How 5G UC Enhances the Efficiency of Global Trade Operations
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC in Global Trade: Background and Objectives
The advent of 5G technology has ushered in a new era of connectivity, promising unprecedented speed, reliability, and capacity. Within this technological revolution, 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) stands out as a game-changer for global trade operations. This report aims to explore how 5G UC can enhance the efficiency of international commerce, setting the stage for a comprehensive analysis of its potential impact.
5G UC, characterized by its high-band spectrum utilization, offers significantly faster data speeds and lower latency compared to its predecessors. In the context of global trade, this technology has the potential to transform various aspects of operations, from supply chain management to customs procedures and financial transactions. The primary objective of this investigation is to identify and evaluate the specific ways in which 5G UC can streamline trade processes, reduce costs, and increase overall operational efficiency.
The evolution of global trade has been closely tied to advancements in communication and transportation technologies. From the telegraph to the internet, each leap forward has accelerated the pace and expanded the scope of international commerce. 5G UC represents the next frontier in this progression, offering the potential to overcome existing bottlenecks and create new opportunities for trade optimization.
As we delve into the background of 5G UC in global trade, it's crucial to understand the current challenges faced by international trade operations. These include delays in customs clearance, inefficiencies in supply chain visibility, and difficulties in real-time tracking of goods. The integration of 5G UC technology aims to address these pain points by enabling faster data transmission, supporting more connected devices, and facilitating real-time decision-making.
The objectives of this technical research report are multifaceted. Firstly, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of 5G UC technology and its relevance to global trade. Secondly, we will explore the potential applications of 5G UC across various aspects of trade operations, including logistics, documentation, and regulatory compliance. Thirdly, we intend to assess the readiness of existing trade infrastructure to adopt and benefit from 5G UC technology.
Furthermore, this report will examine the potential economic impact of 5G UC on global trade, considering factors such as reduced transaction costs, improved resource allocation, and enhanced market access for businesses of all sizes. We will also investigate the challenges and barriers to the widespread adoption of 5G UC in trade operations, including issues related to infrastructure development, international standards, and cybersecurity concerns.
5G UC, characterized by its high-band spectrum utilization, offers significantly faster data speeds and lower latency compared to its predecessors. In the context of global trade, this technology has the potential to transform various aspects of operations, from supply chain management to customs procedures and financial transactions. The primary objective of this investigation is to identify and evaluate the specific ways in which 5G UC can streamline trade processes, reduce costs, and increase overall operational efficiency.
The evolution of global trade has been closely tied to advancements in communication and transportation technologies. From the telegraph to the internet, each leap forward has accelerated the pace and expanded the scope of international commerce. 5G UC represents the next frontier in this progression, offering the potential to overcome existing bottlenecks and create new opportunities for trade optimization.
As we delve into the background of 5G UC in global trade, it's crucial to understand the current challenges faced by international trade operations. These include delays in customs clearance, inefficiencies in supply chain visibility, and difficulties in real-time tracking of goods. The integration of 5G UC technology aims to address these pain points by enabling faster data transmission, supporting more connected devices, and facilitating real-time decision-making.
The objectives of this technical research report are multifaceted. Firstly, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of 5G UC technology and its relevance to global trade. Secondly, we will explore the potential applications of 5G UC across various aspects of trade operations, including logistics, documentation, and regulatory compliance. Thirdly, we intend to assess the readiness of existing trade infrastructure to adopt and benefit from 5G UC technology.
Furthermore, this report will examine the potential economic impact of 5G UC on global trade, considering factors such as reduced transaction costs, improved resource allocation, and enhanced market access for businesses of all sizes. We will also investigate the challenges and barriers to the widespread adoption of 5G UC in trade operations, including issues related to infrastructure development, international standards, and cybersecurity concerns.
Market Demand Analysis for 5G UC in Trade
The global trade industry is experiencing a significant transformation with the advent of 5G UC (Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication) technology. Market demand for 5G UC in trade operations is rapidly growing as businesses seek to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance in their supply chain and logistics processes.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the need for real-time visibility and tracking of goods throughout the supply chain. 5G UC enables seamless connectivity and data transfer between various stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, logistics providers, and customs authorities. This enhanced connectivity allows for more accurate and timely information exchange, reducing delays and improving decision-making capabilities.
The demand for 5G UC in trade is also fueled by the increasing complexity of global supply chains. As businesses expand their operations across multiple countries and regions, they require more sophisticated communication and coordination tools. 5G UC provides the necessary infrastructure to support advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence, and blockchain, which are becoming increasingly crucial in managing complex trade operations.
Another significant factor driving market demand is the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility in trade. 5G UC enables more efficient route planning, load optimization, and energy management in transportation and logistics, leading to reduced carbon emissions and improved resource utilization. This aligns with the global push for greener trade practices and meets the demands of environmentally conscious consumers and regulatory bodies.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for 5G UC in trade operations. The crisis highlighted the vulnerabilities in global supply chains and the need for more resilient and flexible systems. 5G UC offers the potential to create more agile and adaptable trade networks that can better withstand disruptions and respond to rapidly changing market conditions.
In the financial aspect of trade, 5G UC is driving demand for faster and more secure cross-border transactions. The technology enables near-instantaneous processing of payments and financial documents, reducing the risk of fraud and improving cash flow for businesses engaged in international trade. This is particularly important in an era where trade finance is becoming increasingly digital and automated.
As trade operations become more data-driven, there is a growing demand for 5G UC to support advanced analytics and predictive modeling. The high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G enable real-time data processing and analysis, allowing businesses to make more informed decisions and optimize their trade strategies based on up-to-the-minute market insights.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the need for real-time visibility and tracking of goods throughout the supply chain. 5G UC enables seamless connectivity and data transfer between various stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, logistics providers, and customs authorities. This enhanced connectivity allows for more accurate and timely information exchange, reducing delays and improving decision-making capabilities.
The demand for 5G UC in trade is also fueled by the increasing complexity of global supply chains. As businesses expand their operations across multiple countries and regions, they require more sophisticated communication and coordination tools. 5G UC provides the necessary infrastructure to support advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence, and blockchain, which are becoming increasingly crucial in managing complex trade operations.
Another significant factor driving market demand is the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility in trade. 5G UC enables more efficient route planning, load optimization, and energy management in transportation and logistics, leading to reduced carbon emissions and improved resource utilization. This aligns with the global push for greener trade practices and meets the demands of environmentally conscious consumers and regulatory bodies.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the demand for 5G UC in trade operations. The crisis highlighted the vulnerabilities in global supply chains and the need for more resilient and flexible systems. 5G UC offers the potential to create more agile and adaptable trade networks that can better withstand disruptions and respond to rapidly changing market conditions.
In the financial aspect of trade, 5G UC is driving demand for faster and more secure cross-border transactions. The technology enables near-instantaneous processing of payments and financial documents, reducing the risk of fraud and improving cash flow for businesses engaged in international trade. This is particularly important in an era where trade finance is becoming increasingly digital and automated.
As trade operations become more data-driven, there is a growing demand for 5G UC to support advanced analytics and predictive modeling. The high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G enable real-time data processing and analysis, allowing businesses to make more informed decisions and optimize their trade strategies based on up-to-the-minute market insights.
Current State and Challenges of 5G UC Implementation
The implementation of 5G UC (Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication) in global trade operations is currently in a transitional phase, with significant progress made in some areas while facing challenges in others. Many major ports and logistics hubs worldwide have begun integrating 5G UC technology into their operations, leveraging its high-speed, low-latency capabilities to enhance efficiency and automation.
In advanced markets such as China, South Korea, and parts of Europe, 5G UC has been successfully deployed in smart ports, enabling real-time tracking of containers, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and remote-controlled cranes. These implementations have shown promising results in reducing operational costs and improving throughput. For instance, the Port of Hamburg in Germany has reported a 5-10% increase in operational efficiency since implementing 5G-enabled solutions.
However, the global rollout of 5G UC in trade operations faces several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the uneven infrastructure development across different regions. While some countries have made substantial investments in 5G networks, others are still in the early stages of deployment or are struggling with spectrum allocation issues. This disparity creates bottlenecks in establishing seamless, end-to-end 5G UC-enabled trade routes.
Another significant challenge is the high cost associated with upgrading existing systems to be 5G UC-compatible. Many ports and logistics companies, particularly in developing economies, find it difficult to justify the substantial capital expenditure required for a complete overhaul of their infrastructure. This financial barrier has led to a fragmented adoption landscape, where only certain segments of the supply chain are 5G UC-enabled.
Cybersecurity concerns also pose a considerable challenge to the widespread implementation of 5G UC in global trade. The increased connectivity and data flow inherent in 5G networks expand the potential attack surface for cybercriminals. Ensuring robust security measures without compromising the speed and efficiency benefits of 5G UC remains a complex task for implementers.
Interoperability issues between different 5G UC systems and existing technologies present another hurdle. The lack of standardized protocols across various countries and operators can lead to compatibility problems, hindering the seamless flow of data and operations across borders. This challenge is particularly acute in the context of global trade, where multiple stakeholders and systems need to interact efficiently.
Regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements vary significantly across different jurisdictions, creating additional complexity for the implementation of 5G UC in global trade operations. Harmonizing these regulations to facilitate cross-border 5G UC-enabled trade processes is a time-consuming and politically sensitive process.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of 5G UC in enhancing global trade efficiency continue to drive innovation and investment in this area. As technology matures and best practices emerge, it is expected that many of these obstacles will be gradually overcome, paving the way for more widespread adoption and integration of 5G UC in global trade operations.
In advanced markets such as China, South Korea, and parts of Europe, 5G UC has been successfully deployed in smart ports, enabling real-time tracking of containers, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and remote-controlled cranes. These implementations have shown promising results in reducing operational costs and improving throughput. For instance, the Port of Hamburg in Germany has reported a 5-10% increase in operational efficiency since implementing 5G-enabled solutions.
However, the global rollout of 5G UC in trade operations faces several challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the uneven infrastructure development across different regions. While some countries have made substantial investments in 5G networks, others are still in the early stages of deployment or are struggling with spectrum allocation issues. This disparity creates bottlenecks in establishing seamless, end-to-end 5G UC-enabled trade routes.
Another significant challenge is the high cost associated with upgrading existing systems to be 5G UC-compatible. Many ports and logistics companies, particularly in developing economies, find it difficult to justify the substantial capital expenditure required for a complete overhaul of their infrastructure. This financial barrier has led to a fragmented adoption landscape, where only certain segments of the supply chain are 5G UC-enabled.
Cybersecurity concerns also pose a considerable challenge to the widespread implementation of 5G UC in global trade. The increased connectivity and data flow inherent in 5G networks expand the potential attack surface for cybercriminals. Ensuring robust security measures without compromising the speed and efficiency benefits of 5G UC remains a complex task for implementers.
Interoperability issues between different 5G UC systems and existing technologies present another hurdle. The lack of standardized protocols across various countries and operators can lead to compatibility problems, hindering the seamless flow of data and operations across borders. This challenge is particularly acute in the context of global trade, where multiple stakeholders and systems need to interact efficiently.
Regulatory frameworks and compliance requirements vary significantly across different jurisdictions, creating additional complexity for the implementation of 5G UC in global trade operations. Harmonizing these regulations to facilitate cross-border 5G UC-enabled trade processes is a time-consuming and politically sensitive process.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of 5G UC in enhancing global trade efficiency continue to drive innovation and investment in this area. As technology matures and best practices emerge, it is expected that many of these obstacles will be gradually overcome, paving the way for more widespread adoption and integration of 5G UC in global trade operations.
Existing 5G UC Solutions for Trade Efficiency
01 Network resource allocation and optimization
5G UC efficiency can be improved through intelligent allocation and optimization of network resources. This includes dynamic spectrum sharing, adaptive beamforming, and load balancing techniques to maximize capacity utilization and enhance overall network performance.- Network resource allocation and optimization: 5G UC efficiency can be improved through intelligent allocation and optimization of network resources. This includes dynamic spectrum sharing, adaptive beamforming, and advanced scheduling algorithms to maximize capacity and minimize latency. These techniques allow for better utilization of available bandwidth and improved overall network performance.
- Advanced antenna technologies: Implementation of advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) and beamforming can significantly enhance 5G UC efficiency. These technologies enable more focused and directional signal transmission, resulting in improved coverage, capacity, and energy efficiency in ultra-capacity networks.
- Edge computing and network slicing: Leveraging edge computing and network slicing techniques can optimize 5G UC efficiency. By bringing computing resources closer to the end-user and creating dedicated virtual networks for specific applications, latency is reduced, and network resources are more efficiently utilized, leading to improved overall performance.
- AI and machine learning integration: Incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into 5G UC networks can enhance efficiency through predictive analytics, automated network optimization, and intelligent traffic management. These technologies enable networks to adapt in real-time to changing conditions and user demands.
- Energy-efficient hardware and protocols: Developing and implementing energy-efficient hardware components and communication protocols can improve the overall efficiency of 5G UC networks. This includes low-power radio frequency (RF) components, energy-aware routing algorithms, and sleep mode optimization for network elements during periods of low activity.
02 Advanced antenna technologies
Implementation of advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO and beamforming can significantly enhance 5G UC efficiency. These technologies enable better spatial multiplexing, improved signal quality, and increased spectral efficiency in ultra-capacity networks.Expand Specific Solutions03 Edge computing and caching
Integrating edge computing and caching mechanisms in 5G UC networks can reduce latency and improve overall efficiency. By processing data closer to the end-user and caching frequently accessed content, network congestion is reduced and response times are improved.Expand Specific Solutions04 AI-driven network optimization
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms can be employed to predict network traffic patterns, optimize resource allocation, and automate network management processes. This leads to improved efficiency and adaptability in 5G UC networks.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-efficient network design
Implementing energy-efficient network architectures and protocols can enhance the overall efficiency of 5G UC networks. This includes adaptive power management, sleep mode optimization for base stations, and energy-aware routing algorithms to reduce power consumption while maintaining high performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC and Global Trade Ecosystem
The 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) technology is in a rapid growth phase, with the global market for 5G infrastructure expected to expand significantly in the coming years. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry among major players such as Qualcomm, Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, and Samsung, who are investing heavily in R&D to develop advanced 5G solutions. These companies are at various stages of technological maturity, with some like Qualcomm and Huawei leading in patent filings and commercial deployments. The market is also seeing increased participation from telecom operators like NTT Docomo and China Telecom, as well as emerging players like Xiaomi and OPPO, who are focusing on 5G-enabled devices and applications to enhance global trade operations.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm's 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) technology enhances global trade operations through its advanced 5G modem-RF systems. The company's Snapdragon X65 5G Modem-RF System supports 5G mmWave and sub-6 GHz bands, enabling ultra-fast data speeds up to 10 Gbps[1]. This high-speed connectivity facilitates real-time tracking of shipments, efficient inventory management, and seamless communication across global supply chains. Qualcomm's 5G solutions also incorporate AI-powered network optimization, reducing latency and improving reliability for critical trade operations[2]. The company's 5G RAN platforms support virtualized and Open RAN architectures, allowing for more flexible and cost-effective network deployments in ports and logistics hubs[3].
Strengths: Industry-leading 5G modem technology, extensive ecosystem partnerships, and strong intellectual property portfolio. Weaknesses: Dependence on smartphone market, potential geopolitical challenges in certain markets.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei's 5G UC solutions for global trade operations focus on creating intelligent ports and smart logistics networks. The company's 5G Super Uplink technology provides ultra-high bandwidth and low latency, enabling real-time monitoring and control of port operations[4]. Huawei's 5G-powered smart container management system uses IoT sensors and AI analytics to optimize container handling and storage, reducing turnaround times by up to 20%[5]. The company's 5G-V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) technology enhances autonomous vehicle operations in ports, improving safety and efficiency. Huawei's end-to-end 5G network slicing capabilities allow for dedicated, customized network resources for different trade operation needs, ensuring quality of service for critical applications[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive 5G portfolio, strong R&D capabilities, and experience in large-scale network deployments. Weaknesses: Geopolitical challenges and restrictions in some markets, potential supply chain disruptions.
Core Innovations in 5G UC for Trade Operations
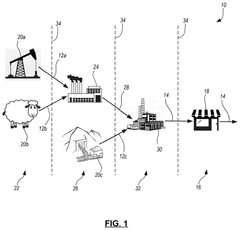
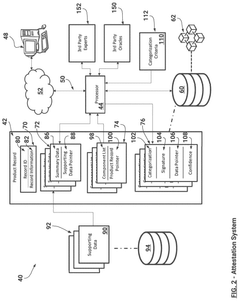
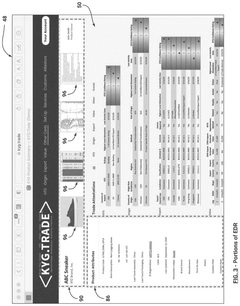
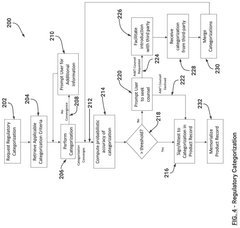
System and method for facilitating global trade and sustainable enviromental social governance management and compliance
PatentPendingUS20250191000A1
Innovation
- A computerized system utilizing a hierarchy of blockchain and distributed ledger technology to provide on-demand access to global trade and SESG documentation and attestations, streamlining data gathering and analysis by making product attribute source documents and categorization determinations accessible to multiple stakeholders.
Industrial automation with 5g and beyond
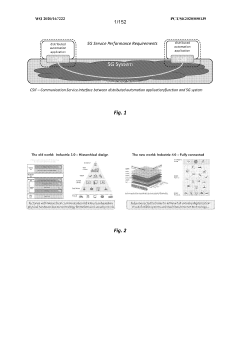
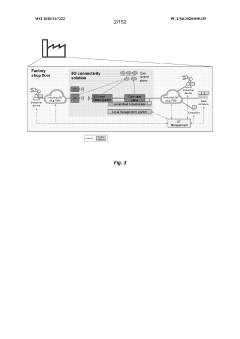
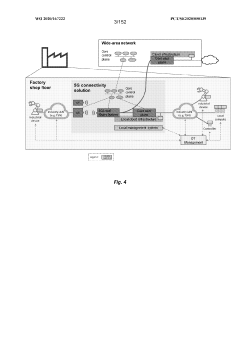
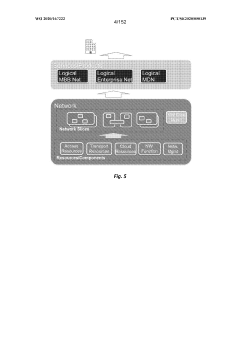
PatentWO2020167222A2
Innovation
- The integration of 5G wireless networks with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) techniques, including methods for establishing TSN data streams, configuring data packets, and managing radio resources, to provide deterministic and reliable communication services within industrial environments.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC in International Trade
The regulatory framework for 5G UC in international trade is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful consideration and coordination among various stakeholders. As 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) technology continues to revolutionize global trade operations, governments and international organizations are working to establish comprehensive guidelines and standards to ensure its safe and effective implementation.
At the forefront of this regulatory effort is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which plays a crucial role in developing global standards for 5G technology. The ITU's IMT-2020 specifications provide a foundation for 5G UC deployment in international trade, addressing key aspects such as spectrum allocation, network architecture, and performance requirements.
National regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and the European Electronic Communications Code (EECC) in the European Union, are adapting their existing frameworks to accommodate 5G UC technology. These agencies are focusing on issues like spectrum licensing, infrastructure deployment, and cybersecurity measures to support the integration of 5G UC in trade operations.
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is also playing a significant role in shaping the regulatory landscape for 5G UC in international trade. The WTO's Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) and the Information Technology Agreement (ITA) provide frameworks for ensuring that technical regulations and standards do not create unnecessary obstacles to trade while promoting the adoption of new technologies like 5G UC.
Data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US, are being adapted to address the unique challenges posed by 5G UC in trade operations. These regulations aim to safeguard sensitive trade data transmitted over 5G networks while enabling the efficient flow of information necessary for global commerce.
Cybersecurity frameworks are being developed and updated to address the specific vulnerabilities associated with 5G UC technology in trade operations. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework and the EU's Network and Information Security (NIS) Directive are examples of initiatives that provide guidelines for securing 5G UC infrastructure and protecting critical trade information.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), are developing technical standards specific to 5G UC applications in trade. These standards aim to ensure interoperability, reliability, and security across different 5G UC implementations in global supply chains and logistics systems.
As the regulatory framework for 5G UC in international trade continues to evolve, collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and international organizations will be crucial. This collaborative approach will help strike a balance between fostering innovation, ensuring security, and promoting fair competition in the global trade ecosystem enhanced by 5G UC technology.
At the forefront of this regulatory effort is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), which plays a crucial role in developing global standards for 5G technology. The ITU's IMT-2020 specifications provide a foundation for 5G UC deployment in international trade, addressing key aspects such as spectrum allocation, network architecture, and performance requirements.
National regulatory bodies, such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and the European Electronic Communications Code (EECC) in the European Union, are adapting their existing frameworks to accommodate 5G UC technology. These agencies are focusing on issues like spectrum licensing, infrastructure deployment, and cybersecurity measures to support the integration of 5G UC in trade operations.
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is also playing a significant role in shaping the regulatory landscape for 5G UC in international trade. The WTO's Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) and the Information Technology Agreement (ITA) provide frameworks for ensuring that technical regulations and standards do not create unnecessary obstacles to trade while promoting the adoption of new technologies like 5G UC.
Data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US, are being adapted to address the unique challenges posed by 5G UC in trade operations. These regulations aim to safeguard sensitive trade data transmitted over 5G networks while enabling the efficient flow of information necessary for global commerce.
Cybersecurity frameworks are being developed and updated to address the specific vulnerabilities associated with 5G UC technology in trade operations. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework and the EU's Network and Information Security (NIS) Directive are examples of initiatives that provide guidelines for securing 5G UC infrastructure and protecting critical trade information.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), are developing technical standards specific to 5G UC applications in trade. These standards aim to ensure interoperability, reliability, and security across different 5G UC implementations in global supply chains and logistics systems.
As the regulatory framework for 5G UC in international trade continues to evolve, collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and international organizations will be crucial. This collaborative approach will help strike a balance between fostering innovation, ensuring security, and promoting fair competition in the global trade ecosystem enhanced by 5G UC technology.
Economic Impact of 5G UC on Global Trade
The economic impact of 5G UC on global trade is expected to be substantial and far-reaching. As 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) networks continue to expand globally, they are poised to revolutionize international commerce by enhancing connectivity, speed, and reliability across supply chains and trade operations.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in global trade is the significant improvement in logistics and supply chain management. The technology enables real-time tracking and monitoring of goods, allowing for more efficient inventory management and reduced transit times. This enhanced visibility and control can lead to substantial cost savings for businesses engaged in international trade, as well as improved customer satisfaction due to more accurate delivery estimates and reduced delays.
Furthermore, 5G UC facilitates the implementation of advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices and artificial intelligence (AI) in trade operations. These technologies can optimize processes, automate decision-making, and provide valuable insights for businesses to streamline their operations. The resulting increase in efficiency and productivity can lead to reduced operational costs and improved competitiveness in the global marketplace.
The high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G UC also enable more seamless communication and collaboration between trade partners across different countries and time zones. This improved connectivity can accelerate decision-making processes, facilitate faster negotiations, and enable more agile responses to market changes. As a result, businesses can capitalize on new opportunities more quickly and effectively, potentially leading to increased trade volumes and economic growth.
In addition, 5G UC has the potential to democratize access to global markets for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). By providing reliable, high-speed connectivity even in remote areas, 5G UC can enable SMEs to participate more actively in international trade, accessing new customers and suppliers worldwide. This increased participation of SMEs in global trade can contribute to economic diversification and resilience, particularly in developing economies.
The financial sector, which plays a crucial role in facilitating global trade, is also set to benefit from 5G UC technology. Faster and more secure transactions, improved fraud detection, and enhanced risk management capabilities can all contribute to smoother trade financing operations. This can potentially reduce the costs associated with trade finance and make it more accessible to a broader range of businesses.
In conclusion, the economic impact of 5G UC on global trade is expected to be transformative, driving efficiency, productivity, and innovation across the entire trade ecosystem. As the technology continues to mature and expand, its effects are likely to become even more pronounced, potentially reshaping the landscape of international commerce and contributing to global economic growth.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in global trade is the significant improvement in logistics and supply chain management. The technology enables real-time tracking and monitoring of goods, allowing for more efficient inventory management and reduced transit times. This enhanced visibility and control can lead to substantial cost savings for businesses engaged in international trade, as well as improved customer satisfaction due to more accurate delivery estimates and reduced delays.
Furthermore, 5G UC facilitates the implementation of advanced technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices and artificial intelligence (AI) in trade operations. These technologies can optimize processes, automate decision-making, and provide valuable insights for businesses to streamline their operations. The resulting increase in efficiency and productivity can lead to reduced operational costs and improved competitiveness in the global marketplace.
The high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G UC also enable more seamless communication and collaboration between trade partners across different countries and time zones. This improved connectivity can accelerate decision-making processes, facilitate faster negotiations, and enable more agile responses to market changes. As a result, businesses can capitalize on new opportunities more quickly and effectively, potentially leading to increased trade volumes and economic growth.
In addition, 5G UC has the potential to democratize access to global markets for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). By providing reliable, high-speed connectivity even in remote areas, 5G UC can enable SMEs to participate more actively in international trade, accessing new customers and suppliers worldwide. This increased participation of SMEs in global trade can contribute to economic diversification and resilience, particularly in developing economies.
The financial sector, which plays a crucial role in facilitating global trade, is also set to benefit from 5G UC technology. Faster and more secure transactions, improved fraud detection, and enhanced risk management capabilities can all contribute to smoother trade financing operations. This can potentially reduce the costs associated with trade finance and make it more accessible to a broader range of businesses.
In conclusion, the economic impact of 5G UC on global trade is expected to be transformative, driving efficiency, productivity, and innovation across the entire trade ecosystem. As the technology continues to mature and expand, its effects are likely to become even more pronounced, potentially reshaping the landscape of international commerce and contributing to global economic growth.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!