
Sulfurous acid (H₂SO₃) is a weak and unstable acid that primarily exists in aqueous solutions. It is formed when sulfur dioxide (SO₂) dissolves in water and plays a significant role in various industrial applications, including bleaching, disinfection, and chemical synthesis. Due to its unstable nature, H₂SO₃ readily decomposes into sulfur dioxide and water. This article explores the properties, uses, hazards, and safety measures associated with H₂SO₃.
What is Sulfurous Acid?
Sulfurous acid is a diprotic acid, meaning it can donate two protons (H⁺) in solution. However, it does not exist in a pure state because it decomposes back into sulfur dioxide and water. Despite its instability, industries commonly use H₂SO₃ for its reducing properties and ability to form sulfite and bisulfite salts.
Chemical Properties
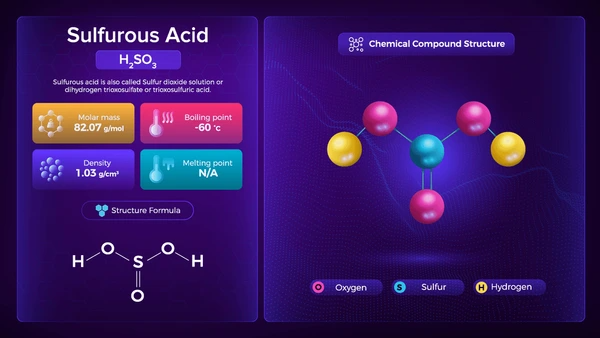
- Molecular Formula: H₂SO₃
- Molar Mass: 82.07 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid with a pungent odor
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water
- Acidity: Weak acid with partial dissociation into bisulfite (HSO₃⁻) and sulfite (SO₃²⁻) ions
Formation of Sulfurous Acid
Sulfurous acid is produced by dissolving sulfur dioxide (SO₂) in water:SO2+H2O⇌H2SO3SO_2 + H_2O ⇌ H_2SO_3SO2+H2O⇌H2SO3
This equilibrium reaction makes H₂SO₃ present in aqueous solutions but difficult to isolate in pure form.
Sulfurous Acid vs. Sulfuric Acid
| Property | Sulfurous Acid (H₂SO₃) | Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation State of Sulfur | +4 | +6 |
| Acid Strength | Weak | Strong |
| Stability | Unstable, decomposes | Highly stable |
| Oxidizing Power | Mild | Strong |
| Industrial Use | Reducing agent, bleaching | Battery acid, dehydration |
Uses of Sulfurous Acid
1. Industrial Applications
- Bleaching Agent: Used in the paper and textile industries for bleaching wood pulp and fabrics.
- Disinfectant: Acts as an antimicrobial agent to prevent bacterial and fungal growth.
- Preservative: Used in food and beverage industries to extend shelf life by inhibiting oxidation.
2. Chemical Synthesis
- Reducing Agent: H₂SO₃ helps in reducing various chemical compounds and prevents oxidation reactions.
- Precursor to Sulfite Salts: Many sulfite-based compounds are derived from H₂SO₃ and used in industrial and food applications.
3. Environmental Relevance
- Acid Rain Formation: H₂SO₃contributes to acid rain when sulfur dioxide emissions react with atmospheric moisture, leading to environmental damage.
Curious about the uses of sulfurous acid? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its applications in food preservation, water treatment, and industrial processes, helping you understand its benefits and safe handling practices.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Sulfamic Acid Production Plant Chengdu Palo Technology Co., Ltd. | Efficient production of sulfamic acid using fuming sulfuric acid and sodium sulfate | Production of sulfonating agents for industrial applications |
| Biological Sulfuric Acid Production Chevron Phillips Chemical Co. LP | Cost-effective on-site generation of sulfuric acid solutions with reduced emissions | Industrial settings requiring sulfuric acid with minimal environmental impact |
| Gold Recovery Process Freeport-McMoRan, Inc. | Enhanced gold recovery from refractory ores using sulfurous acid leaching | Gold mining operations dealing with complex ore compositions |
| Low Temperature SO2 Oxidation Catalyst TDA Research, Inc. | Improved SO2 to SO3 conversion at lower temperatures, reducing energy costs | Sulfuric acid production plants aiming for energy efficiency |
| Nano-Sulfur Composition Suzhou Canastar New-Materials Technology Corporation | Enhanced sulfur activity and bioavailability through stable nano-state formulation | Agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and other industries requiring high-performance sulfur products |
Hazards and Safety Considerations
1. Reactivity and Decomposition
- H₂SO₃ decomposes easily, releasing sulfur dioxide gas, which can be hazardous if inhaled.
- Heating H₂SO₃ accelerates its breakdown into SO₂ and water.
2. Corrosive Effects
- Causes skin and eye irritation upon contact.
- Inhalation of sulfur dioxide fumes can result in respiratory distress, coughing, and lung irritation.
3. Environmental Impact
- Contributes to air pollution through sulfur dioxide emissions.
- Can lead to acidification of water bodies and soil when released into the environment.
Safe Handling and Storage Practices
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Eye Protection: Safety goggles or face shields to prevent eye exposure.
- Skin Protection: Acid-resistant gloves and protective clothing to minimize skin contact.
- Respiratory Protection: Use appropriate respirators when handling in poorly ventilated areas.
2. Storage Guidelines
- Store in tightly sealed, non-metallic containers to prevent leaks and contamination.
- Keep in a cool, well-ventilated environment away from oxidizing agents and strong acids.
3. Emergency Procedures
- Spill Response: Neutralize small spills with a weak base like sodium bicarbonate and clean with absorbent materials.
- First Aid Measures: In case of contact, rinse affected areas with plenty of water and seek medical attention if irritation persists.
FAQs About Sulfurous Acid
1. What is sulfurous acid used for?
Industries mainly use H₂SO₃ as a reducing agent, disinfectant, and bleaching agent in various processes. It also serves as a precursor for sulfite and bisulfite salts.
2. Why is sulfurous acid considered unstable?
It decomposes readily into sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and water, making it difficult to isolate in a pure form.
3. How should sulfurous acid be stored safely?
Store H₂SO₃ in sealed, corrosion-resistant containers away from strong oxidizing agents and heat sources.
4. Can sulfurous acid cause burns?
Yes, it is a corrosive substance that can cause skin and eye burns. Direct contact should be avoided.
5. Is sulfurous acid the same as sulfuric acid?
No, H₂SO₃ is a weaker acid with sulfur in the +4 oxidation state, while sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a strong acid with sulfur in the +6 oxidation state and higher stability.
Conclusion
Sulfurous acid plays a crucial role in various industrial applications, including bleaching, disinfection, and chemical synthesis. However, its instability and potential hazards require careful handling, proper storage, and adherence to safety protocols. While it is not as strong or widely used as sulfuric acid, H₂SO₃ remains an important chemical in both industrial and environmental contexts.ng, proper storage, and adherence to safety protocols to mitigate risks associated with its use.
To get detailed scientific explanations of sulfurous acid, try Patsnap Eureka.


