
What is Ammonium Carbonate?
Ammonium carbonate, represented by the formula (NH4)2CO3, forms as a white crystalline solid consisting of ammonium cations (NH4+) and carbonate anions (CO3^2-). Moreover, this salt arises from the reaction between ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
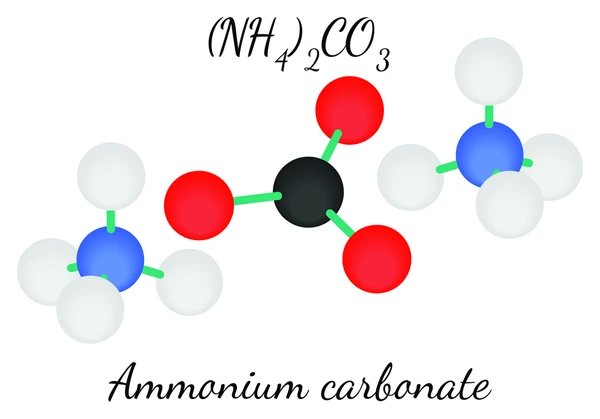
Properties of Ammonium Carbonate
- Physical Properties: Ammonium carbonate is a white crystalline solid with a slight ammonia odor. It is highly soluble in water, forming ammoniacal solutions.
- Thermal Stability: Ammonium carbonate decomposes upon heating, releasing ammonia and carbon dioxide gases 920. The thermal stability of the N2H7+ complex cation is high, up to 170°C.
- Concentration and Solubility: The concentration of ammonium carbonate in aqueous solutions can vary widely, from dilute solutions to highly concentrated solutions approaching saturation
Production of Ammonium Carbonate
Carbonation Method
- Reacting ammonia and carbon dioxide in water to form ammonium carbonate solution
- Controlling pH, temperature, and pressure to precipitate ammonium bicarbonate crystals
- Centrifuging and drying the crystals to obtain the final product
Amine-based CO2 Capture
- Capturing CO2 from flue gas using amine-based absorbents
- Reacting the CO2-rich amine solution with ammonia to form ammonium bicarbonate
- Crystallization, hydrogenation, and thermal decomposition to produce ammonium formate and formic acid
Ammonium Carbonization
- Reacting calcium carbonate with ammonium chloride to generate CO2 and ammonium carbonate
- Refining the ammonium carbonate hydrate to produce lightweight magnesium carbonate
- Recycling CO2 and ammonia gas back into the reaction solution
Process Optimization and Innovations
- Using chilled amine solutions (0-20°C) for improved CO2 capture efficiency
- Employing multi-stage absorption and zone control for better CO2 utilization
- Recycling byproducts (CO2, ammonia, ammonium chloride) to improve raw material utilization
- Exploring alternative raw materials and catalysts for sustainable production

Applications of Ammonium Carbonate
Fertilizer and Agricultural Applications
Ammonium carbonate is widely used as a fertilizer due to its high nitrogen content and ability to supply nitrogen to plants quickly. It is a neutral fertilizer that can improve soil quality by changing pH, loosening soil, and reducing active aluminum content. It promotes healthy growth of roots, stems, and leaves, enhances flowering, and increases fruit sugar content. Ammonium carbonate fertilizers are suitable for various soil types and crops, including economic crops, flowers, fruit trees, and greenhouse/field-grown vegetables.
Chemical Synthesis and Industrial Processes
- Industries use ammonium carbonate as a precursor to produce ammonium salts, including ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium formate, which find applications in baking, fire extinguishers, and as reducing agents.
- Manufacturers utilize it in synthesizing quaternary ammonium compounds, commonly employed as surfactants, phase transfer catalysts, and antimicrobial agents.
- Its solutions can capture carbon dioxide and react with metal hydroxides to produce carbonates like magnesium carbonate and calcium carbonate, used in various industries.
Pharmaceutical and Household Applications
- It has been used as an expectorant and smelling salt in traditional medicine.
- It finds applications in household cleaning products like ammonia-based window cleaners and as a leavening agent in baking.
- Recent research explores using ammonium carbonate/bicarbonate solutions for urea synthesis and biocide formation.
Emerging and Innovative Applications
- Researchers are investigating ammonium carbonate as a precursor for carbon capture and utilization technologies, enabling the conversion of carbon dioxide into value-added chemicals like formic acid.
- Its ability to form stable carbamate/bicarbonate salts with amines is being explored for carbon dioxide capture and storage applications.
- Ammonium carbonate-derived carbon nitrides have shown improved photocatalytic properties, with potential applications in environmental remediation and energy conversion.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonium Carbonate Fertiliser | Provides quick-release nitrogen to plants, improves soil quality by adjusting pH and reducing aluminium toxicity. Promotes healthy growth, flowering, and fruit sugar content. | Suitable for various soil types and crops, including economic crops, flowers, fruit trees, and greenhouse/field-grown vegetables. |
| Ammonium Bicarbonate Production | Ammonium carbonate is a precursor for producing ammonium bicarbonate, which is used as a leavening agent in baking and as a fire extinguishing agent. | Food industry, baking, and fire safety applications. |
| Quaternary Ammonium Compound Synthesis | Ammonium carbonate is used as a raw material for synthesising quaternary ammonium compounds, which are widely used as surfactants, phase transfer catalysts, and antimicrobial agents. | Chemical industry, personal care products, and disinfectants. |
| Carbon Dioxide Capture | Ammonium carbonate solutions can effectively capture and react with carbon dioxide, forming carbonates that can be used in various industrial processes. | Carbon capture and utilisation technologies, chemical processing, and environmental applications. |
| Metal Carbonate Production | Ammonium carbonate solutions can react with metal hydroxides to produce metal carbonates, which have applications in various industries. | Chemical industry, construction materials, and environmental remediation. |

Latest innovations in Ammonium Carbonate
Improved Production Methods
- Ammonia-based decarburization systems: These involve separating the ammonium bicarbonate generation, CO2 absorption, and ammonia removal steps into different areas to improve efficiency and reduce ammonia escape. The CO2 from flue gas can be utilized to produce ammonium bicarbonate as a nitrogen fertilizer.
- Carbon capture and conversion: Researchers developed processes that capture CO2 using amine solutions, convert it to ammonium bicarbonate, and hydrogenate it into high-yield formic acid. Specific amine solutions with organic solvents enhance separation.
- High-purity CO2 utilization: Scientists proposed methods to produce ammonium bicarbonate from high-purity CO2 sources, such as coal combustion flue gas. This involves pre-carbonization and main carbonization steps to obtain high-efficiency, large particle size ammonium bicarbonate crystals.
Novel Applications
- Formic acid production: Hydrogenating ammonium bicarbonate with CO2 produces formic acid, offering a pathway for carbon capture and utilization.
- Amine-based CO2 capture: Reacting CO2-saturated amine solutions with magnesium hydroxide forms ammonium bicarbonate, with properties adjustable through amines and reaction times.
- Quaternary ammonium compound synthesis: Ammonium bicarbonate helps create quaternary ammonium alkyl carbonates and carboxylates, useful as phase transfer catalysts and surfactants.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Carbon neutrality: There is a need for innovations towards carbon-neutral processes that do not rely on fossil fuels for ammonium bicarbonate production.
- Improved efficiency: Researchers must continuously enhance ammonia and CO2 absorption rates in production while cutting energy consumption.
- Scalability: With growing demand, manufacturers must develop scalable, cost-effective methods to meet global ammonium bicarbonate needs.
Technical Challenges
| Improved Ammonium Bicarbonate Production Methods | Developing more efficient and environmentally-friendly methods for producing ammonium bicarbonate, such as ammonia-based decarburization systems, carbon capture and conversion processes, and utilization of high-purity CO2 sources. |
| Novel Applications of Ammonium Bicarbonate | Exploring new applications of ammonium bicarbonate, such as its use as an intermediate for producing formic acid from CO2 through hydrogenation, and in amine-based CO2 capture processes. |
| Particle Size and Morphology Control | Controlling the particle size, shape, and morphology of ammonium bicarbonate crystals to obtain desired properties for specific applications. |
| Integration with Carbon Capture Technologies | Integrating ammonium bicarbonate production with carbon capture technologies to enable efficient utilization of CO2 from industrial flue gases or other sources. |
| Process Intensification and Optimization | Intensifying and optimizing the ammonium bicarbonate production process through process integration, energy efficiency improvements, and advanced process control strategies. |
To get detailed scientific explanations of the aluminum chloride, try Patsnap Eureka.

Learn more
Hypertonic vs. Hypotonic vs. Isotonic: What’s the Difference?
Acetophenone: A Key Compound in Fragrance and Industry
Magnesium Nitrate: Key Uses, Definition, and Innovations
