
Propanoic acid, also known as propionic acid, is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C₃H₆O₂. It is a colorless liquid with a strong, pungent odor and is widely used in food preservation, chemical synthesis, and agricultural applications. Propanoic acid plays an essential role in industrial and biological processes, but due to its corrosive nature, proper handling and storage are necessary. This article explores the properties, uses, hazards, safety measures, and key considerations related to propanoic acid.
What is Propanoic Acid?
Propanoic acid is a short-chain carboxylic acid that is both naturally occurring and industrially produced. It is commonly found in dairy products, certain bacteria, and animal feed. In aqueous solutions, it behaves like other weak acids, partially dissociating to form propionate ions.
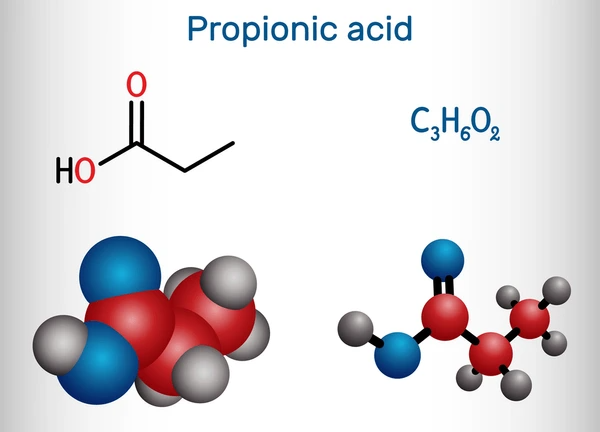
Chemical Properties
- Molecular Formula: C₃H₆O₂
- Molar Mass: 74.08 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Odor: Pungent, similar to rancid butter
- Density: 0.993 g/cm³ at 20°C
- Boiling Point: 141°C
- Melting Point: -20.5°C
- Solubility: Miscible with water, ethanol, and ether
Physical States
Propanoic acid exists as a liquid under standard conditions. It forms hydrogen-bonded dimers in both liquid and vapor phases, similar to other carboxylic acids such as acetic acid.
Propanoic Acid vs. Other Carboxylic Acids
| Property | Propanoic Acid (C₃H₆O₂) | Acetic Acid (C₂H₄O₂) | Butyric Acid (C₄H₈O₂) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 74.08 g/mol | 60.05 g/mol | 88.11 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 141°C | 118°C | 163.7°C |
| Odor | Pungent, body odor-like | Vinegar-like | Rancid butter |
| Solubility | Miscible with water | Miscible with water | Slightly soluble in water |
Wondering how propanoic acid compares to other carboxylic acids? Eureka Technical Q&A provides expert insights into its properties, applications, and differences, helping you understand its role in food preservation, industrial processes, and chemical synthesis.
Uses of Propanoic Acid
1. Industrial Applications
- Food Preservative: Used as a mold inhibitor in bread and baked goods, typically in the form of calcium or sodium propionate.
- Agricultural Use: Added to animal feed to prevent mold growth and improve feed storage life.
- Herbicides: Used as an active ingredient in weed control formulations.
- Plastic and Polymer Production: Serves as an intermediate in manufacturing cellulose-based plastics and synthetic resins.
2. Laboratory and Chemical Research
- Synthetic Reactions: Used in the synthesis of esters, anhydrides, and polymers.
- pH Control: Acts as a buffering agent in chemical reactions.
3. Medical and Pharmaceutical Use
- Antifungal Agent: Used in pharmaceuticals to inhibit fungal growth in topical treatments.
Hazards and Safety Considerations
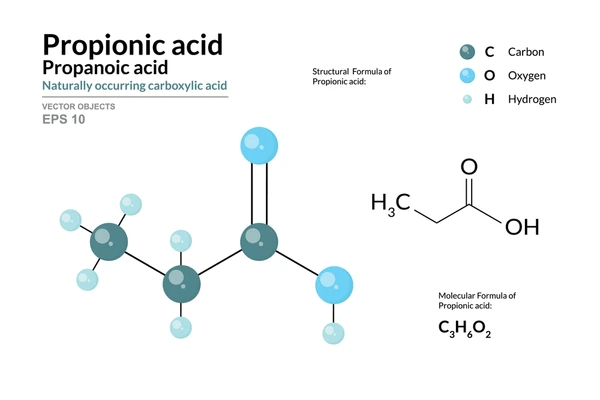
1. Health Hazards
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Direct contact can cause severe irritation and burns.
- Respiratory Irritation: Inhalation of vapors may cause coughing and difficulty breathing.
- Ingestion Risks: Can lead to nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal distress.
2. Flammability
- Flash Point: 54°C (129°F)
- Explosion Risk: Can form explosive vapor-air mixtures in high concentrations.
3. Reactivity
- Reacts with strong oxidizing agents, leading to potential hazardous reactions.
- Corrosive to metals, causing degradation over time.
Safe Handling and Storage Practices
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Eye Protection: Safety goggles or face shields to prevent eye contact.
- Skin Protection: Acid-resistant gloves and protective clothing.
- Respiratory Protection: Use of respirators in poorly ventilated areas.
2. Engineering Controls
- Ventilation: Always handle in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood.
- Spill Containment: Implement spill control measures to manage accidental leaks.
3. Storage Guidelines
- Store in tightly sealed, corrosion-resistant containers.
- Keep in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from oxidizing agents.
4. Emergency Procedures
- First Aid: In case of contact, rinse affected areas with plenty of water and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Fire Response: Use dry chemical powder or carbon dioxide to extinguish fires involving C₃H₆O₂.
FAQs
1. What is propanoic acid used for?
C₃H₆O₂ is widely used as a food preservative, herbicide component, and chemical intermediate in industrial applications.
2. Is propanoic acid dangerous?
While useful, C₃H₆O₂ is corrosive and can cause irritation or burns upon contact. Proper safety measures must be followed when handling it.
3. How should propanoic acid be stored?
It should be stored in tightly sealed, corrosion-resistant containers in cool, dry, well-ventilated areas away from strong oxidizers.
4. Is propanoic acid flammable?
Yes, C₃H₆O₂ has a flash point of 54°C and can form explosive vapor-air mixtures in certain conditions.
5. How do you neutralize a spill of propanoic acid?
Spills should be neutralized using a weak base such as sodium bicarbonate, followed by thorough cleaning with absorbent materials.
Conclusion
Propanoic acid is an essential chemical in food preservation, agriculture, and industrial manufacturing. Despite its many benefits, it poses health and safety risks if not handled properly. By following safety protocols for storage and handling, industries and laboratories can use C₃H₆O₂ effectively while minimizing potential hazards.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Propanoic Acid, try Patsnap Eureka.


