Calculation method and application of river blocking by debris flow
A calculation method and technology of debris flow, applied in the direction of calculation, data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as affecting the accuracy of debris flow blocking rivers, unfavorable debris flow prevention and control effects, calculation errors, etc. factors, the effect of judgment results concise and to the point
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] A method for calculating river blockage by debris flow, comprising the following steps:
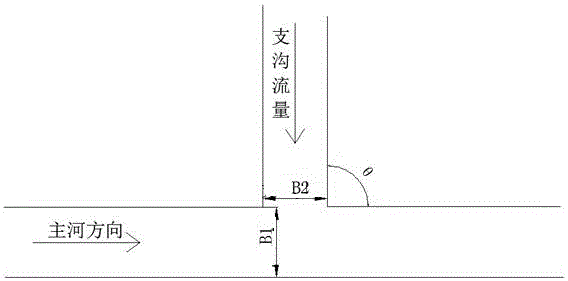
[0053] a. The confluence angle between the tributary ditch and the main river measured on the spot or on the topographic map ;
[0054] b. Measure the average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries B. 1 , unit m, main river flow Qm, unit m 3 / s, according to formula 1 to determine the single-width discharge Q of the main river 1 , unit m 2 / s;
[0055] (Formula 1);
[0056] c. Measure the average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary on the spot B 2 , unit m, debris flow flow , unit m 3 / s, according to the formula 2 to determine the flow rate of the single width of the tributary ditch 2 , unit m 2 / s;
[0057] (Formula 2);
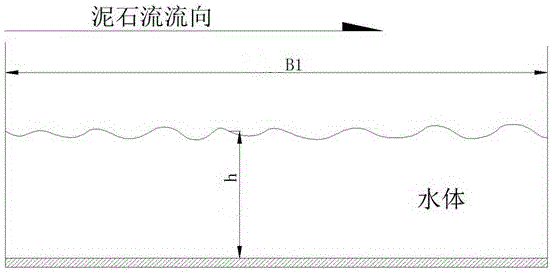
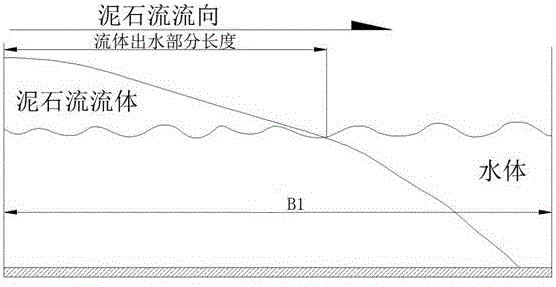
[0058] d. The single-width flow Q of the main river 1 and tributary single width flow 2 Substitute into Equation 3 to determine the single-width disch...
Embodiment 2
[0069] A method for calculating river blockage by debris flow, comprising the following steps:
[0070] a. The confluence angle between the tributary ditch and the main river measured on the spot or on the topographic map ;
[0071] b. Measure the average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries B. 1 , unit m, main river flow Qm, unit m 3 / s, according to formula 1 to determine the single-width discharge Q of the main river 1 , unit m 2 / s;
[0072] (Formula 1);
[0073] c. Measure the average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary on the spot B 2 , unit m, debris flow flow , unit m 3 / s, according to the formula 2 to determine the flow rate of the single width of the tributary ditch 2 , unit m 2 / s;
[0074] (Formula 2);
[0075] d. The single-width flow Q of the main river 1 and tributary single width flow 2 Substitute into Equation 3 to determine the single-width disch...
Embodiment 3
[0086] A method for calculating river blockage by debris flow, comprising the following steps:
[0087] a. The confluence angle between the tributary ditch and the main river measured on the spot or on the topographic map ;
[0088] b. Measure the average width of the main river at the intersection of the main river and the tributaries B. 1 , unit m, main river flow Qm, unit m 3 / s, according to formula 1 to determine the single-width discharge Q of the main river 1 , unit m 2 / s;
[0089] (Formula 1);
[0090] c. Measure the average width of the tributary at the intersection of the main river and the tributary on the spot B 2 , unit m, debris flow flow , unit m 3 / s, according to the formula 2 to determine the flow rate of the single width of the tributary ditch 2, unit m 2 / s;
[0091] (Formula 2);
[0092] d. The single-width flow Q of the main river 1 and tributary single width flow 2 Substitute into Equation 3 to determine the single-width discha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com