Cellulose Acetate in Cosmetics: Benefits and Developments
Cellulose Acetate Evolution in Cosmetics
Cellulose acetate has undergone a significant evolution in the cosmetics industry, transforming from a simple film-forming agent to a multifunctional ingredient with diverse applications. Initially introduced in the 1950s as a replacement for celluloid in various products, cellulose acetate found its way into cosmetics due to its unique properties and versatility.
In the early stages of its use in cosmetics, cellulose acetate primarily served as a film-former in nail polishes and hair sprays. Its ability to create a smooth, glossy finish made it an ideal choice for these applications. As research progressed, formulators discovered additional benefits of cellulose acetate, leading to its incorporation in a wider range of cosmetic products.
The 1970s and 1980s saw a surge in cellulose acetate's popularity as a thickening agent and stabilizer in various cosmetic formulations. Its ability to improve the texture and consistency of creams, lotions, and gels made it a valuable ingredient in skincare products. During this period, manufacturers also began exploring its potential as a delivery system for active ingredients, recognizing its capacity to form microspheres and encapsulate various compounds.
The 1990s marked a turning point in cellulose acetate's evolution, as environmental concerns and the demand for sustainable ingredients gained prominence. Researchers focused on developing more eco-friendly production methods and exploring biodegradable variants of cellulose acetate. This shift led to the creation of modified cellulose acetate derivatives with enhanced properties and reduced environmental impact.
In the 2000s, advancements in nanotechnology opened new avenues for cellulose acetate in cosmetics. Nanofibers and nanoparticles of cellulose acetate began to be utilized in advanced skincare formulations, offering improved penetration of active ingredients and enhanced efficacy. This period also saw the development of cellulose acetate-based materials for controlled release of fragrances and other volatile compounds in cosmetic products.
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest in cellulose acetate's potential as a natural alternative to synthetic polymers in cosmetics. Its biocompatibility and biodegradability have made it an attractive option for brands focusing on clean and green beauty. Innovations in cellulose acetate technology have led to the creation of novel textures and sensory experiences in cosmetic products, further expanding its applications in the industry.
Today, cellulose acetate continues to evolve, with ongoing research focusing on enhancing its functional properties and sustainability profile. The development of bio-based cellulose acetate and its integration with other natural polymers represents the latest frontier in its evolution, promising even more diverse and eco-friendly applications in the cosmetics sector.
Market Demand for Sustainable Cosmetic Ingredients
The demand for sustainable cosmetic ingredients has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing consumer awareness of environmental issues and a shift towards more eco-friendly products. Cellulose acetate, a biodegradable and renewable material derived from wood pulp or cotton fibers, has emerged as a promising sustainable ingredient in the cosmetics industry.
Market research indicates that the global natural and organic cosmetics market is expected to grow significantly, with consumers increasingly seeking products that align with their values of sustainability and environmental responsibility. This trend has created a substantial opportunity for ingredients like cellulose acetate, which can replace synthetic and petroleum-based materials in various cosmetic formulations.
Cellulose acetate's versatility in cosmetic applications has contributed to its rising demand. It can be used as a film-forming agent in nail polishes, a thickener in creams and lotions, and a stabilizer in various cosmetic products. Its ability to enhance texture, improve product stability, and provide a smooth application experience has made it an attractive option for cosmetic manufacturers looking to meet consumer demands for sustainable yet high-performance products.
The market for cellulose acetate in cosmetics is also being driven by regulatory pressures and industry initiatives to reduce the use of microplastics and other environmentally harmful ingredients. As governments worldwide implement stricter regulations on cosmetic ingredients, manufacturers are turning to sustainable alternatives like cellulose acetate to comply with these new standards while maintaining product quality.
Consumer preferences for natural and plant-based ingredients have further bolstered the demand for cellulose acetate. Its plant-derived nature resonates with consumers seeking "clean" and "green" beauty products, leading to increased adoption by both established cosmetic brands and emerging clean beauty companies.
The potential for innovation in cellulose acetate-based cosmetic ingredients is also driving market growth. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring new modifications and applications of cellulose acetate to enhance its properties and expand its use in various cosmetic formulations. This ongoing innovation is expected to create new market opportunities and further increase demand for cellulose acetate in the cosmetics industry.
Current Applications and Challenges
Cellulose acetate has found widespread applications in the cosmetics industry, primarily due to its versatility and unique properties. Currently, it is extensively used in various cosmetic formulations, including nail polishes, hair sprays, and makeup products. In nail polishes, cellulose acetate serves as a film-forming agent, providing durability and shine to the final product. Its ability to create a smooth, glossy finish has made it a popular choice among manufacturers.
In hair care products, particularly hair sprays, cellulose acetate acts as a holding agent, offering long-lasting style retention without leaving a sticky residue. Its lightweight nature ensures that hair remains flexible and natural-looking while maintaining the desired shape. Additionally, cellulose acetate is utilized in makeup products such as mascaras and eyeliners, where it contributes to improved texture and longevity of the cosmetic application.
Despite its widespread use, the application of cellulose acetate in cosmetics faces several challenges. One significant issue is the environmental concern associated with its disposal. As a synthetic polymer, cellulose acetate can take a considerable time to biodegrade, contributing to plastic pollution. This has led to increased pressure on cosmetic companies to find more sustainable alternatives or develop improved biodegradable formulations of cellulose acetate.
Another challenge lies in the formulation process itself. Achieving the right balance of cellulose acetate in cosmetic products can be complex, as its concentration directly affects the product's performance and user experience. Too much cellulose acetate can lead to a stiff, unnatural feel, while too little may compromise the product's efficacy. Formulators must carefully optimize the cellulose acetate content to ensure optimal performance without sacrificing user comfort.
Furthermore, there is growing consumer demand for "clean" and natural cosmetics, which poses a challenge for synthetic ingredients like cellulose acetate. While it is derived from natural cellulose, the acetylation process renders it a semi-synthetic material. This classification can be problematic in marketing to consumers who prefer entirely natural or organic products. Cosmetic companies are thus challenged to either find natural alternatives or educate consumers about the safety and benefits of cellulose acetate in their formulations.
Regulatory compliance presents another hurdle for cellulose acetate in cosmetics. As global regulations become more stringent, particularly regarding the use of microplastics in rinse-off products, manufacturers must ensure that their cellulose acetate-containing formulations meet evolving standards. This may require reformulation or the development of new, compliant versions of existing products, which can be both time-consuming and costly for cosmetic companies.
Formulation Techniques with Cellulose Acetate
01 Biodegradability and environmental friendliness
Cellulose acetate is a biodegradable material derived from natural sources, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic polymers. Its ability to decompose naturally reduces environmental impact and contributes to sustainable product development.- Biodegradability and environmental friendliness: Cellulose acetate is a biodegradable material derived from natural sources, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic polymers. Its ability to decompose naturally reduces environmental impact and contributes to sustainable product development.
- Versatility in applications: Cellulose acetate offers versatility in various applications due to its unique properties. It can be used in textiles, filters, packaging materials, and even in the production of eyeglass frames. This versatility makes it a valuable material across multiple industries.
- Improved material properties: Cellulose acetate can be modified to enhance its properties, such as increased strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. These improvements expand its potential applications and make it suitable for use in demanding environments.
- Biocompatibility and medical applications: The biocompatibility of cellulose acetate makes it suitable for various medical applications. It can be used in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and other biomedical devices, offering advantages in terms of safety and effectiveness.
- Optical clarity and film-forming properties: Cellulose acetate possesses excellent optical clarity and film-forming properties, making it ideal for use in photographic films, protective coatings, and optical displays. These characteristics contribute to its widespread use in the imaging and electronics industries.
02 Versatility in textile and fiber applications
Cellulose acetate offers excellent properties for textile and fiber applications, including moisture absorption, breathability, and softness. It can be used to create comfortable and functional fabrics for clothing, upholstery, and industrial textiles.Expand Specific Solutions03 Optical clarity and film-forming properties
Cellulose acetate possesses high optical clarity and excellent film-forming properties, making it suitable for use in various optical and packaging applications. It can be used to produce clear films, sheets, and coatings with good mechanical strength and transparency.Expand Specific Solutions04 Improved material properties through modification
Cellulose acetate can be chemically modified or blended with other materials to enhance its properties, such as improved heat resistance, mechanical strength, or water resistance. This versatility allows for the development of tailored materials for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Biocompatibility and medical applications
Cellulose acetate exhibits good biocompatibility, making it suitable for various medical and pharmaceutical applications. It can be used in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and other biomedical devices, offering controlled release properties and low toxicity.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Cosmetic Cellulose Acetate
The cellulose acetate market in cosmetics is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and biodegradable ingredients. The industry is in a phase of rapid innovation and expansion, with a projected market size reaching billions of dollars globally. Technological maturity varies among key players, with companies like Daicel Corp., L'Oréal SA, and Shiseido Co., Ltd. leading in research and development. These firms are investing heavily in advanced formulations and applications of cellulose acetate in cosmetics. Emerging players such as ExoCoBio, Inc. and COSMAX, Inc. are also making strides in developing novel cellulose acetate-based products. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established multinational corporations and innovative startups, all vying for market share in this rapidly evolving sector.
Daicel Corp.
L'Oréal SA
Innovative Cellulose Acetate Derivatives
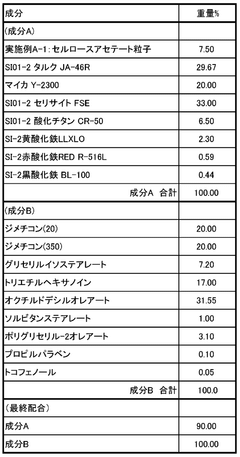
- Cellulose acetate particles with a specific range of average particle diameter, sphericity, relative specific surface area, and total degree of acetyl substitution are produced by mixing cellulose acetate with a plasticizer and thermoplastic polymers, then melt-kneaded and processed to achieve the desired properties, including high oil absorption and biodegradability.
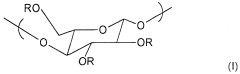
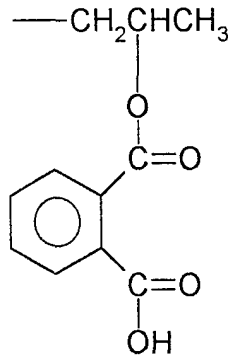
- A cosmetic composition incorporating cellulose esters like cellulose acetate phthalate, acetotrimellitate, or hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose phthalate, which provide film-forming properties, improve humidity resistance, and reduce VOC content, while maintaining softness and disentangling ease.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
The environmental impact and biodegradability of cellulose acetate in cosmetics are crucial considerations in the context of sustainable product development. Cellulose acetate, derived from natural cellulose, offers a more eco-friendly alternative to synthetic polymers commonly used in cosmetic formulations. Its biodegradability is a significant advantage, as it can break down into non-toxic components under appropriate conditions, reducing long-term environmental accumulation.
However, the biodegradation process of cellulose acetate is relatively slow compared to some other natural materials. In aquatic environments, it may take several months to years for complete decomposition, depending on factors such as temperature, microbial activity, and oxygen availability. This slower degradation rate can still lead to short-term accumulation in ecosystems if not properly managed.
The production of cellulose acetate involves chemical processes that may have environmental implications. While less energy-intensive than the production of many synthetic polymers, it still requires careful management of chemical inputs and waste streams to minimize ecological impact. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting green chemistry principles to optimize production processes and reduce environmental footprint.
In cosmetic applications, cellulose acetate's biodegradability offers advantages in products like disposable wipes or single-use packaging. When these items are discarded, they have the potential to break down more readily than their non-biodegradable counterparts. This property aligns with growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible personal care products.
The use of cellulose acetate in cosmetics also contributes to reducing microplastic pollution. Unlike synthetic microbeads, which have been banned in many countries due to their persistent environmental impact, cellulose acetate-based particles can serve as a biodegradable alternative in exfoliating products.
Recent developments in cellulose acetate technology have focused on enhancing its biodegradability and expanding its applications in cosmetics. Researchers are exploring modifications to the polymer structure to accelerate decomposition rates without compromising performance in cosmetic formulations. Additionally, efforts are underway to develop cellulose acetate-based materials with improved water solubility, further reducing environmental persistence.
As the cosmetics industry moves towards more sustainable practices, the environmental profile of cellulose acetate positions it as a promising material for future developments. Its renewable sourcing, biodegradability, and versatility make it an attractive option for companies seeking to reduce their ecological footprint while meeting consumer expectations for product performance and safety.
Regulatory Framework for Cellulose Acetate in Cosmetics
The regulatory framework for cellulose acetate in cosmetics is a complex and evolving landscape that varies across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the regulation of cosmetic products and ingredients, including cellulose acetate. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, cellulose acetate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food packaging and is also permitted in cosmetics, provided it does not cause adulteration or misbranding of the product.
The European Union, through the European Commission's Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009, has established a comprehensive framework for cosmetic products. Cellulose acetate is listed in the EU Cosmetic Ingredient Database (CosIng) and is allowed for use in cosmetic formulations. However, manufacturers must ensure that their products meet safety standards and comply with good manufacturing practices (GMP) as outlined in ISO 22716:2007.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare regulates cosmetics under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. Cellulose acetate is included in the list of approved ingredients for quasi-drugs and cosmetics. Similarly, in China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) oversees cosmetic regulations, and cellulose acetate is permitted for use in cosmetic products, subject to safety assessments and compliance with the Cosmetic Supervision and Administration Regulation (CSAR).
Globally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed standards relevant to cosmetic ingredients, including ISO 16128, which provides guidelines on definitions and criteria for natural and organic cosmetic ingredients. While not specifically addressing cellulose acetate, these standards influence the broader regulatory approach to cosmetic ingredients.
Environmental considerations are increasingly shaping regulatory frameworks. The growing concern over microplastics has led to discussions about potential restrictions on certain polymer-based ingredients in cosmetics. While cellulose acetate is biodegradable, regulators are closely monitoring its environmental impact and may introduce new guidelines or restrictions in the future.
Industry self-regulation also plays a role in the governance of cellulose acetate use. Organizations such as the Personal Care Products Council (PCPC) in the US and Cosmetics Europe in the EU provide guidelines and best practices for their members, which often exceed regulatory requirements.
As sustainability becomes a more prominent focus in cosmetic regulations, there is a trend towards promoting the use of bio-based and renewable materials. Cellulose acetate, being derived from natural cellulose, aligns well with this trend. However, manufacturers must remain vigilant about potential changes in regulations that may affect its use or require additional safety or environmental impact assessments.