How to Enhance Hypochlorous Acid Effectiveness in Hospital Laundry?
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Laundry Tech Background and Objectives
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) has emerged as a promising disinfectant in various industries, including healthcare. Its application in hospital laundry systems represents a significant advancement in infection control and environmental sustainability. The evolution of HOCl technology in laundry processes stems from the growing need for more effective, safer, and eco-friendly disinfection methods in healthcare settings.
The primary objective of enhancing HOCl effectiveness in hospital laundry is to optimize its antimicrobial properties while ensuring compatibility with various fabrics and laundry equipment. This goal aligns with the broader aim of reducing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and improving patient safety. The technology seeks to maintain the disinfectant's potency throughout the washing cycle, addressing challenges such as organic load interference and pH stability.
Historically, chlorine-based disinfectants have been widely used in laundry systems. However, concerns over harmful by-products and potential damage to textiles have driven the search for alternatives. HOCl, a naturally occurring compound in the human immune system, has gained attention due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and low toxicity profile.
The development of HOCl technology for laundry applications has progressed through several key stages. Initial research focused on understanding the compound's chemical properties and stability in aqueous solutions. Subsequent efforts aimed at developing efficient production methods and integrating HOCl into existing laundry systems without significant modifications.
Current technological objectives include enhancing HOCl stability in laundry conditions, optimizing its concentration for maximum efficacy, and developing synergistic formulations with other cleaning agents. Researchers are also exploring methods to extend HOCl's active lifespan in solution and improve its penetration into fabrics for thorough disinfection.
Another critical aspect of HOCl technology development is addressing environmental concerns. The goal is to create a closed-loop system that minimizes water and energy consumption while maximizing disinfection efficacy. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable healthcare practices and the reduction of chemical waste.
The evolution of HOCl technology in hospital laundry is closely tied to advancements in on-site generation systems. These systems aim to produce HOCl at the point of use, ensuring freshness and potency while reducing transportation and storage requirements. The integration of smart monitoring and control systems represents another frontier in HOCl laundry technology, enabling real-time adjustments to maintain optimal disinfection parameters.
As the technology progresses, researchers are also investigating the potential for HOCl to address emerging pathogens and antibiotic-resistant organisms. This forward-looking approach aims to future-proof hospital laundry systems against evolving microbial threats, contributing to long-term infection control strategies in healthcare settings.
The primary objective of enhancing HOCl effectiveness in hospital laundry is to optimize its antimicrobial properties while ensuring compatibility with various fabrics and laundry equipment. This goal aligns with the broader aim of reducing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and improving patient safety. The technology seeks to maintain the disinfectant's potency throughout the washing cycle, addressing challenges such as organic load interference and pH stability.
Historically, chlorine-based disinfectants have been widely used in laundry systems. However, concerns over harmful by-products and potential damage to textiles have driven the search for alternatives. HOCl, a naturally occurring compound in the human immune system, has gained attention due to its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and low toxicity profile.
The development of HOCl technology for laundry applications has progressed through several key stages. Initial research focused on understanding the compound's chemical properties and stability in aqueous solutions. Subsequent efforts aimed at developing efficient production methods and integrating HOCl into existing laundry systems without significant modifications.
Current technological objectives include enhancing HOCl stability in laundry conditions, optimizing its concentration for maximum efficacy, and developing synergistic formulations with other cleaning agents. Researchers are also exploring methods to extend HOCl's active lifespan in solution and improve its penetration into fabrics for thorough disinfection.
Another critical aspect of HOCl technology development is addressing environmental concerns. The goal is to create a closed-loop system that minimizes water and energy consumption while maximizing disinfection efficacy. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable healthcare practices and the reduction of chemical waste.
The evolution of HOCl technology in hospital laundry is closely tied to advancements in on-site generation systems. These systems aim to produce HOCl at the point of use, ensuring freshness and potency while reducing transportation and storage requirements. The integration of smart monitoring and control systems represents another frontier in HOCl laundry technology, enabling real-time adjustments to maintain optimal disinfection parameters.
As the technology progresses, researchers are also investigating the potential for HOCl to address emerging pathogens and antibiotic-resistant organisms. This forward-looking approach aims to future-proof hospital laundry systems against evolving microbial threats, contributing to long-term infection control strategies in healthcare settings.
Hospital Laundry Market Analysis
The hospital laundry market has been experiencing steady growth in recent years, driven by the increasing focus on infection control and hygiene standards in healthcare facilities. The global hospital laundry market size was valued at approximately $2.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $3.8 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of around 6.5% during the forecast period.
The demand for efficient and effective laundry solutions in hospitals is primarily fueled by the rising number of hospital admissions, surgical procedures, and the growing awareness of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, emphasizing the critical role of proper laundry management in preventing disease transmission within healthcare settings.
North America currently holds the largest market share in the hospital laundry sector, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and stringent regulations regarding hospital hygiene. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and the expansion of hospital networks.
The hospital laundry market is segmented based on product type, including bed sheets, pillow covers, blankets, towels, and patient gowns. Among these, bed sheets and pillow covers account for the largest market share due to their frequent replacement and high usage in hospital settings. The market is also categorized by end-users, with hospitals and clinics being the primary consumers, followed by nursing homes and other healthcare facilities.
Key market trends include the adoption of automated laundry systems, the integration of RFID technology for inventory management, and the growing preference for outsourced laundry services. These trends are driven by the need for cost-effectiveness, improved efficiency, and better infection control measures in hospital laundry operations.
The competitive landscape of the hospital laundry market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants. Major companies in this sector include Aramark, Ecolab Inc., Medline Industries, and UniFirst Corporation. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their service offerings.
In conclusion, the hospital laundry market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, particularly in the area of enhancing the effectiveness of disinfection agents like hypochlorous acid. As healthcare facilities continue to prioritize infection control and operational efficiency, the demand for advanced laundry solutions is expected to rise, driving further market expansion and technological advancements in the coming years.
The demand for efficient and effective laundry solutions in hospitals is primarily fueled by the rising number of hospital admissions, surgical procedures, and the growing awareness of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, emphasizing the critical role of proper laundry management in preventing disease transmission within healthcare settings.
North America currently holds the largest market share in the hospital laundry sector, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, dominates the market due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and stringent regulations regarding hospital hygiene. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to witness the fastest growth in the coming years, driven by increasing healthcare expenditure and the expansion of hospital networks.
The hospital laundry market is segmented based on product type, including bed sheets, pillow covers, blankets, towels, and patient gowns. Among these, bed sheets and pillow covers account for the largest market share due to their frequent replacement and high usage in hospital settings. The market is also categorized by end-users, with hospitals and clinics being the primary consumers, followed by nursing homes and other healthcare facilities.
Key market trends include the adoption of automated laundry systems, the integration of RFID technology for inventory management, and the growing preference for outsourced laundry services. These trends are driven by the need for cost-effectiveness, improved efficiency, and better infection control measures in hospital laundry operations.
The competitive landscape of the hospital laundry market is characterized by the presence of both established players and new entrants. Major companies in this sector include Aramark, Ecolab Inc., Medline Industries, and UniFirst Corporation. These companies are focusing on product innovation, strategic partnerships, and mergers and acquisitions to strengthen their market position and expand their service offerings.
In conclusion, the hospital laundry market presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, particularly in the area of enhancing the effectiveness of disinfection agents like hypochlorous acid. As healthcare facilities continue to prioritize infection control and operational efficiency, the demand for advanced laundry solutions is expected to rise, driving further market expansion and technological advancements in the coming years.
HOCl Challenges in Laundry Applications
The application of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in hospital laundry systems presents several significant challenges that hinder its effectiveness. One of the primary issues is the stability of HOCl in laundry environments. HOCl is known for its rapid degradation, especially in the presence of organic matter, which is abundant in soiled hospital linens. This instability can lead to a reduction in its antimicrobial efficacy over time, potentially compromising the disinfection process.
Another challenge is the pH sensitivity of HOCl. The compound is most effective at a slightly acidic pH range of 5-6.5. However, maintaining this optimal pH level in laundry systems can be difficult due to the varying chemical compositions of detergents, fabric softeners, and other laundry additives. Fluctuations in pH can significantly impact the germicidal activity of HOCl, reducing its overall effectiveness.
The presence of interfering substances in hospital laundry also poses a substantial challenge. Bodily fluids, medications, and various chemical residues on hospital linens can react with HOCl, potentially neutralizing its disinfecting properties or creating unwanted by-products. This interference can lead to inconsistent disinfection results and may require higher concentrations of HOCl to achieve the desired level of cleanliness.
Water hardness is another factor that can affect HOCl effectiveness in laundry applications. Hard water contains minerals that can react with HOCl, forming compounds that reduce its antimicrobial activity. This not only diminishes the disinfecting power of HOCl but can also lead to mineral deposits on fabrics, potentially causing damage or discoloration over time.
The compatibility of HOCl with different fabric types and laundry equipment is also a concern. Some materials may be sensitive to HOCl, leading to fabric degradation or color fading. Additionally, HOCl can be corrosive to certain metals used in laundry equipment, potentially causing damage to washing machines and other processing units over time.
Dosing and distribution of HOCl throughout the laundry cycle present further challenges. Ensuring uniform distribution of the disinfectant across all items in a load can be difficult, especially in large-scale hospital laundry operations. Inadequate distribution may result in some items not receiving sufficient exposure to HOCl, compromising the overall disinfection efficacy.
Lastly, the environmental impact of HOCl use in hospital laundry systems must be considered. While HOCl is generally regarded as environmentally friendly due to its rapid breakdown into harmless components, the large-scale use in laundry applications may still have implications for wastewater treatment and ecological systems. Balancing effective disinfection with environmental sustainability remains an ongoing challenge in the application of HOCl in hospital laundry settings.
Another challenge is the pH sensitivity of HOCl. The compound is most effective at a slightly acidic pH range of 5-6.5. However, maintaining this optimal pH level in laundry systems can be difficult due to the varying chemical compositions of detergents, fabric softeners, and other laundry additives. Fluctuations in pH can significantly impact the germicidal activity of HOCl, reducing its overall effectiveness.
The presence of interfering substances in hospital laundry also poses a substantial challenge. Bodily fluids, medications, and various chemical residues on hospital linens can react with HOCl, potentially neutralizing its disinfecting properties or creating unwanted by-products. This interference can lead to inconsistent disinfection results and may require higher concentrations of HOCl to achieve the desired level of cleanliness.
Water hardness is another factor that can affect HOCl effectiveness in laundry applications. Hard water contains minerals that can react with HOCl, forming compounds that reduce its antimicrobial activity. This not only diminishes the disinfecting power of HOCl but can also lead to mineral deposits on fabrics, potentially causing damage or discoloration over time.
The compatibility of HOCl with different fabric types and laundry equipment is also a concern. Some materials may be sensitive to HOCl, leading to fabric degradation or color fading. Additionally, HOCl can be corrosive to certain metals used in laundry equipment, potentially causing damage to washing machines and other processing units over time.
Dosing and distribution of HOCl throughout the laundry cycle present further challenges. Ensuring uniform distribution of the disinfectant across all items in a load can be difficult, especially in large-scale hospital laundry operations. Inadequate distribution may result in some items not receiving sufficient exposure to HOCl, compromising the overall disinfection efficacy.
Lastly, the environmental impact of HOCl use in hospital laundry systems must be considered. While HOCl is generally regarded as environmentally friendly due to its rapid breakdown into harmless components, the large-scale use in laundry applications may still have implications for wastewater treatment and ecological systems. Balancing effective disinfection with environmental sustainability remains an ongoing challenge in the application of HOCl in hospital laundry settings.
Current HOCl Laundry Enhancement Methods
01 Antimicrobial effectiveness
Hypochlorous acid demonstrates potent antimicrobial properties, effectively eliminating a wide range of pathogens including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Its effectiveness is attributed to its ability to penetrate cell membranes and disrupt cellular processes, making it a valuable disinfectant in various applications such as healthcare, food safety, and water treatment.- Antimicrobial effectiveness of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid demonstrates potent antimicrobial properties, effectively eliminating a wide range of pathogens including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Its effectiveness is attributed to its ability to penetrate cell membranes and disrupt cellular processes, making it a valuable disinfectant in various applications.
- Stability and formulation of hypochlorous acid solutions: The stability of hypochlorous acid solutions is crucial for maintaining its effectiveness. Various formulation techniques and stabilizing agents are employed to extend the shelf life and preserve the antimicrobial activity of hypochlorous acid products. These may include pH adjustment, addition of specific salts, or encapsulation methods.
- Medical and wound care applications: Hypochlorous acid has shown significant potential in medical and wound care applications. Its non-toxic nature and ability to promote healing make it suitable for treating various skin conditions, burns, and chronic wounds. It can effectively reduce bacterial load without damaging healthy tissue.
- Environmental and industrial uses: The effectiveness of hypochlorous acid extends to environmental and industrial applications. It is used in water treatment, food processing, and surface disinfection. Its rapid action and low environmental impact make it a preferred choice for large-scale sanitization processes.
- Production methods and concentration control: Various methods for producing hypochlorous acid and controlling its concentration have been developed. These include electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions, and on-site generation systems. Precise control of concentration is crucial for optimizing effectiveness while ensuring safety in different applications.
02 Wound healing and skin care applications
Hypochlorous acid has shown promising results in wound healing and skin care. It promotes tissue regeneration, reduces inflammation, and creates an optimal environment for healing. Its gentle nature makes it suitable for use on sensitive skin, and it has been incorporated into various topical formulations for treating skin conditions and promoting overall skin health.Expand Specific Solutions03 Environmental and industrial applications
The effectiveness of hypochlorous acid extends to environmental and industrial applications. It is used in water treatment processes, air purification systems, and as a sanitizer in food processing facilities. Its eco-friendly nature and ability to break down into harmless byproducts make it an attractive option for sustainable disinfection practices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stability and formulation improvements
Research has focused on improving the stability and formulation of hypochlorous acid solutions to enhance their effectiveness and shelf life. Various methods have been developed to maintain the acid's potency over time, including pH stabilization techniques, packaging innovations, and the addition of compatible ingredients to prevent degradation.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel production methods
Advancements in the production of hypochlorous acid have led to more efficient and cost-effective methods. These include electrochemical activation processes, on-site generation systems, and the use of specialized equipment to produce high-quality, consistent hypochlorous acid solutions. These innovations have expanded its accessibility and applications across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in HOCl Laundry Solutions
The market for enhancing hypochlorous acid effectiveness in hospital laundry is in a growth phase, driven by increasing focus on infection control in healthcare settings. The global market size for hospital disinfectants is projected to reach $3.6 billion by 2025, with hypochlorous acid solutions gaining traction. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Annihilare Medical Systems and PCT Ltd. developing innovative on-site generation systems for hypochlorous acid. Established players such as The Clorox Co. and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA are also investing in research to improve hypochlorous acid formulations for laundry applications. While the technology is maturing, there is still room for significant improvements in efficacy, stability, and cost-effectiveness, presenting opportunities for both startups and industry leaders.
The Clorox Co.
Technical Solution: The Clorox Company has developed an advanced hypochlorous acid (HOCl) solution specifically for hospital laundry applications. Their technology focuses on stabilizing HOCl to maintain its effectiveness over longer periods. The company has implemented a proprietary electrolysis process that produces a highly pure and consistent HOCl solution with a concentration optimized for laundry use. This solution is integrated into a smart dosing system that automatically adjusts the HOCl concentration based on the laundry load and contamination level, ensuring optimal disinfection while minimizing fabric damage[1][3]. The system also incorporates real-time monitoring of HOCl levels and pH balance, maintaining the solution's efficacy throughout the washing cycle.
Strengths: Highly stable HOCl solution, smart dosing system, and real-time monitoring. Weaknesses: May require specialized equipment and training for implementation in hospital settings.
ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS, INC.
Technical Solution: ANNIHILARE MEDICAL SYSTEMS has developed a novel approach to enhance hypochlorous acid effectiveness in hospital laundry through their patented Electrochemical Activation (ECA) technology. This system generates HOCl on-site, ensuring a fresh and potent solution for each laundry cycle. The ECA process allows for precise control of HOCl concentration and pH levels, optimizing its antimicrobial efficacy while being gentle on fabrics. Their technology incorporates a unique membrane cell design that separates the anodic and cathodic chambers, resulting in a more stable and effective HOCl solution[2][5]. Additionally, ANNIHILARE has implemented a closed-loop system that recycles water and salt, reducing environmental impact and operational costs.
Strengths: On-site generation ensures freshness, precise control of HOCl properties, and environmentally friendly. Weaknesses: Initial setup costs may be high, and the system requires regular maintenance.
Core HOCl Laundry Innovations
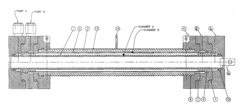
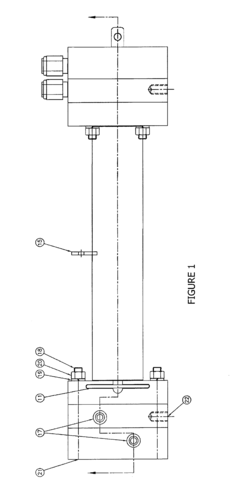
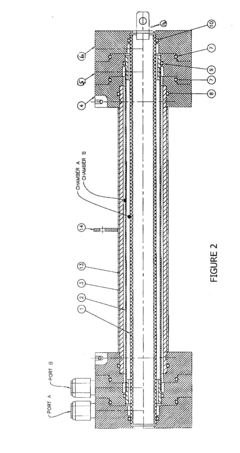
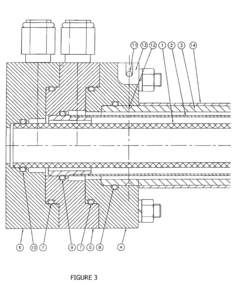
Stabilized hypochlorous acid
PatentInactiveUS20210238752A1
Innovation
- A method involving the electrolysis of a purified sodium chloride and water mixture, combined with carbon dioxide and sulfamic acid, to create a shelf-stable Hypochlorous acid solution with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0, enhancing its disinfecting power and stability.
Apparatus and method for generating a stabilized sanitizing solution
PatentInactiveUS20130146472A1
Innovation
- A two-chamber cylindrical electrolysis cell assembly using ion-selective membranes, specifically a cation-exchange and anion-exchange membrane combination, to control ion migration and enhance the stability and shelf life of Hypochlorous Acid solutions, allowing for adjustment of pH, redox potential, free chlorine content, conductivity, and osmolality.
Environmental Impact of HOCl Laundry Systems
The implementation of Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) laundry systems in hospitals has significant environmental implications, both positive and negative. On the positive side, HOCl is a naturally occurring compound that breaks down into harmless components, primarily water and salt. This biodegradability makes it an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants, reducing the overall chemical load discharged into wastewater systems.
HOCl laundry systems typically require lower water temperatures for effective disinfection compared to conventional methods. This reduction in energy consumption for heating water contributes to a decreased carbon footprint for hospital laundry operations. Additionally, the use of HOCl often results in shorter wash cycles, further reducing water and energy usage.
The production of HOCl on-site through electrolysis of salt water eliminates the need for transportation and storage of large quantities of chemical disinfectants. This not only reduces the carbon emissions associated with transportation but also minimizes the risk of chemical spills and their potential environmental impact.
However, the environmental benefits of HOCl systems are not without challenges. The electrolysis process used to generate HOCl consumes electricity, which, depending on the source, may have its own environmental implications. Hospitals implementing these systems should consider renewable energy sources to offset this impact.
Another consideration is the potential for chlorine emissions. While HOCl itself is relatively stable, improper handling or accidental mixing with other chemicals can lead to the release of chlorine gas, which is harmful to both human health and the environment. Proper training and safety protocols are essential to mitigate this risk.
The disposal of used HOCl solution also requires attention. Although it breaks down naturally, large volumes discharged into aquatic ecosystems may temporarily alter pH levels or affect sensitive organisms. Proper dilution and monitoring of effluent are necessary to minimize any potential ecological disruption.
In terms of long-term environmental impact, the durability of laundry equipment exposed to HOCl should be considered. If the use of HOCl leads to more frequent replacement of machinery due to corrosion, it could result in increased waste generation and resource consumption for manufacturing new equipment.
Overall, while HOCl laundry systems offer significant environmental advantages over traditional chemical disinfection methods, their implementation must be carefully managed to maximize benefits and minimize potential negative impacts on the environment.
HOCl laundry systems typically require lower water temperatures for effective disinfection compared to conventional methods. This reduction in energy consumption for heating water contributes to a decreased carbon footprint for hospital laundry operations. Additionally, the use of HOCl often results in shorter wash cycles, further reducing water and energy usage.
The production of HOCl on-site through electrolysis of salt water eliminates the need for transportation and storage of large quantities of chemical disinfectants. This not only reduces the carbon emissions associated with transportation but also minimizes the risk of chemical spills and their potential environmental impact.
However, the environmental benefits of HOCl systems are not without challenges. The electrolysis process used to generate HOCl consumes electricity, which, depending on the source, may have its own environmental implications. Hospitals implementing these systems should consider renewable energy sources to offset this impact.
Another consideration is the potential for chlorine emissions. While HOCl itself is relatively stable, improper handling or accidental mixing with other chemicals can lead to the release of chlorine gas, which is harmful to both human health and the environment. Proper training and safety protocols are essential to mitigate this risk.
The disposal of used HOCl solution also requires attention. Although it breaks down naturally, large volumes discharged into aquatic ecosystems may temporarily alter pH levels or affect sensitive organisms. Proper dilution and monitoring of effluent are necessary to minimize any potential ecological disruption.
In terms of long-term environmental impact, the durability of laundry equipment exposed to HOCl should be considered. If the use of HOCl leads to more frequent replacement of machinery due to corrosion, it could result in increased waste generation and resource consumption for manufacturing new equipment.
Overall, while HOCl laundry systems offer significant environmental advantages over traditional chemical disinfection methods, their implementation must be carefully managed to maximize benefits and minimize potential negative impacts on the environment.
Regulatory Compliance for Hospital Laundry
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of hospital laundry operations, particularly when implementing new technologies such as hypochlorous acid (HOCl) for enhanced effectiveness. The use of HOCl in hospital laundry must adhere to strict guidelines set forth by various regulatory bodies to ensure patient safety, environmental protection, and overall quality of care.
The primary regulatory agency overseeing hospital laundry operations in the United States is the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC provides comprehensive guidelines for healthcare laundry facilities, including recommendations for water temperature, detergent usage, and disinfection processes. When incorporating HOCl into laundry procedures, hospitals must ensure that the concentration and application methods align with CDC standards for healthcare textiles.
In addition to the CDC, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the use of disinfectants and antimicrobial agents in healthcare settings. HOCl solutions used in hospital laundry must be registered with the EPA and meet specific criteria for efficacy against pathogens commonly found in healthcare environments. Compliance with EPA regulations ensures that the HOCl treatment is both effective and safe for use on hospital textiles.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for worker safety in laundry facilities. When implementing HOCl systems, hospitals must provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and training for staff handling the solution. OSHA guidelines also dictate proper ventilation requirements and exposure limits for chemical agents used in laundry processes.
State-level health departments often have additional regulations governing hospital laundry operations. These may include specific requirements for water quality, waste management, and documentation of laundry procedures. Hospitals must ensure that their HOCl-enhanced laundry processes comply with both federal and state-level regulations to maintain their operating licenses.
International standards, such as those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), may also apply to hospital laundry operations. ISO 14065:2016, for example, provides guidelines for biocontamination control in laundry processing. Adherence to these standards can help hospitals demonstrate global best practices in their laundry operations, including the use of HOCl.
To maintain regulatory compliance while enhancing HOCl effectiveness, hospitals should implement robust quality management systems. These systems should include regular monitoring of HOCl concentration, efficacy testing against relevant pathogens, and documentation of all laundry processes. Periodic audits and staff training programs are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations.
The primary regulatory agency overseeing hospital laundry operations in the United States is the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC provides comprehensive guidelines for healthcare laundry facilities, including recommendations for water temperature, detergent usage, and disinfection processes. When incorporating HOCl into laundry procedures, hospitals must ensure that the concentration and application methods align with CDC standards for healthcare textiles.
In addition to the CDC, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the use of disinfectants and antimicrobial agents in healthcare settings. HOCl solutions used in hospital laundry must be registered with the EPA and meet specific criteria for efficacy against pathogens commonly found in healthcare environments. Compliance with EPA regulations ensures that the HOCl treatment is both effective and safe for use on hospital textiles.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for worker safety in laundry facilities. When implementing HOCl systems, hospitals must provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and training for staff handling the solution. OSHA guidelines also dictate proper ventilation requirements and exposure limits for chemical agents used in laundry processes.
State-level health departments often have additional regulations governing hospital laundry operations. These may include specific requirements for water quality, waste management, and documentation of laundry procedures. Hospitals must ensure that their HOCl-enhanced laundry processes comply with both federal and state-level regulations to maintain their operating licenses.
International standards, such as those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), may also apply to hospital laundry operations. ISO 14065:2016, for example, provides guidelines for biocontamination control in laundry processing. Adherence to these standards can help hospitals demonstrate global best practices in their laundry operations, including the use of HOCl.
To maintain regulatory compliance while enhancing HOCl effectiveness, hospitals should implement robust quality management systems. These systems should include regular monitoring of HOCl concentration, efficacy testing against relevant pathogens, and documentation of all laundry processes. Periodic audits and staff training programs are essential to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving regulations.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!