Sodium percarbonate (Na₂CO₃·1.5H₂O₂) is a solid, crystalline compound that serves as a stable source of hydrogen peroxide. Known for its eco-friendly decomposition into water, oxygen, and soda ash, it has become a cornerstone of green chemistry in consumer goods, industrial cleaning, water treatment, and advanced oxidation processes.
This blog delves into the composition, functional properties, cross-sector applications, and future directions of sodium percarbonate, with insights into its growing relevance in sustainable technologies through PatSnap’s Eureka AI Agent.
Composition & Properties
Chemically, sodium percarbonate is a peroxygen compound composed of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide in a crystalline adduct form. Upon dissolution in water, it releases hydrogen peroxide, making it a powerful oxidizing and bleaching agent. Key properties include:
- Appearance: White, free-flowing powder or granules
- Decomposition: Into H₂O₂ and Na₂CO₃
- Oxidizing strength: Comparable to 27% liquid hydrogen peroxide
- Stability: More stable than H₂O₂ in dry conditions
- Environmental impact: Non-toxic byproducts
Its solid-state stability and environmental safety make it preferable over chlorine-based alternatives for various oxidation and bleaching processes.
Comparative Advantages & Limitations
✅ Advantages
- Eco-Friendly Decomposition
Sodium percarbonate breaks down into water, oxygen, and soda ash, leaving no toxic residue—making it highly suitable for green chemistry applications. - Strong Oxidizing Power
It releases active oxygen upon dissolution, providing powerful cleaning, bleaching, and disinfecting effects without harsh chlorine-based agents. - Dry & Stable Formulation
Compared to liquid hydrogen peroxide, sodium percarbonate is a dry, solid, and shelf-stable oxidant, simplifying storage, handling, and transportation. - Broad Application Versatility
Effective across home care, industrial cleaning, wastewater treatment, agriculture, and medical sanitation—its functionality spans both consumer and B2B sectors. - Low Toxicity & Biocompatibility
Exhibits relatively low toxicity in controlled applications, especially when compared to other strong oxidants and biocides, making it suitable for cosmetic and hygiene use. - Odorless & Non-Corrosive (at Dilute Concentrations)
Unlike chlorine bleach, sodium percarbonate does not produce irritating fumes and is safer for delicate surfaces when used in appropriate formulations.

Limitations
- Moisture Sensitivity
Sodium percarbonate decomposes in humid conditions, requiring air-tight packaging and low-humidity storage environments to preserve activity. - Limited Thermal Stability
At elevated temperatures, it may undergo premature decomposition, reducing its effectiveness in certain industrial processes involving heat. - Lower Shelf Life Compared to Pure Carbonates
Although more stable than liquid peroxides, it still has a shorter shelf life than pure carbonates or inert cleaning agents. - pH Sensitivity
Its effectiveness can vary depending on the pH of the solution; optimal performance typically occurs in mildly alkaline conditions. - Not Compatible with Certain Organic Materials
May cause degradation or bleaching of colored textiles, natural rubbers, or sensitive polymers, limiting its scope in specific material systems.
Application Domains
1. Household & Industrial Cleaning Formulations
Sodium percarbonate plays a foundational role in the cleaning products industry due to its ability to release hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solutions. This property enables powerful stain removal, bleaching, and deodorizing effects across a range of formulations.
Related Reports:
- How Sodium Percarbonate Functions in Oxygen-Based Bleaching Processes
- The Role of Sodium Percarbonate in Eco-Friendly Cleaning Solutions
- Efficiency of Sodium Percarbonate in Hard Surface Cleaners
- Comparison of Sodium Percarbonate and Borax as Cleaning Agents
- How Sodium Percarbonate Improves Carpet Cleaning Formulations
- Sodium Percarbonate’s Impact on Contract Cleaners’ Efficiency
- Innovations in Sodium Percarbonate for Cold Brew Coffee Cleanliness
- Evaluating Sodium Percarbonate in Retail Industry Cleaning Efforts

2. Water Treatment & Environmental Remediation
As a solid-source oxidizer, sodium percarbonate is increasingly utilized in environmental applications including in-situ chemical oxidation (ISCO), contaminated soil remediation, and wastewater treatment. It decomposes into safe byproducts, making it eco-compatible.
Related Reports:
- Sodium Percarbonate Application in Wastewater Treatment
- Structures and Mechanisms: Sodium Percarbonate in Pathogen Removal
- Evaluating Sodium Percarbonate’s Role in Natural Pool Sanitizers
- Exploring Sodium Percarbonate’s Benefits in Drinking Water Systems
- Examining Sodium Percarbonate’s Utility in Hydroponics System Cleanliness
3. Textile, Paper & Pulp Processing
Thanks to its oxidizing power and bleaching ability, sodium percarbonate is a key additive in eco-friendly textile and pulp processing workflows. It provides color removal, brightening, and fiber purification without generating toxic residues.
Related Reports:
- Impact of Sodium Percarbonate on Textile Brightness Retention
- How Sodium Percarbonate Influences Laundry Detergents’ Cleaning Power
- Optimization of Sodium Percarbonate for Apparel Industry Use
- Influence of Sodium Percarbonate on Bio-based Textile Development
- The Interplay between Sodium Percarbonate and Recycled Textile Strength
- How Sodium Percarbonate Reduces Artificial Dye Usage in Textiles
4. Food, Beverage & Agriculture
Sodium percarbonate has emerged as a valuable agent in food processing, agricultural hygiene, and beverage safety due to its powerful oxidizing and antimicrobial properties. From sterilizing equipment to enhancing food preservation and safety protocols, its eco-friendly decomposition into water and oxygen makes it particularly suitable for sustainable practices across the food value chain.
Related Reports:
- Sodium Percarbonate in Food Processing: Safety Measures and Benefits
- Evaluating Sodium Percarbonate’s Efficiency in Eco-Friendly Drain Cleaners
- Sodium Percarbonate’s Role in Brewery Hygiene Optimization
- Use of Sodium Percarbonate in Culinary Utensil Sterilization Processes
5. Healthcare, Hygiene & Biomedical
Sodium percarbonate isn’t just a laundry additive—it’s becoming a high-performance oxidizer in health-critical environments. But how is it shaping the future of:
Sterile surface maintenance in surgical units?
Preservative systems in natural or water-based cosmetics?
On-site neutralization of infectious biomedical waste?
Veterinary antiseptics with minimal toxic residues?
Dental materials that balance cleaning power with biocompatibility?
Gender-aware skincare formulations where oxidation meets hormonal nuance?
These are no longer peripheral experiments—they’re redefining how oxidation chemistry fits into human-centered innovation.
👉 Wondering how sodium percarbonate is being re-engineered to meet the safety, efficacy, and formulation demands of next-gen biomedical and hygiene systems?
Explore how sodium percarbonate is enabling cleaner, safer, and smarter healthcare innovations through PatSnap Eureka AI Agent.
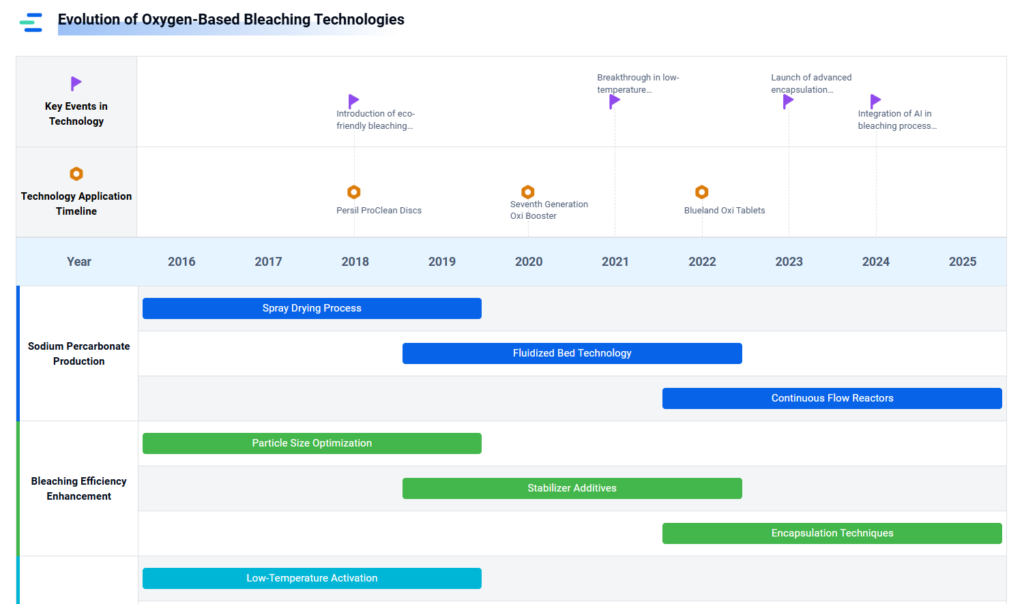
Emerging Trends & Innovation Outlook
Several R&D initiatives are pushing the frontier of sodium percarbonate innovation:
- Encapsulation technologies for moisture resistance
- Nanostructured percarbonate composites for extended release
- Hybrid peroxygen systems combining SPC with MnO₂ or peracids
- Smart bleaching systems responsive to pH or temperature
- Circular chemistry efforts in peroxide-based green oxidants
- Textile coloration + cleaning hybrids using percarbonate for dual function

Sodium percarbonate’s low toxicity and high oxidative potential make it a versatile enabler of green transformation across both mature and emerging sectors.
Conclusion
Sodium percarbonate is more than a bleach—it’s a clean oxidizer that aligns with the global demand for safer, greener chemistries. Its versatility across home care, remediation, energy, and manufacturing speaks to its transformative potential.
As new encapsulation technologies, formulation synergies, and sector-specific delivery mechanisms emerge, sodium percarbonate is poised to play a central role in sustainable material science and industrial innovation.
FAQ
Yes, it decomposes into non-toxic byproducts: water, oxygen, and soda ash.
It is a dry, solid adduct that releases H₂O₂ when dissolved—easier to store and transport.
Yes, but must meet purity standards. Applications include disinfecting surfaces and oral hygiene.
Typically 1–2 years in dry, sealed packaging.
Yes, it is commonly used in pond, pool, and remediation formulations for this purpose.
Want to explore supplier patents, degradation pathways, or industrial use cases of sodium percarbonate?
👉 Use PatSnap Eureka AI Agent to uncover hidden application trends, accelerate product benchmarking, and extract deeper technical insights—instantly.