
Introduction: WAN vs LAN – What’s the Difference?
When it comes to networking, WAN vs LAN highlights the key difference between connecting devices locally or across broader distances. A LAN (Local Area Network) connects devices within a small, defined area like a home or office, while a WAN (Wide Area Network) links multiple LANs over large geographical areas, such as cities or even countries.
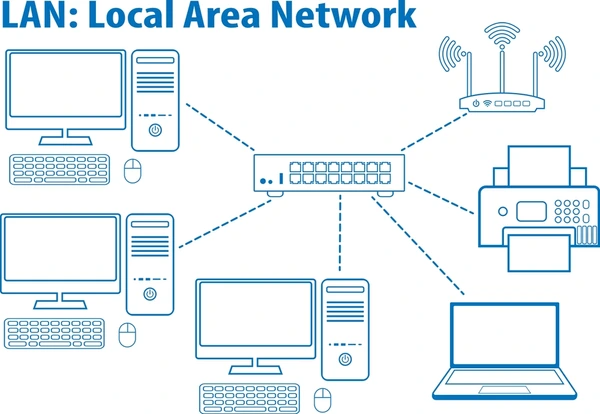
What Is a LAN?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers and devices within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or building. LANs are typically confined to a single broadcast domain and have a smaller coverage area compared to WANs.
Key Characteristics of LANs:
- Limited geographical coverage, usually within a radius of a few hundred meters
- Enables resource sharing (e.g., printers, file servers) among connected devices
- Can be wired (e.g., Ethernet) or wireless (e.g., Wi-Fi)
- Commonly used topologies include star, ring, bus, and hub/tree
- Provides high-speed data transfer rates within the local area
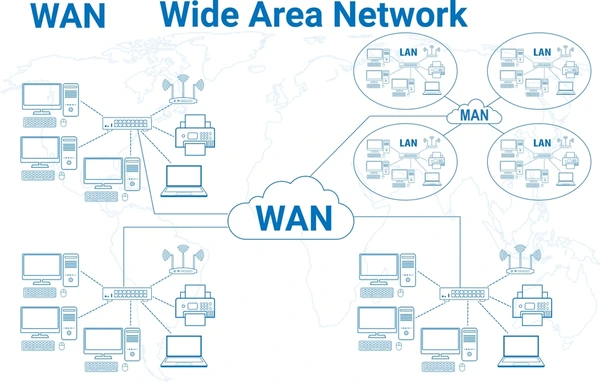
What Is a WAN?
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a geographically dispersed telecommunications network that spans a large geographical area, typically covering multiple cities, regions, or countries. It interconnects Local Area Networks (LANs) and enables data communication over long distances.
Key Characteristics of WANs:
- Covers a broad geographical area, ranging from a few hundred to thousands of kilometers
- Utilizes various communication technologies, such as WIMAX, UMTS, GPRS, CDMA, GSM, HSDPA, 3G, and 4G, to transfer data
- Enables communication between remote locations and facilitates various scenarios like group calls, private calls, data calls, and emergency calls
- Relies on third-party carriers and service providers to provide transmission services
- Includes both public data networks (e.g., Internet) and private enterprise networks
Key Differences Between WAN and LAN
Geographic Coverage
WANs span large geographic areas, often across cities, regions, or countries, while LANs are confined to a limited area, such as a building, office, or campus. WANs interconnect LANs and other networks, enabling communication between users and devices in different locations.
Transmission Media and Bandwidth
WANs typically rely on leased lines, satellite links, or other long-distance communication channels, which often have lower bandwidths and higher latencies compared to LANs. LANs, on the other hand, use high-speed wired or wireless connections within a limited area, providing generous bandwidths and low latencies.
Network Ownership and Control
LANs are typically owned and managed by a single organization, allowing for greater control over the network infrastructure and resources. WANs often involve third-party carriers or service providers, with a measure of network control outside the enterprise’s direct control.
Protocols and Standards
LANs commonly use Ethernet, Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11), or other local area networking protocols and standards. WANs employ a variety of protocols and technologies, such as the Internet Protocol (IP), Frame Relay, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), and others, to facilitate long-distance communication.
Applications and Use Cases
LANs are primarily used for resource sharing, file management, and local communication within an organization. WANs are essential for enabling wide-area client-server applications, remote access to centralized resources (e.g., file servers, mail servers), and interconnecting geographically dispersed offices or locations.
Conclusion: WAN vs LAN – Which One Do You Need?
WAN vs LAN comes down to scale and purpose. For local connections with high speed, a LAN is ideal. For linking multiple locations or accessing global networks, a WAN is the way to go. Understanding their differences helps you optimize your networking setup for efficiency and performance.
FAQs
- What is the main purpose of a LAN vs a WAN?
A LAN connects devices within a small area, while a WAN links multiple LANs over larger distances. - Can a LAN connect to a WAN?
Yes, a LAN can connect to a WAN, often through a router that links the local network to the internet. - Which is faster, WAN or LAN?
LANs are faster due to their smaller size and high-speed technologies like Ethernet and Wi-Fi. - Do homes typically use LAN or WAN?
Homes primarily use LAN for internal connections, but they access the internet through a WAN. - How secure is a WAN compared to a LAN?
LANs are generally more secure due to controlled access, while WANs require additional security measures like VPNs and firewalls.
To get detailed scientific explanations of wan vs. lan, try Patsnap Eureka.

