
The radius of gyration or gyradius plays a fundamental role in structural analysis, mechanics, and molecular physics. It quantifies how a body’s mass or molecular structure is distributed around an axis, affecting stability, rotational motion, and structural performance. But why is the gyradius important? The answer lies in moment of inertia, structural integrity, and polymer science. This article explores the concept of the gyradius, its applications, and its impact across multiple industries.
What is the Radius of Gyration?
The radius of gyration (![]() ) is a measure of how a body’s mass or particles are distributed around an axis of rotation. It is defined as the distance from the axis at which the entire mass can be assumed to be concentrated without altering the moment of inertia.
) is a measure of how a body’s mass or particles are distributed around an axis of rotation. It is defined as the distance from the axis at which the entire mass can be assumed to be concentrated without altering the moment of inertia.

Key Properties
- Symbol:
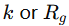
- Unit: Meters (m)
- Application: Used in mechanics, polymer science, and structural engineering
- Significance: Determines stability, resistance to rotation, and shape factors
💡 Did You Know?
The concept of radius of gyration applies not only to rigid bodies but also to biomolecules, polymers, and even galaxies!
The Science Behind the Radius of Gyration
The gyradius is derived from the moment of inertia, which describes an object’s resistance to rotational motion.
Formula for Radius of Gyration
For a rigid body, the gyradius is defined as: 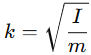
Where:
- I = Moment of inertia about the axis
- m = Total mass of the body
For polymer molecules, the formula is given by: 
Where:
-
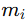 = Mass of each particle
= Mass of each particle 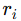 = Distance of each particle from the center of mass
= Distance of each particle from the center of mass
Why is the Radius of Gyration Important?
- Defines stability and resistance to bending in structural engineering
- Determines molecular size and shape in polymer science
- Affects rotational inertia in mechanical design
💡 Tip: In tall buildings and bridges, a lower gyradius ensures higher structural stability.
Comparing Radius of Gyration in Different Fields
The gyradius varies based on the object’s mass distribution. Here’s how it compares across different structures and molecules:
| Application | Formula | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Engineering | Columns, beams, and bridge supports | |
| Rotational Mechanics |  | Gears, flywheels, and rotating shafts |
| Polymer Science |  | DNA structure, protein folding, and nanoparticles |
| Astrophysics | Galaxy rotation and star cluster distribution |
💡 Did You Know?
A lower gyradius means a more compact structure, while a higher gyradius suggests a more spread-out mass distribution.
Applications of the Radius of Gyration in Different Industries
💡 Curious about how the radius of gyration is applied across industries? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its role in structural engineering, biomechanics, and material science, helping you understand its impact on stability, strength, and motion analysis.
Structural and Civil Engineering 🏗️
- Determines stability and strength of columns and beams.
- Prevents buckling in skyscrapers and bridges.
Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering 🚀
- Helps design efficient rotating machinery, including turbines and gyroscopes.
- Optimizes moment of inertia for spacecraft and satellite stability.
Polymer and Molecular Science 🧪
- Measures molecular size and flexibility in polymers and proteins.
- Predicts how macromolecules fold and interact in biological systems.
Sports Science and Biomechanics 🏋️
- Determines stability and performance in athletic movements.
- Used in gymnastics, cycling, and weightlifting to optimize motion.
Challenges and Limitations of the Radius of Gyration
While the gyradius is a powerful concept, it has limitations in some scenarios:
Approximations in Complex Systems ❌
- The formula assumes simplified mass distributions, which may not hold for irregular objects.
Dependence on Axis Selection ❌
- The value of kkk changes based on the chosen axis, making standardization difficult.
Limitations in Biological Applications ❌
- In polymers and proteins, experimental measurements may not always match theoretical calculations.
⚠️ Tip: The gyradius should be used alongside other parameters for more precise analyses.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer Solvent Interaction Simulator Universidad Autonóma Metropolitana | Systematic calculation of radius of gyration for block copolymers in various solvents, providing insights into polymer-solvent interactions and spatial conformations. | Polymer research and development, especially in industries requiring precise control of polymer properties in different solvents. |
| GPC/SEC Radius of Gyration Analyzer The National Research Council | Online measurement of macromolecule dimensions as a function of molar mass using multiangle light-scattering detector and SEC techniques. | Quality control and research in polymer manufacturing, pharmaceutical industry, and materials science. |
| Protein Structure Compactness Predictor Russian Academy of Sciences | Statistical analysis of radius of gyration for 3769 protein domains, providing insights into structural compactness of different protein classes. | Drug discovery, protein engineering, and biotechnology research focusing on protein folding and structure prediction. |
| Advanced LED Display Toshiba Corp. | Utilization of block copolymers to create microphase-separated structures and etched surfaces, optimizing light emission and enhancing luminous efficiency. | High-performance displays, energy-efficient lighting solutions, and advanced optoelectronic devices. |
| Radius of Gyration Educational Kit The California State University | Simple apparatus for measuring radius of gyration of circular objects using principles of rolling, free fall, and energy conservation. | Physics education, particularly in mechanics and rotational dynamics, suitable for both classroom and remote learning environments. |
Future Trends in Radius of Gyration Research
AI-Powered Structural Analysis 🔹
- Artificial intelligence enhances gyradius calculations for optimized building designs.
Advancements in Polymer Science 🔹
- Nano-scale research improves drug delivery systems and biomaterials.
Space and Astrophysics Applications 🔹
- Helps understand gravitational stability and rotational behavior in celestial bodies.
How Eureka by PatSnap Accelerates Research on Radius of Gyration
What is Eureka by PatSnap?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered innovation intelligence tool that helps R&D teams discover new advancements in structural mechanics, polymer science, and rotational dynamics.
How It Benefits Radius of Gyration Research
✅ Patent Analysis: Identifies the latest innovations related to structural stability, materials science, and molecular engineering.
✅ Competitive Intelligence: Helps engineers and researchers benchmark against cutting-edge developments.
✅ Technology Roadmapping: Tracks emerging trends in nanotechnology, biomechanics, and astrophysics.
🚀 For researchers, engineers, and material scientists, Eureka by PatSnap accelerates research and enhances innovation strategies.
Conclusion
The radius of gyration remains a critical concept across multiple disciplines, from civil engineering and mechanical design to molecular science and biomechanics. Scientists and engineers optimize structures, improve polymer functionality, and enhance industrial applications by understanding mass distribution and rotational resistance.
With the help of AI-driven tools like Eureka by PatSnap, researchers and innovators can stay ahead of new developments and push the boundaries of technology.
🚀 Want to explore the latest advancements in structural mechanics and nanoscience? Sign up for Eureka by PatSnap today and accelerate your innovation journey!
FAQs
1️⃣ What does the radius of gyration measure?
It measures mass distribution around an axis, affecting stability and rotational motion.
2️⃣ How is the gyradius used in engineering?
It helps design structurally stable buildings, bridges, and machinery by determining resistance to bending and rotation.
3️⃣ Is the radius of gyration important in polymers?
Yes. It determines molecular size, folding behavior, and macromolecular interactions.
4️⃣ Does the gyradius apply to astrophysics?
Yes. It helps in analyzing the rotational stability of galaxies and celestial objects.
5️⃣ How can I stay updated on research in radius of gyration applications?
Using AI-powered tools like Eureka by PatSnap helps track latest patents, innovations, and scientific advancements.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Radius of Gyration, try Patsnap Eureka.


