transfers hypochlorous acid solution from a manufacturing apparatus to a bag-on-valve canning system using a connected pipe, minimizing exposure to atmosphere and light, and includes a propellant to maintain pressure and stability, along with optional additives like silane quaternary ammonium ions for extended antimicrobial activity.
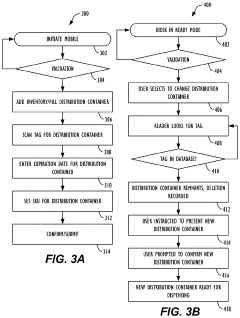
Material Tracking System
PatentInactiveUS20200160259A1
Innovation
- A system utilizing electronically readable identifiers, communication equipment, and processing units to track the expiration and usage of hypochlorous acid in containers, alerting when the disinfectant is past its effective period, ensuring its potency and safety for use.
Regulatory Framework for Hospital Disinfectants
The regulatory framework for hospital disinfectants plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of surface treatments, including those utilizing hypochlorous acid. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the primary regulatory body overseeing the registration and use of disinfectants in healthcare settings.
Under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), all disinfectants used in hospitals must be registered with the EPA. This process involves rigorous testing to demonstrate the product's effectiveness against specific pathogens and its safety for use in healthcare environments. The EPA's List N provides a comprehensive inventory of disinfectants approved for use against SARS-CoV-2, including those containing hypochlorous acid.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a role in regulating certain disinfectants, particularly those used on medical devices. Products that make claims about disinfecting or sanitizing medical devices may fall under the FDA's jurisdiction and require additional clearance or approval.
At the state level, regulations may vary, with some states imposing additional requirements or restrictions on the use of disinfectants in healthcare settings. Hospital administrators must be aware of both federal and state regulations to ensure compliance.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for hospital disinfectants can differ significantly. The European Union, for example, regulates these products under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which requires a thorough assessment of efficacy and safety before market authorization.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for manufacturers of hospital disinfectants, including those based on hypochlorous acid. These practices ensure consistent product quality and safety throughout the manufacturing process.
Labeling requirements for hospital disinfectants are stringent and regulated by the EPA. Labels must include detailed information on active ingredients, usage instructions, safety precautions, and efficacy claims. For hypochlorous acid-based products, specific concentration levels and contact times must be clearly stated to ensure proper use and effectiveness.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, regulatory bodies continually update their guidelines and requirements. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, led to expedited review processes for certain disinfectants, highlighting the adaptability of regulatory frameworks in response to public health emergencies.
Understanding and navigating this complex regulatory environment is crucial for healthcare facilities and manufacturers alike when considering the implementation of hypochlorous acid-based surface treatments in hospital settings.
Under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), all disinfectants used in hospitals must be registered with the EPA. This process involves rigorous testing to demonstrate the product's effectiveness against specific pathogens and its safety for use in healthcare environments. The EPA's List N provides a comprehensive inventory of disinfectants approved for use against SARS-CoV-2, including those containing hypochlorous acid.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) also plays a role in regulating certain disinfectants, particularly those used on medical devices. Products that make claims about disinfecting or sanitizing medical devices may fall under the FDA's jurisdiction and require additional clearance or approval.
At the state level, regulations may vary, with some states imposing additional requirements or restrictions on the use of disinfectants in healthcare settings. Hospital administrators must be aware of both federal and state regulations to ensure compliance.
Internationally, regulatory frameworks for hospital disinfectants can differ significantly. The European Union, for example, regulates these products under the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), which requires a thorough assessment of efficacy and safety before market authorization.
Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is essential for manufacturers of hospital disinfectants, including those based on hypochlorous acid. These practices ensure consistent product quality and safety throughout the manufacturing process.
Labeling requirements for hospital disinfectants are stringent and regulated by the EPA. Labels must include detailed information on active ingredients, usage instructions, safety precautions, and efficacy claims. For hypochlorous acid-based products, specific concentration levels and contact times must be clearly stated to ensure proper use and effectiveness.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, regulatory bodies continually update their guidelines and requirements. The COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, led to expedited review processes for certain disinfectants, highlighting the adaptability of regulatory frameworks in response to public health emergencies.
Understanding and navigating this complex regulatory environment is crucial for healthcare facilities and manufacturers alike when considering the implementation of hypochlorous acid-based surface treatments in hospital settings.
Environmental Impact of HOCl Solutions
The environmental impact of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) solutions in hospital surface treatments is a critical consideration for healthcare facilities aiming to balance effective disinfection with ecological responsibility. HOCl, known for its potent antimicrobial properties, offers a promising alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of hospital cleaning protocols.
One of the primary environmental advantages of HOCl solutions is their rapid biodegradability. Unlike many conventional disinfectants that persist in the environment, HOCl quickly breaks down into harmless components: water and salt. This characteristic significantly reduces the risk of long-term environmental contamination and minimizes the potential for harmful residues to accumulate in water systems or soil.
The production of HOCl solutions through electrolysis of saltwater is another environmentally favorable aspect. This process requires minimal raw materials and energy input, resulting in a lower carbon footprint compared to the manufacture of complex chemical disinfectants. Additionally, on-site generation of HOCl reduces the need for transportation and packaging of cleaning products, further decreasing the overall environmental impact.
In terms of air quality, HOCl solutions present a notable improvement over many traditional disinfectants. They do not release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or strong odors, contributing to better indoor air quality in healthcare settings. This characteristic not only benefits the environment but also enhances the comfort and health of hospital staff and patients.
The use of HOCl in surface treatments also addresses concerns related to antimicrobial resistance. As a naturally occurring compound, HOCl is less likely to contribute to the development of resistant microorganisms compared to synthetic antibacterial agents. This aspect is crucial for maintaining the long-term efficacy of disinfection practices while minimizing the environmental release of substances that could promote resistance.
However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impacts of increased chloride levels in wastewater resulting from widespread HOCl use. While the concentrations are generally low and pose minimal risk, proper wastewater management practices should be implemented to mitigate any potential effects on aquatic ecosystems.
In conclusion, the adoption of HOCl solutions for hospital surface treatments offers significant environmental benefits. Its rapid biodegradability, low-impact production process, and reduced contribution to air pollution and antimicrobial resistance make it an environmentally responsible choice for healthcare facilities. As hospitals increasingly prioritize sustainability alongside infection control, HOCl emerges as a promising solution that aligns with both environmental stewardship and public health objectives.
One of the primary environmental advantages of HOCl solutions is their rapid biodegradability. Unlike many conventional disinfectants that persist in the environment, HOCl quickly breaks down into harmless components: water and salt. This characteristic significantly reduces the risk of long-term environmental contamination and minimizes the potential for harmful residues to accumulate in water systems or soil.
The production of HOCl solutions through electrolysis of saltwater is another environmentally favorable aspect. This process requires minimal raw materials and energy input, resulting in a lower carbon footprint compared to the manufacture of complex chemical disinfectants. Additionally, on-site generation of HOCl reduces the need for transportation and packaging of cleaning products, further decreasing the overall environmental impact.
In terms of air quality, HOCl solutions present a notable improvement over many traditional disinfectants. They do not release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or strong odors, contributing to better indoor air quality in healthcare settings. This characteristic not only benefits the environment but also enhances the comfort and health of hospital staff and patients.
The use of HOCl in surface treatments also addresses concerns related to antimicrobial resistance. As a naturally occurring compound, HOCl is less likely to contribute to the development of resistant microorganisms compared to synthetic antibacterial agents. This aspect is crucial for maintaining the long-term efficacy of disinfection practices while minimizing the environmental release of substances that could promote resistance.
However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impacts of increased chloride levels in wastewater resulting from widespread HOCl use. While the concentrations are generally low and pose minimal risk, proper wastewater management practices should be implemented to mitigate any potential effects on aquatic ecosystems.
In conclusion, the adoption of HOCl solutions for hospital surface treatments offers significant environmental benefits. Its rapid biodegradability, low-impact production process, and reduced contribution to air pollution and antimicrobial resistance make it an environmentally responsible choice for healthcare facilities. As hospitals increasingly prioritize sustainability alongside infection control, HOCl emerges as a promising solution that aligns with both environmental stewardship and public health objectives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!