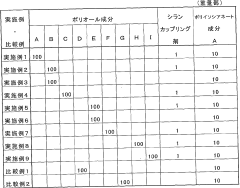
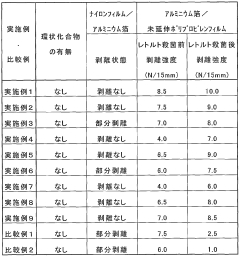
How Isocyanates Innovate in Flexible Packaging Solutions?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Evolution in Packaging
The evolution of isocyanates in flexible packaging solutions has been marked by significant technological advancements and innovative applications. Initially developed in the 1930s, isocyanates have undergone substantial transformations to meet the ever-changing demands of the packaging industry.
In the early stages, isocyanates were primarily used in rigid foam applications. However, as the need for more versatile and flexible packaging materials grew, researchers began exploring ways to incorporate isocyanates into softer, more pliable structures. This led to the development of polyurethane-based adhesives and coatings, which revolutionized the flexible packaging sector.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a surge in research focused on improving the performance and safety of isocyanate-based materials. Scientists worked on reducing toxicity concerns associated with certain isocyanates, particularly methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI). This period also witnessed the introduction of aliphatic isocyanates, which offered superior UV resistance and color stability compared to their aromatic counterparts.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the 1980s and 1990s, the packaging industry faced pressure to develop more sustainable solutions. This led to the exploration of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. Researchers began investigating the potential of using plant-based oils and other natural materials as precursors for isocyanate production, aiming to reduce reliance on petroleum-based feedstocks.
The turn of the millennium brought about a focus on enhancing the barrier properties of flexible packaging materials. Isocyanate-based coatings and adhesives played a crucial role in improving moisture and oxygen resistance, extending the shelf life of packaged products. This period also saw advancements in isocyanate-terminated prepolymers, which offered improved processing characteristics and final product performance.
Recent years have witnessed a shift towards water-based and solvent-free isocyanate systems, driven by stricter environmental regulations and consumer demand for more eco-friendly packaging. These developments have led to the creation of high-performance, low-VOC adhesives and coatings that maintain the excellent properties of traditional isocyanate-based materials while reducing environmental impact.
The ongoing evolution of isocyanates in packaging continues to focus on enhancing sustainability, improving barrier properties, and developing smart packaging solutions. Current research efforts are exploring the integration of isocyanate-based materials with nanotechnology and active packaging concepts, paving the way for innovative flexible packaging solutions that offer extended shelf life, improved product protection, and enhanced consumer convenience.
In the early stages, isocyanates were primarily used in rigid foam applications. However, as the need for more versatile and flexible packaging materials grew, researchers began exploring ways to incorporate isocyanates into softer, more pliable structures. This led to the development of polyurethane-based adhesives and coatings, which revolutionized the flexible packaging sector.
The 1960s and 1970s saw a surge in research focused on improving the performance and safety of isocyanate-based materials. Scientists worked on reducing toxicity concerns associated with certain isocyanates, particularly methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI). This period also witnessed the introduction of aliphatic isocyanates, which offered superior UV resistance and color stability compared to their aromatic counterparts.
As environmental concerns gained prominence in the 1980s and 1990s, the packaging industry faced pressure to develop more sustainable solutions. This led to the exploration of bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources. Researchers began investigating the potential of using plant-based oils and other natural materials as precursors for isocyanate production, aiming to reduce reliance on petroleum-based feedstocks.
The turn of the millennium brought about a focus on enhancing the barrier properties of flexible packaging materials. Isocyanate-based coatings and adhesives played a crucial role in improving moisture and oxygen resistance, extending the shelf life of packaged products. This period also saw advancements in isocyanate-terminated prepolymers, which offered improved processing characteristics and final product performance.
Recent years have witnessed a shift towards water-based and solvent-free isocyanate systems, driven by stricter environmental regulations and consumer demand for more eco-friendly packaging. These developments have led to the creation of high-performance, low-VOC adhesives and coatings that maintain the excellent properties of traditional isocyanate-based materials while reducing environmental impact.
The ongoing evolution of isocyanates in packaging continues to focus on enhancing sustainability, improving barrier properties, and developing smart packaging solutions. Current research efforts are exploring the integration of isocyanate-based materials with nanotechnology and active packaging concepts, paving the way for innovative flexible packaging solutions that offer extended shelf life, improved product protection, and enhanced consumer convenience.
Flexible Packaging Market Trends
The flexible packaging market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and sustainability concerns. This sector has shown remarkable resilience and adaptability, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) consistently outpacing many other packaging segments.
One of the key trends shaping the flexible packaging market is the increasing demand for convenience and on-the-go products. As consumers lead busier lifestyles, there is a growing preference for packaged foods and beverages that are easy to carry, store, and consume. This has led to innovations in pouch designs, resealable features, and portion-controlled packaging solutions.
Sustainability has emerged as a critical factor influencing market dynamics. With heightened environmental awareness, there is a strong push towards eco-friendly packaging materials and designs. This trend has spurred the development of recyclable and biodegradable flexible packaging options, as well as the use of mono-material structures that are easier to recycle.
The e-commerce boom has also significantly impacted the flexible packaging market. As online shopping continues to grow, there is an increased need for packaging solutions that can withstand the rigors of shipping while maintaining product integrity. This has led to innovations in protective packaging and the development of tamper-evident features.
In terms of materials, there is a notable shift towards high-performance films and laminates. These advanced materials offer improved barrier properties, extended shelf life, and enhanced product protection. The use of nanotechnology in flexible packaging is also gaining traction, enabling the development of packaging with antimicrobial properties and improved strength-to-weight ratios.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest end-user of flexible packaging, but other sectors such as pharmaceuticals, personal care, and household products are also driving market growth. In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing demand for child-resistant and senior-friendly packaging solutions, spurring innovations in easy-open yet secure designs.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market for flexible packaging, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and a burgeoning middle class. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-value, technologically advanced packaging solutions.
As the market evolves, there is an increasing emphasis on smart packaging technologies. The integration of QR codes, NFC tags, and other interactive elements is enabling brands to enhance consumer engagement and provide valuable product information. This trend is expected to accelerate with the advancement of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
One of the key trends shaping the flexible packaging market is the increasing demand for convenience and on-the-go products. As consumers lead busier lifestyles, there is a growing preference for packaged foods and beverages that are easy to carry, store, and consume. This has led to innovations in pouch designs, resealable features, and portion-controlled packaging solutions.
Sustainability has emerged as a critical factor influencing market dynamics. With heightened environmental awareness, there is a strong push towards eco-friendly packaging materials and designs. This trend has spurred the development of recyclable and biodegradable flexible packaging options, as well as the use of mono-material structures that are easier to recycle.
The e-commerce boom has also significantly impacted the flexible packaging market. As online shopping continues to grow, there is an increased need for packaging solutions that can withstand the rigors of shipping while maintaining product integrity. This has led to innovations in protective packaging and the development of tamper-evident features.
In terms of materials, there is a notable shift towards high-performance films and laminates. These advanced materials offer improved barrier properties, extended shelf life, and enhanced product protection. The use of nanotechnology in flexible packaging is also gaining traction, enabling the development of packaging with antimicrobial properties and improved strength-to-weight ratios.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest end-user of flexible packaging, but other sectors such as pharmaceuticals, personal care, and household products are also driving market growth. In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing demand for child-resistant and senior-friendly packaging solutions, spurring innovations in easy-open yet secure designs.
Regionally, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market for flexible packaging, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and a burgeoning middle class. North America and Europe continue to be significant markets, with a focus on high-value, technologically advanced packaging solutions.
As the market evolves, there is an increasing emphasis on smart packaging technologies. The integration of QR codes, NFC tags, and other interactive elements is enabling brands to enhance consumer engagement and provide valuable product information. This trend is expected to accelerate with the advancement of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
Isocyanate Tech Challenges
Isocyanates, while offering numerous advantages in flexible packaging solutions, face several significant technical challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. One of the primary concerns is their high reactivity with moisture, which can lead to premature curing and reduced shelf life of the packaging materials. This sensitivity to humidity necessitates stringent control measures during production, storage, and application processes, increasing manufacturing complexity and costs.
Another major challenge lies in the potential health and environmental risks associated with isocyanates. These compounds are known to be potent respiratory sensitizers and can cause severe allergic reactions in some individuals. This has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and the need for robust safety protocols in manufacturing facilities. The challenge extends to ensuring that residual free isocyanates in the final packaging products are below acceptable limits, requiring advanced curing and post-processing techniques.
The optimization of isocyanate-based adhesives for flexible packaging presents another technical hurdle. Achieving the right balance between flexibility, strength, and barrier properties often involves complex formulation adjustments. The cross-linking density of isocyanate-based polymers must be carefully controlled to maintain the desired mechanical properties without compromising the flexibility essential for packaging applications.
Furthermore, the compatibility of isocyanates with various substrate materials used in flexible packaging can be problematic. Different surface energies and chemical compositions of substrates may lead to adhesion issues or unwanted reactions, necessitating the development of specialized primers or surface treatments. This challenge is particularly pronounced when dealing with multi-layer packaging structures, where each layer may require a different approach to ensure optimal bonding.
The development of bio-based or more sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived isocyanates represents another significant technical challenge. While there is growing demand for environmentally friendly packaging solutions, creating bio-based isocyanates that match the performance of conventional ones in terms of reactivity, durability, and cost-effectiveness remains an ongoing research focus.
Lastly, the volatility of isocyanate monomers poses challenges in processing and application. Controlling the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing and ensuring complete reaction of isocyanates to prevent off-gassing in the final product are critical considerations. This necessitates advanced process control systems and curing technologies to minimize environmental impact and ensure product safety.
Another major challenge lies in the potential health and environmental risks associated with isocyanates. These compounds are known to be potent respiratory sensitizers and can cause severe allergic reactions in some individuals. This has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and the need for robust safety protocols in manufacturing facilities. The challenge extends to ensuring that residual free isocyanates in the final packaging products are below acceptable limits, requiring advanced curing and post-processing techniques.
The optimization of isocyanate-based adhesives for flexible packaging presents another technical hurdle. Achieving the right balance between flexibility, strength, and barrier properties often involves complex formulation adjustments. The cross-linking density of isocyanate-based polymers must be carefully controlled to maintain the desired mechanical properties without compromising the flexibility essential for packaging applications.
Furthermore, the compatibility of isocyanates with various substrate materials used in flexible packaging can be problematic. Different surface energies and chemical compositions of substrates may lead to adhesion issues or unwanted reactions, necessitating the development of specialized primers or surface treatments. This challenge is particularly pronounced when dealing with multi-layer packaging structures, where each layer may require a different approach to ensure optimal bonding.
The development of bio-based or more sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived isocyanates represents another significant technical challenge. While there is growing demand for environmentally friendly packaging solutions, creating bio-based isocyanates that match the performance of conventional ones in terms of reactivity, durability, and cost-effectiveness remains an ongoing research focus.
Lastly, the volatility of isocyanate monomers poses challenges in processing and application. Controlling the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing and ensuring complete reaction of isocyanates to prevent off-gassing in the final product are critical considerations. This necessitates advanced process control systems and curing technologies to minimize environmental impact and ensure product safety.
Current Isocyanate Solutions
01 Synthesis and production of isocyanates
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel reaction pathways, catalysts, and production techniques to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate manufacturing.- Synthesis and production of isocyanates: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing isocyanates are described. These include novel catalysts, reaction conditions, and precursor materials to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in isocyanate production.
- Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry: Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents describe various applications, including coatings, adhesives, foams, and elastomers, as well as novel formulations and processing techniques.
- Isocyanate-based catalysts and additives: Several patents focus on the development of isocyanate-based catalysts and additives for various chemical processes. These include novel catalyst systems, stabilizers, and modifiers that enhance reaction rates, selectivity, or product properties.
- Safety and handling of isocyanates: Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, patents address safety concerns and handling procedures. This includes methods for reducing toxicity, improving storage stability, and developing safer alternatives or modified isocyanates with reduced health risks.
- Isocyanate-free alternatives and substitutes: Some patents explore alternatives to traditional isocyanates, aiming to address environmental and health concerns. These include bio-based isocyanates, isocyanate-free polyurethanes, and alternative chemistries that mimic isocyanate functionality.
02 Applications of isocyanates in polymer chemistry
Isocyanates are widely used in polymer chemistry, particularly in the production of polyurethanes. The patents discuss different formulations, reaction conditions, and additives to enhance the properties of isocyanate-based polymers for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-based coatings and adhesives
The use of isocyanates in coatings and adhesives is explored, detailing formulations, curing mechanisms, and performance characteristics. These innovations aim to improve durability, adhesion, and chemical resistance in various industrial and consumer applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Given the reactive nature of isocyanates, several patents focus on improving safety in handling and storage. This includes developing stabilizers, protective equipment, and methods to reduce exposure risks associated with isocyanate compounds.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isocyanate modifications and derivatives
Research into modifying isocyanates or creating novel derivatives is presented. These modifications aim to enhance specific properties, reduce toxicity, or create new functionalities for specialized applications in various industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Flexible Packaging Players
The isocyanate market in flexible packaging solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance materials. The industry is in a mature stage but continues to evolve with technological advancements. Market size is expanding due to the rising adoption of flexible packaging across various sectors. Technologically, companies like Wanhua Chemical, BASF, Covestro, and Dow are at the forefront, developing innovative isocyanate-based solutions. These key players are focusing on eco-friendly formulations and enhanced performance characteristics to meet stringent regulatory requirements and consumer preferences. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense R&D activities and strategic collaborations to gain a competitive edge in this dynamic market.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed innovative isocyanate-based solutions for flexible packaging. Their approach involves using modified methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and toluene diisocyanate (TDI) to create high-performance polyurethane adhesives. These adhesives offer excellent bonding strength, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making them ideal for multi-layer film structures in food packaging and other applications[1]. Wanhua has also introduced water-based polyurethane dispersions (PUDs) that incorporate isocyanate technology, providing environmentally friendly options without compromising on performance[2]. Their isocyanate-terminated prepolymers enable customized adhesive formulations to meet specific packaging requirements, such as heat resistance and low migration properties[3].
Strengths: Wide range of isocyanate-based solutions, strong R&D capabilities, environmentally friendly options. Weaknesses: Potential health and safety concerns associated with isocyanate handling, regulatory challenges in some markets.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a comprehensive portfolio of isocyanate-based solutions for flexible packaging. Their Elastollan® thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) range, derived from isocyanates, offers excellent flexibility, transparency, and barrier properties for packaging films[4]. BASF's Lupranate® isocyanates are used in laminating adhesives, providing high bond strength and chemical resistance in multi-layer packaging structures[5]. The company has also introduced bio-based isocyanates, such as their Hexamethylene Diisocyanate (HDI) derivatives, which contribute to more sustainable packaging solutions without compromising performance[6]. BASF's isocyanate technology enables the development of solvent-free and low-monomer adhesive systems, addressing both environmental and safety concerns in flexible packaging applications.
Strengths: Diverse product portfolio, strong focus on sustainability, global presence. Weaknesses: Complex supply chain management, potential exposure to raw material price fluctuations.
Breakthrough Isocyanate Patents
Adhesive composition and soft packaging material composite film
PatentWO2004011570A1
Innovation
- A polyisocyanate-based adhesive composition using a polyester polyamide polyol with amide bonds formed from dimer acid and polyamine, which reduces cyclic compound elution and maintains adhesive strength and flexibility, incorporating a silane coupling agent for enhanced adhesion.
Isocyanate composition and its use in the preparation of expanded polyurethane with improved physico-mechanical properties
PatentInactiveEP1385894A1
Innovation
- Development of MDI-based isocyanate compositions that use water as the sole expanding agent, combining methylene diphenyl isocyanate with specific polyether polyols and polymeric methylene diphenyl isocyanate to create flexible expanded polyurethanes with improved properties, including high elongation and dynamic fatigue resistance.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of isocyanates in flexible packaging solutions has significant environmental implications that require careful consideration. These chemicals, while innovative in their applications, pose potential risks to ecosystems and human health throughout their lifecycle.
During the production phase, the synthesis of isocyanates involves the use of hazardous materials and energy-intensive processes. This contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources. Additionally, the manufacturing process may generate toxic by-products that require proper disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
In the application stage, isocyanates used in flexible packaging can potentially leach into food or other packaged products. This raises concerns about food safety and the potential for human exposure to these chemicals. While modern packaging technologies have improved containment, the long-term effects of low-level exposure remain a subject of ongoing research.
The disposal of flexible packaging containing isocyanates presents another environmental challenge. These materials are not easily biodegradable and can persist in landfills for extended periods. Incineration of isocyanate-containing packaging may release harmful emissions, including nitrogen oxides and other toxic compounds, necessitating advanced pollution control measures.
However, it's important to note that isocyanates also contribute to environmental sustainability in certain aspects. Their use in flexible packaging often results in lighter, more durable materials that can reduce overall packaging waste. This can lead to decreased transportation-related emissions and energy consumption in the supply chain.
Furthermore, advancements in isocyanate chemistry have led to the development of more environmentally friendly formulations. Water-based systems and bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are emerging as promising alternatives, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of flexible packaging solutions.
The recyclability of isocyanate-based packaging materials is an area of ongoing research and development. While current recycling processes for these materials are limited, innovations in chemical recycling and depolymerization techniques show potential for improving the circularity of isocyanate-containing packaging in the future.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of packaging materials, including those containing isocyanates. This has led to stricter regulations on emissions, disposal, and recycling, driving the industry towards more sustainable practices and technologies.
During the production phase, the synthesis of isocyanates involves the use of hazardous materials and energy-intensive processes. This contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and the depletion of non-renewable resources. Additionally, the manufacturing process may generate toxic by-products that require proper disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
In the application stage, isocyanates used in flexible packaging can potentially leach into food or other packaged products. This raises concerns about food safety and the potential for human exposure to these chemicals. While modern packaging technologies have improved containment, the long-term effects of low-level exposure remain a subject of ongoing research.
The disposal of flexible packaging containing isocyanates presents another environmental challenge. These materials are not easily biodegradable and can persist in landfills for extended periods. Incineration of isocyanate-containing packaging may release harmful emissions, including nitrogen oxides and other toxic compounds, necessitating advanced pollution control measures.
However, it's important to note that isocyanates also contribute to environmental sustainability in certain aspects. Their use in flexible packaging often results in lighter, more durable materials that can reduce overall packaging waste. This can lead to decreased transportation-related emissions and energy consumption in the supply chain.
Furthermore, advancements in isocyanate chemistry have led to the development of more environmentally friendly formulations. Water-based systems and bio-based isocyanates derived from renewable resources are emerging as promising alternatives, potentially reducing the environmental footprint of flexible packaging solutions.
The recyclability of isocyanate-based packaging materials is an area of ongoing research and development. While current recycling processes for these materials are limited, innovations in chemical recycling and depolymerization techniques show potential for improving the circularity of isocyanate-containing packaging in the future.
Regulatory bodies worldwide are increasingly focusing on the environmental impact of packaging materials, including those containing isocyanates. This has led to stricter regulations on emissions, disposal, and recycling, driving the industry towards more sustainable practices and technologies.
Regulatory Compliance Overview
The regulatory landscape for isocyanates in flexible packaging solutions is complex and evolving, with various agencies and standards governing their use. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which requires manufacturers to report new uses and potential risks. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets exposure limits and safety standards for workers handling isocyanates in manufacturing processes.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation plays a crucial role in controlling isocyanate use. REACH mandates the registration of substances, including isocyanates, and requires manufacturers to provide safety data and risk assessments. The EU has also implemented specific restrictions on certain isocyanates, such as methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), in consumer products.
Food contact regulations are particularly relevant for flexible packaging applications. In the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates materials that come into contact with food, including packaging made with isocyanates. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with FDA regulations, such as 21 CFR 175.105 for adhesives and 21 CFR 177.1390 for laminate structures.
Globally, many countries have adopted similar regulatory frameworks or follow international standards. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines for testing and quality control of isocyanate-based products, which are often referenced in regulatory compliance efforts.
Environmental regulations also impact isocyanate use in flexible packaging. Many jurisdictions have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission limits, affecting the formulation and application of isocyanate-based adhesives and coatings. Additionally, waste management and disposal regulations must be considered throughout the product lifecycle.
As sustainability concerns grow, regulations are increasingly focusing on the recyclability and biodegradability of packaging materials. This trend is driving innovation in isocyanate chemistry to develop more environmentally friendly solutions that maintain performance while meeting stricter regulatory requirements.
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation from manufacturers. Companies must invest in robust quality control systems, conduct regular testing, and maintain detailed documentation to demonstrate regulatory adherence. As regulations continue to evolve, staying informed and proactively addressing emerging requirements is crucial for success in the flexible packaging market.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation plays a crucial role in controlling isocyanate use. REACH mandates the registration of substances, including isocyanates, and requires manufacturers to provide safety data and risk assessments. The EU has also implemented specific restrictions on certain isocyanates, such as methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI), in consumer products.
Food contact regulations are particularly relevant for flexible packaging applications. In the US, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates materials that come into contact with food, including packaging made with isocyanates. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with FDA regulations, such as 21 CFR 175.105 for adhesives and 21 CFR 177.1390 for laminate structures.
Globally, many countries have adopted similar regulatory frameworks or follow international standards. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides guidelines for testing and quality control of isocyanate-based products, which are often referenced in regulatory compliance efforts.
Environmental regulations also impact isocyanate use in flexible packaging. Many jurisdictions have implemented volatile organic compound (VOC) emission limits, affecting the formulation and application of isocyanate-based adhesives and coatings. Additionally, waste management and disposal regulations must be considered throughout the product lifecycle.
As sustainability concerns grow, regulations are increasingly focusing on the recyclability and biodegradability of packaging materials. This trend is driving innovation in isocyanate chemistry to develop more environmentally friendly solutions that maintain performance while meeting stricter regulatory requirements.
Compliance with these diverse regulations requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation from manufacturers. Companies must invest in robust quality control systems, conduct regular testing, and maintain detailed documentation to demonstrate regulatory adherence. As regulations continue to evolve, staying informed and proactively addressing emerging requirements is crucial for success in the flexible packaging market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!