
Energy transformation, also known as energy conversion, refers to the process of changing energy from one form to another. This fundamental concept underlies both natural phenomena and human-engineered systems, driving the functionality of technologies that power modern society.
Forms of Energy and Their Transformations
Energy exists in various forms, including:
- Kinetic Energy: Energy of motion.
- Potential Energy: Stored energy based on position or configuration.
- Thermal Energy: Energy related to the temperature of an object.
- Chemical Energy: Energy stored in chemical bonds.
- Electrical Energy: Energy from the flow of electric charge.
- Radiant Energy: Energy carried by electromagnetic waves.
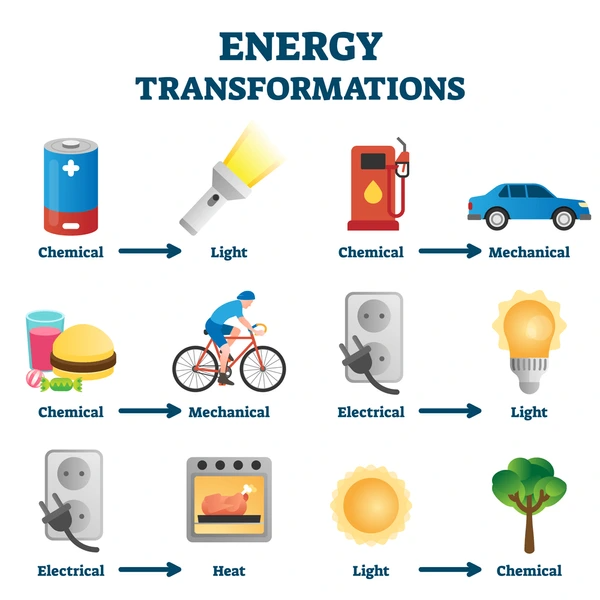
Transformations between these energy forms occur constantly. For example, in photosynthesis, plants convert radiant energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules. Similarly, in a hydroelectric dam, the gravitational potential energy of water is transformed into electrical energy.
Principles Governing Energy Transformations
Two fundamental laws of thermodynamics govern energy transformations:
- First Law of Thermodynamics (Conservation of Energy): Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change forms.
- Second Law of Thermodynamics: In any energy transformation, some energy is dissipated as heat, increasing the system’s entropy.
These principles imply that while energy transformations are essential, they are not always 100% efficient due to inevitable energy losses, primarily as heat.
Real-World Examples of Energy Transformations
Photosynthesis
In the natural world, photosynthesis is a prime example of energy transformation. Plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose, which they use for growth and development.
Coal-Fired Power Plants
In coal-fired power plants, energy transformations occur as follows:
- Chemical Energy to Thermal Energy: Burning coal releases chemical energy as heat.
- Thermal Energy to Mechanical Energy: The heat converts water into steam, which drives turbines.
- Mechanical Energy to Electrical Energy: Turbines spin generators, producing electricity.
Each stage involves energy losses, making the overall process less than 100% efficient.
Automobiles
In automobiles, energy transformations include:
- Chemical Energy to Thermal Energy: Combustion of fuel releases heat.
- Thermal Energy to Mechanical Energy: Expanding gases move pistons.
- Mechanical Energy to Kinetic Energy: Pistons’ motion turns the wheels, propelling the vehicle.
Understanding these transformations is crucial for improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
💡 Curious about real-world energy transformations? Eureka Technical Q&A provides detailed insights into various energy conversion processes, helping you understand how energy changes form in everyday applications.
Case Studies in Energy Transformation
Ethiopia’s Grand Renaissance Dam
Ethiopia’s Grand Renaissance Dam exemplifies energy transformation on a national scale. The dam converts the kinetic energy of the Blue Nile River into electrical energy, aiming to enhance energy access and stimulate economic growth. However, it also presents challenges related to cross-border water resource management and environmental impacts.
Renewable Energy in a Small Community
A small community’s transition to renewable energy showcases a unique case of energy transformation. By adopting wind and solar power, coupled with energy storage and smart management systems, the community achieved a sustainable energy model. This shift not only reduced reliance on fossil fuels but also promoted environmental stewardship and energy independence.
Conclusion
Energy transformation is a fundamental concept that drives both natural processes and human-engineered systems. Understanding the various forms of energy and their transformations is crucial for developing efficient technologies and sustainable energy solutions. Real-world examples and case studies highlight the practical applications and challenges of energy transformation, emphasizing its significance in our daily lives and the broader context of global energy dynamics.
FAQs
- Why is energy transformation important?
Energy transformation is essential because it allows the utilization of energy in forms that are practical for specific applications, enabling the functioning of various technologies and biological processes. - Can energy be created or destroyed during transformation?
No, according to the First Law of Thermodynamics, energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change forms. - Are energy transformations 100% efficient?
No, due to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, some energy is always lost as heat during transformations, making them less than 100% efficient. - How does energy transformation impact daily life?
Energy transformations power everyday activities, from powering vehicles and heating homes to enabling electronic devices and supporting bodily functions.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Energy Transformation, try Patsnap Eureka.


