
Introduction to Starter Solenoid
A starter solenoid is a critical component in the starting system of an internal combustion engine. Its primary function is to engage the starter motor’s pinion gear with the engine’s flywheel ring gear, enabling the starter motor to crank the engine for starting.

How the Starter Solenoid Works
When the ignition key turns, a low-current circuit energizes the solenoid coil, generating a magnetic field. The magnetic field pulls the plunger into the coil, causing the push rod to engage the pinion gear with the ring gear. Once fully engaged, the solenoid contacts close, allowing high current to flow to the starter motor. The starter motor then cranks the engine, rotating the flywheel to start combustion. After the engine starts, the solenoid de-energizes, and the return spring disengages the pinion gear.
Types of Starter Solenoids
- Parallel Contact Design: Some solenoid switches use two parallel contact sets. The lower current set closes first, followed by the main contacts, preventing arcing damage.
- Tandem Solenoid Design: Tandem solenoid switches in idle-stop systems have separate solenoids for pinion engagement and contact operation, enabling engine restarts while still spinning.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting of Starter Solenoid

Common Issues with Starter Solenoids
- Worn or Damaged Contacts: Over time, solenoid contacts wear or pit, reducing current flow and preventing sufficient magnetic force for starter motor engagement.
- Stuck or Binding Plunger: The solenoid plunger can stick due to debris, corrosion, or wear, hindering starter motor engagement.
- Faulty Coil Winding: Coil windings may develop shorts or open circuits due to insulation breakdown, overheating, or manufacturing defects, reducing magnetic field strength.
Troubleshooting Techniques
- Visual inspection: Carefully inspect the solenoid for signs of damage, corrosion, or debris. Check the electrical connections and ensure they are clean and secure.
- Resistance testing: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the solenoid coil. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify potential issues with the coil winding.
- Voltage testing: With the solenoid connected, check the voltage at the solenoid terminals while attempting to engage the starter motor. Low voltage can indicate a wiring or battery issue.
- Plunger movement test: Manually attempt to move the plunger within the solenoid. If it is stuck or binds, disassembly and cleaning may be required.
- Replacement: If the solenoid is found to be defective or beyond repair, replacement with a new or remanufactured unit is recommended.
Applications of Starter Solenoid

Automotive Applications
Starter Solenoid for Internal Combustion Engines
- Starter solenoids are a critical component in the starting system of internal combustion engines in vehicles. Their primary function is to engage the starter motor pinion gear with the engine’s flywheel ring gear during cranking.
- The solenoid coil is energized to move a plunger, which shifts the pinion gear into mesh with the ring gear. This allows the starter motor to crank the engine for starting.
- Advanced solenoid designs incorporate features like soft engagement, current-limiting resistors, and contact monitoring for improved performance and reliability.
Hybrid Engagement System
- Optimized solenoid assemblies with hybrid engagement systems combine soft engagement and engagement springs for smooth pinion-ring gear meshing.
- Soft engagement allows the pinion to gradually engage the ring gear, reducing wear and noise.
- Engagement springs enable separation of the plunger from the operating rod for high-torque engagement when obstruction is strong.
Industrial Equipment Applications
Starter Solenoids for Industrial Machinery
- Solenoids are used in starter motors for low-horsepower internal combustion engines powering various industrial equipment like generators, pumps, and compressors.
- The compact and cost-effective design of solenoids makes them suitable for such applications.
Solenoid Valves
- Solenoid valves find widespread use in chemical, electrical, and petroleum industries for fluid control.
- Their advantages include fast and safe response, high reliability, and compact design.
Soft Start Systems
- Soft start devices incorporating solenoids are used with electric motors in industrial applications to reduce initial torque and inrush current during startup.
- This extends the service life of motors and reduces mechanical stress on the system.
Manual Activation
Manual activation devices with a push rod connected to the solenoid plunger allow starting the engine manually in case of electrical or mechanical failures.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Starter Solenoid for Internal Combustion Engines | Enables smooth and reliable engine cranking by engaging the starter motor pinion gear with the engine’s flywheel ring gear. Advanced designs incorporate soft engagement, current-limiting resistors, and contact monitoring for improved performance and durability. | Essential component in the starting system of internal combustion engines in automotive vehicles. |
| Hybrid Engagement System | Combines soft engagement and engagement springs for smooth and controlled meshing of the pinion and ring gears, reducing wear and noise during engine starting. | Automotive applications requiring reliable and durable engine starting systems. |
| Starter Solenoid for Industrial Equipment | Robust and heavy-duty designs with high current-carrying capacity and corrosion resistance enable reliable starting of large industrial engines and machinery. | Starting systems for generators, compressors, pumps, and other industrial equipment powered by internal combustion engines. |
| Integrated Starter Solenoid Assembly | Compact and modular design integrates the solenoid, starter motor, and other components into a single unit, reducing complexity and improving packaging efficiency. | Automotive and industrial applications with space constraints, such as compact vehicles or machinery. |
| Smart Starter Solenoid | Incorporates diagnostic capabilities, fault detection, and communication interfaces for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, improving system reliability and uptime. | Industrial and automotive applications requiring advanced diagnostics and maintenance capabilities. |
Latest Technical Innovations in Starter Solenoid
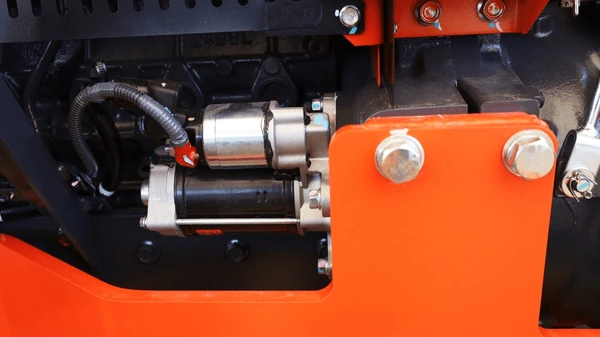
Solenoid Design Innovations
- Compact and Lightweight Designs: Developers focus on compact, lightweight solenoid designs for starter motors in low horsepower engines, optimizing coil assemblies, housings, and materials.
- Permanent Magnet Integration: Some solenoids use permanent magnets for bi-directional assist, reducing current needs and preventing overheating, improving efficiency.
- Diode Holder Integration: Solenoids integrate diode holders near the coil, housing diodes electrically connected to it, improving performance and efficiency.
Electrical and Control Advancements
- Theft Prevention and Control Circuits: Solenoids use control circuits that energize the electromagnetic system after verifying an ID code, enhancing theft prevention.
- Current-Limiting Resistance: Technologies add current-limiting resistance to solenoid switches, regulating current draw and improving efficiency.
- Solenoid Contact Health Monitoring: Systems monitor solenoid activation coil and contacts, providing fault indications to detect potential issues early.
Alternative Designs and Approaches
- Non-Solenoidal Starter Motor Designs: Novel designs use a spring-coupled drive mechanism, reducing starting current, weight, and cost while improving battery life.
- Soft Start Devices: Soft starters extend the service life of electric motors by minimizing mechanical stress during startup.
- Shielded Solenoid Designs: Solenoid designs for particle beam applications use bucking coils, split coils, and shielding to reduce disturbances and improve performance.
Technical Challenges
| Compact and Lightweight Solenoid Design | Developing small, compact, and lightweight solenoid designs for starter motors, especially in low horsepower internal combustion engine applications. |
| Permanent Magnet Integration | Incorporating permanent magnets into solenoids to provide bi-directional assist, reducing the current required to maintain the plunger in the energised position. |
| Diode Holder Integration | Featuring integrated diode holders within the solenoid housing, adjacent to the coil, for housing diodes electrically connected to the coil. |
| Theft Prevention and Control Circuits | Including control circuits that energise the electromagnetic circuit based on ID code verification, enhancing vehicle theft prevention. |
| Current-Limiting Resistance Integration | Incorporating current-limiting resistance into the solenoid switch to regulate current and prevent overheating. |
To get detailed scientific explanations of starter solenoids, try Patsnap Eureka.

