
What is an Accumulator?
An accumulator is a crucial computing circuit in digital circuit design, commonly used for adding or accumulating binary numbers. It plays a key role in operations like multiplication, where it accumulates partial products. Accumulators are often implemented using efficient methods like the Wallace tree compression technique, which compresses bit values layer by layer for faster results. This article will explore the functions, design, and applications of accumulators in digital circuits, highlighting their importance in modern computing.
How Accumulators Work
Electrochemical Cells
Energy storage devices rely on electrochemical cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa. Each cell includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and an electrolyte that facilitates electrochemical reactions.
Li-ion Technology
Lithium-ion batteries, a common energy storage solution, operate by moving lithium ions between two materials with different potentials. During discharge, lithium ions travel from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, creating an electric current until the ions are fully depleted.
Battery Management System (BMS)
In modern energy systems, a Battery Management System (BMS) ensures efficient and safe operation. It optimizes charging and discharging processes, helping to extend battery life and maintain reliable energy performance.
Types of Accumulators
Hydraulic Energy Storage
Hydraulic systems use energy storage devices to hold hydraulic energy as compressed gas or spring force. These devices absorb shocks, dampen pulsations, and cushion sudden load increases.
Types of Hydraulic Storage
- Piston Type: Utilizes a piston to compress gas within an oil bath.
- Bladder Type: Features a flexible bladder to contain the compressed gas.
- Diaphragm Type: Employs a diaphragm to separate gas from hydraulic fluid.
Pneumatic Energy Storage
Compressed air or gas powers pneumatic systems, commonly found in tools and conveyors requiring consistent pneumatic force.
Types of Pneumatic Storage
- Spring Loaded: Compresses air using a spring mechanism.
- Piston Type: Relies on a piston to compress the air.
Electrical Energy Storage
Electrical systems utilize energy storage devices to buffer against sudden energy demand changes.
Types of Electrical Storage
- Supercapacitors: Store energy through electrostatic double-layer capacitance.
- Rechargeable Batteries: Convert and store energy chemically for later use.
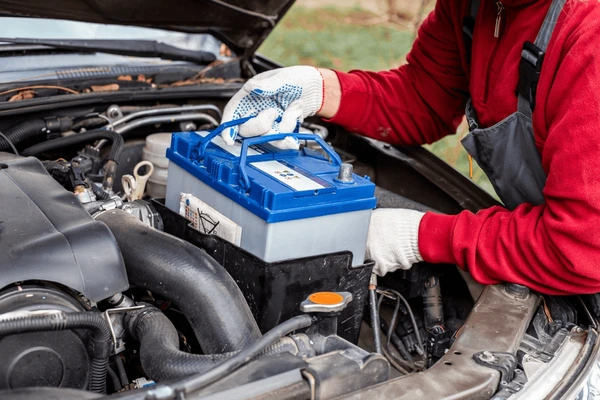

Advantages of Using Accumulators
Efficiency and Performance
Energy storage systems offer efficient energy management, enabling optimal use of resources to improve decision-making and operational performance. For high-current, short-duration discharges, supercapacitors deliver over 10% greater efficiency compared to traditional systems, making them a preferred choice in many applications.
Flexibility and Scalability
Energy storage devices integrate seamlessly into various systems without significant increases in size or cost. They enhance power regeneration in vehicles without adding complexity or overheating. Supercapacitors charge faster than batteries, offer a longer lifespan, and require lower maintenance, making them a flexible and cost-effective solution.
Reliability and Safety
Live monitoring of energy levels, usage, and charge status ensures better system management while reducing human error. Supercapacitors avoid chemical processes, providing greater safety, environmental benefits, and improved longevity compared to traditional options.
Integration and Compatibility
Energy storage systems integrate easily with existing infrastructures, enabling automatic data exchange and boosting overall system compatibility. They support low-voltage ride-through and grid code compliance, ensuring smooth operation in distributed energy applications and modern energy networks.
Applications of Accumulators
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Systems
Energy storage systems play a critical role in UPS systems, providing reliable power during outages. Advanced monitoring systems detect internal resistance changes early, ensuring better reliability and preventing unexpected failures.
Energy Storage Systems
In modern energy storage setups, electrochemical modules are combined and managed by battery management systems (BMS). These systems optimize charging, discharging, and overall performance, extending the service life of the batteries.
Charging Applications
Innovative charging apparatus allow energy storage devices to efficiently recharge from external sources, ensuring they are ready to store energy for future needs.
Dynamic Power Storage in Marine Systems
In marine environments, energy storage solutions reduce power fluctuations in closed electrical systems. These setups, which combine electric machines, hydraulic pumps, and energy storage devices, improve stability and performance.
Motor Vehicles
In vehicles, energy storage systems provide power for electrical drives, offering high capacity and performance through the combination of multiple electrochemical cells. This ensures efficient energy delivery for demanding applications.
Industrial Applications
Energy storage is essential in industries like shipping, railways, and manufacturing, where high-capacity and high-power solutions are needed to support heavy operations reliably.

Latest Technical Innovations in Accumulators
Advances in Capacitor Technology
Recent innovations in high-energy capacitors have improved energy density, reliability, and performance. With longer DC life, faster discharge rates, and higher power capabilities, they are ideal for pulsed power systems. New designs featuring a second electrode and dielectric structure boost feature density, reduce cell size, and lower fabrication costs, simplifying modern electronic applications.
Innovations in Capacitor Systems
Compact capacitor assemblies now provide temporary power during high-demand periods, integrating easily into circuit boards without voltage drops. Additionally, advanced capacitor units in hybrid and idling stop vehicles store energy for regenerative braking and powering high-output motors, enhancing efficiency and performance.
To get detailed scientific explanations of accumulators, try Patsnap Eureka.

