
What Is HMI (Human-Machine Interface)?
A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) serves as a vital bridge between humans and machines, enabling seamless communication and control. By providing intuitive tools for exchanging information and executing commands, HMI systems enhance productivity, streamline processes, and improve user experiences across industries. In this article, we’ll explore the key features, benefits, and applications of HMI technology, and how it’s transforming modern automation.
Components of a Human-Machine Interface
1. Input Devices
- Users interact with machines through input tools like keyboards, touchscreens, joysticks, and gesture or voice recognition systems.
- These devices allow for precise control and seamless command entry.
2. Output Devices
- Machines provide feedback to users through output tools such as LCD or LED displays, speakers, and haptic feedback systems.
- These outputs help users understand machine status and performance in real time.
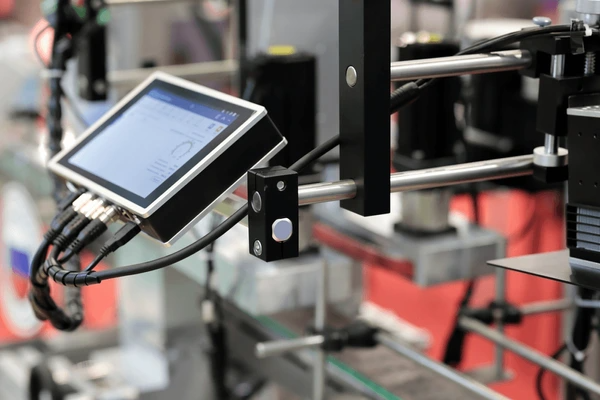
3. Processing Unit
- A central microprocessor or computer processes inputs, executes commands, and generates appropriate outputs.
- It ensures smooth operation by running specialized software tailored to specific applications.
4. Software Interface
These interfaces simplify complex processes and make interactions intuitive for users.
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) translate user inputs into commands and present machine outputs clearly.
Benefits of Using HMIs in Industries
1. Boosting Operational Efficiency
- Interfaces allow operators to monitor and control processes in real time, increasing productivity and reducing downtime.
- Centralized data visualization and control streamline operations and enable quick, informed decision-making.
- When integrated with automation systems, they further enhance efficiency and minimize human errors.
2. Enhancing Safety and Reducing Risks
- Clear visual indicators and alarms help identify potential hazards and system malfunctions promptly.
- Operators can take immediate corrective action, reducing the risk of accidents and equipment damage.
- Interfaces can enforce safety protocols and prevent unauthorized or unsafe actions to ensure workplace safety.

3. Simplifying User Experience and Training
- Intuitive graphical interfaces make it easier to interact with complex systems, boosting operator productivity.
- Reduced training times lower costs and enable quicker onboarding of new staff.
- Interactive features improve understanding and confidence in system operation.
4. Enabling Remote Monitoring and Control
- Web-based and mobile interfaces provide real-time access to data and controls from anywhere.
- Centralized management becomes possible for geographically dispersed operations, reducing on-site staffing needs.
- Remote capabilities improve responsiveness and operational flexibility.
5. Supporting Data Collection and Analysis
- Interfaces collect and log operational data for better decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Integrated systems enable predictive maintenance, quality control, and performance optimization.
- Real-time analytics help identify trends and drive efficiency across operations.
6. Offering Flexibility and Scalability
- Easily customized to meet the needs of various industries and processes, they adapt to specific requirements.
- Systems can be scaled or updated as operations grow or change, providing a future-proof solution.
- This flexibility ensures long-term value and adaptability to evolving industrial demands.
Common Applications of HMI Technology
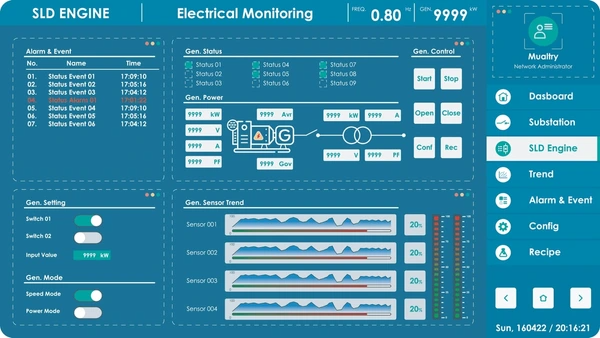
1. Industrial Automation and Control
- Advanced interfaces enable real-time monitoring and control of machinery and processes, ensuring efficiency and safety.
- They support data logging and alarm management for seamless operations.
- Common uses include:
- Manufacturing plants: assembly lines, robotics, and CNC machines
- Process control systems: chemical, oil and gas, and power generation
- Building automation: HVAC, lighting, and security systems
2. Automotive and Transportation
- Interfaces improve driver interaction and safety in modern vehicles through innovative features.
- Key applications include:
- In-vehicle infotainment systems and digital instrument clusters
- Driver assistance systems: parking aids and lane departure warnings
- Augmented reality displays for navigation and diagnostics
3. Healthcare and Medical Devices
- Interfaces are vital for monitoring and operating medical equipment, ensuring precise patient care.
- Applications include:
- Patient monitoring systems for vital signs and medical imaging
- Surgical robotics and assistive medical devices
- Rehabilitation and therapy equipment
4. Consumer Electronics and Home Automation
- Intuitive interfaces enhance the user experience across consumer electronics and smart home systems.
- Examples include:
- Smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices
- Smart home appliances like thermostats, lighting, and security systems
- Voice-controlled assistants such as Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant
5. Aerospace and Defense
- Interface systems ensure accurate control of sophisticated aerospace and defense operations.
- Common applications include:
- Aircraft cockpit displays and controls
- Ground control stations for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
- Military command and control systems
6. Emerging Applications
- Innovations are expanding the reach of interfaces into new and advanced domains.
- Notable examples include:
- Virtual and augmented reality for training, simulation, and entertainment
- Autonomous vehicles and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
- Robotics and human-robot collaboration across diverse industries
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Hydraulic Winch Management System | Designed with Visual Basic for real-time monitoring and control of hydraulic winch operations through an ActiveX-based HMI, enabling data collection via serial communication. | Mining sites requiring flexible, low-cost, safe and reliable winch control systems. |
| Automotive HMI System | Enables safe and efficient driver interaction with vehicle systems through an HMI, providing service reminders and maintenance tracking to prevent malfunctions. | Automotive applications requiring enhanced driver-vehicle communication and maintenance tracking. |
| Industrial Automation Interface Systems Rockwell Automation Technologies, Inc. | Browser-based system with applets and XAML integration for real-time data access and secure control of industrial devices, improving interaction and efficiency across multiple devices. | Industrial automation environments requiring efficient and secure HMIs for monitoring and controlling processes and machinery. |
To get detailed scientific explanations of Human-Machine Interface, try Patsnap Eureka.

