Detecting potential root causes of data quality issues using data lineage graphs
a data quality and root cause technology, applied in the field of data lineage graphs to detect potential root causes of data quality issues, can solve problems such as the processing of data quality issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
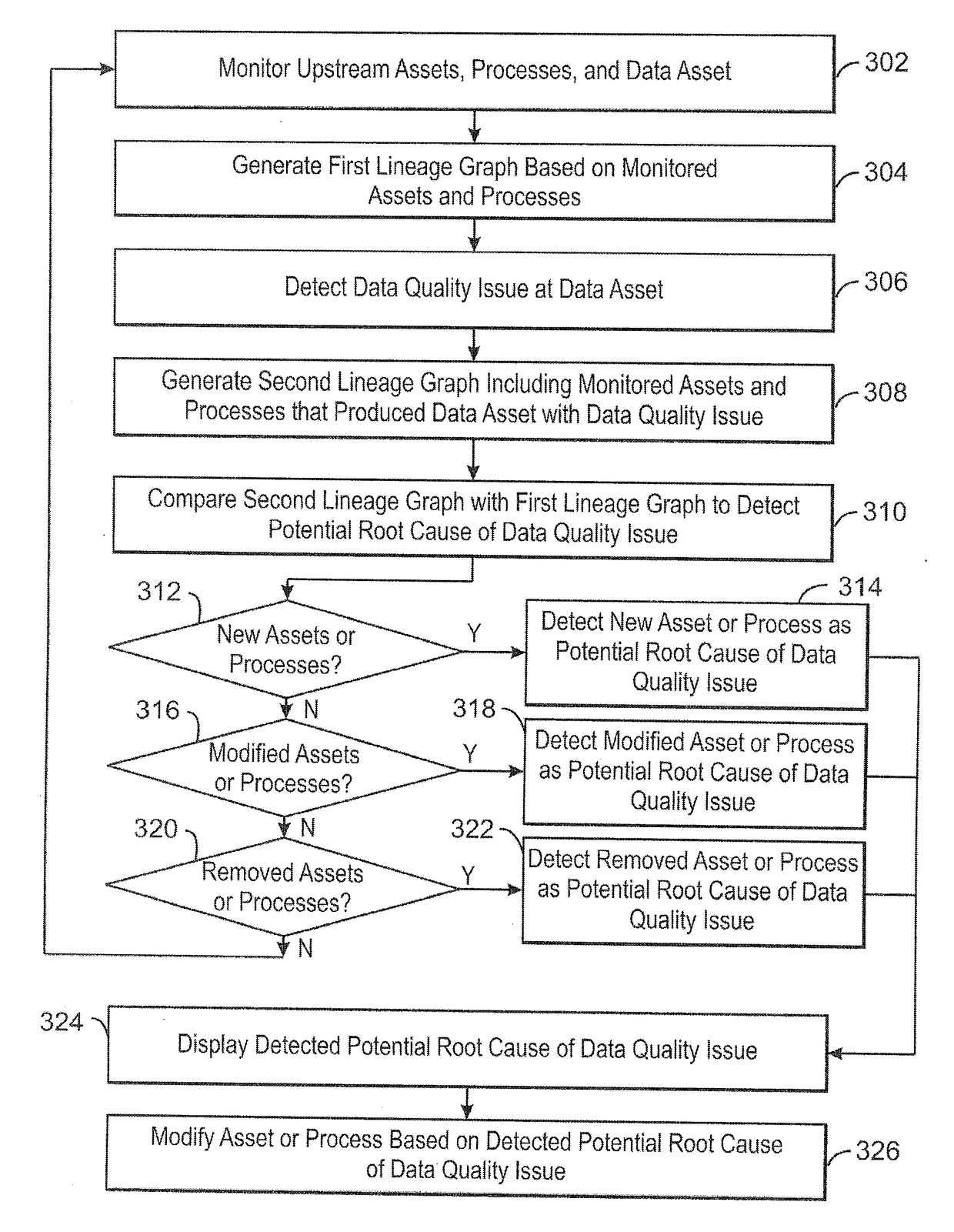
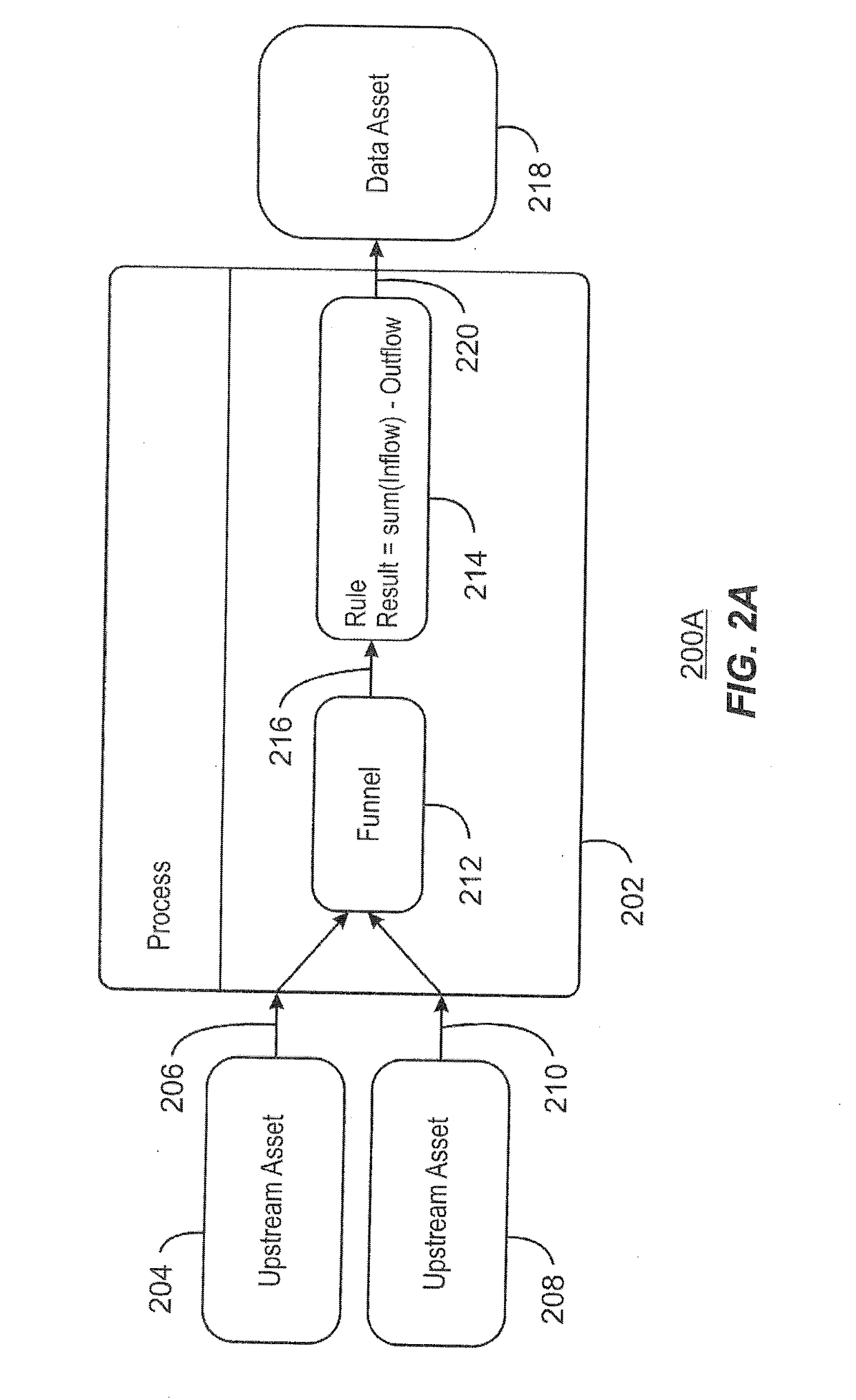
[0012]Many enterprises today rely on data assets to run their operational systems. A data asset, as used herein, refers to processed data that exists within a context of a larger data flow. For example, one or more processes may process data from one or more upstream assets and write the processed data to the data asset. An upstream asset, as used herein, refers to any source of data, including operational systems, data warehouses, and data marts, among other suitable data sources. A data asset, as used herein, refers to a target store of processed data. The processes can aggregate information such as, check information, cleaning information, mapping information between two values, and the like. For example, the processes can include extract, transform, and load (ETL) jobs reading from operational systems and writing to a data warehouse. Another example of a process is a data lifecycle management tool reading from a warehouse to create test data stored in a data asset. A further exa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com